Final ID: MDP55
Genetic Determinant for Prognosis of Dilated Cardiomyopathy: The role of NAV3 in Cardiac Fibrosis
Methods: A GWAS was performed using DNA from 686 patients with recent onset DCM who were on standard HF therapy using change in left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) at a median of 6 months after initial diagnosis. Cultured human cardiac fibroblasts (HCFs) were used to functionally validate the GWAS findings in vitro. RNA-seq followed by pathway analysis after NAV3 knock-down (KD) using siRNA in HCFs were performed to explore potential biological mechanisms.
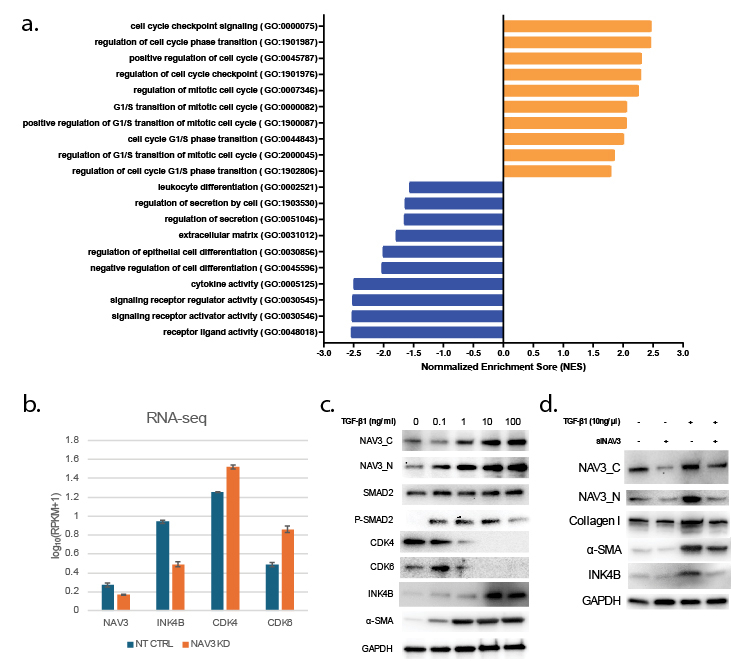
Results: A genetic variant, rs11105445(G>A), identified from the GWAS, mapping to the neuron navigator 3 (NAV3) gene (rs11105445, p=2.37E-07; beta 2.74 ± 0.53) was associated with improvement in LVEF. Functional genomic experiments demonstrated that, both in LV tissue and in cultured fibroblasts, the minor allele A was associated with decreased transcription of NAV3 (pvalue: 0.0335 and 0.0432) suggesting that ↓NAV3 expression might be associated with improvement in LVEF. TGF-β1 can induce HCF transdifferentiation into myofibroblasts and we demonstrate that it also increases NAV3 expression. NAV3 KD which mimics the GWAS variant significantly suppressed TGF-β1 induced HCF transdifferentiation demonstrated by decreased expression of α-smooth muscle actin (ACTA2) and collagen I (COL1A1). RNA-seq after NAV3 KD followed by pathway analysis suggested that NAV3 exerted its effect by regulating ECM and cell cycle processes, especially G1/S transition. We demonstrate that NAV3 KD suppressed TGF-β1 induced G1/S arrest by regulating CDK4, CDK6 and INK4B (cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2B/P15, CDK4 inhibitor).
Conclusion: Decreased expression of NAV3 is associated with myocardial recovery in DCM, most likely due to its role in suppressing HCF differentiation by regulating TGF-β1 induced G1/S arrest. The role of NAV3 as a novel therapeutic target in DCM needs to be explored.
- Wang, Min ( Mayo Clinic , Rochester , Minnesota , United States )
- Merlo, Marco ( Cardiovascular Department, Ospedali Riuniti and University , Trieste , Italy )
- Sinagra, Gianfranco ( Azienda Sanitaria Universitaria Giuliano-Isontina (ASUGI), University of Trieste , Trieste , Italy )
- Pinet, Florence ( INSERUM U1167 , Lille Cedex , France )
- Krejci, Jan ( Institut Pasteur , Paris , France )
- Liu, Duan ( Mayo Clinic , Rochester , Minnesota , United States )
- Weinshilboum, Richard ( MAYO CLINIC , Rochester , Minnesota , United States )
- Pereira, Naveen ( Mayo Clinic , Rochester , Minnesota , United States )
- Wang, Li ( Tianjin First Central Hospital , Tianjin , Tianjin , China )
- Ghazal, Rachad ( Mayo Clinic , Rochester , Minnesota , United States )
- Seal, Mayah ( Mayo Clinic , Rochester , Minnesota , United States )
- Nguyen, Thanh Thanh ( Mayo Clinic , Rochester , Minnesota , United States )
- Mcnamara, Dennis ( University of Pittsburgh , Pittsburgh , Pennsylvania , United States )
- Barlera, Simona ( Mario Negri Institute , Milano , Italy )
- Pileggi, Silvana ( The Mario Negri Institute of Pharmacological Research , Milan , Italy )
- Mestroni, Luisa ( UNIVERSITY COLORADO , Aurora , Colorado , United States )
Meeting Info:
Session Info:
Latest Advances in Human Genetics and Genomics
Saturday, 11/16/2024 , 12:50PM - 02:15PM
Moderated Digital Poster Session
More abstracts on this topic:
Qian Chunqi, Fernandez Zachary, Wang Donna, Ma Shuangtao
A Cellular Mechanism Mediating Lipomatous Metaplasia In the Infarcted Heart.Tuleta Izabela, Frangogiannis Nikolaos, Venugopal Harikrishnan, Huang Shuaibo, Humeres Claudio, Hernandez Velasco Silvia, Hanna Anis, Kubota Akihiko, O'leary Kevin, Zheng Deyou
More abstracts from these authors:
Wang Li, Miller Jordan, Pereira Naveen, Wang Min, Vyas Hridyanshu, Roos Carolyn, Huang Runqing, Liu Duan, Ghazal Rachad, Lambert Laura, Weinshilboum Richard
CUB domain-containing protein 1 Regulates Extracellular Matrix Remodeling and Src Kinase-Mediated Signaling in Human Cardiac FibroblastsSrinivas Akshatha Narayanrao, Ghazal Rachad, Liu Duan, Choi Kyoung, Weinshilboum Richard, Tschumperlin Daniel, Pereira Naveen