Final ID: MDP706
Associations of the Glasgow Prognostic Score with Adverse Outcomes in Patients with Acute Coronary Syndrome and Atrial Fibrillation
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Glasgow Prognostic Score (GPS), including c-reactive protein and albumin, has been used to assess inflammatory status in many diseases. The aim of this study was to evaluate the associations of GPS on prognosis in patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS) and atrial fibrillation (AF).
Methods: We conducted a prospective observational study and consecutively recruited 1153 patients with AF combined with ACS. The primary endpoint was all-cause mortality and the secondary endpoint was major adverse cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events (MACCEs). Three multivariable adjusted Cox proportional hazards models were performed to evaluate the associations between GPS and endpoints.
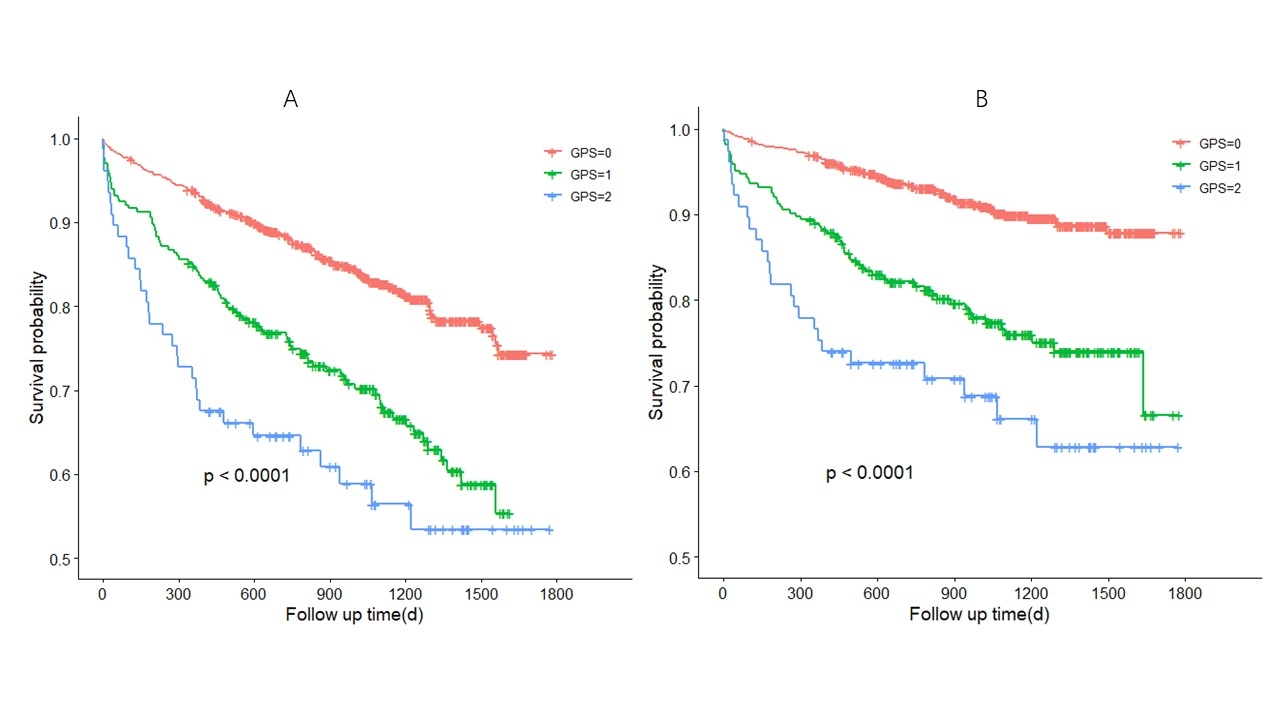
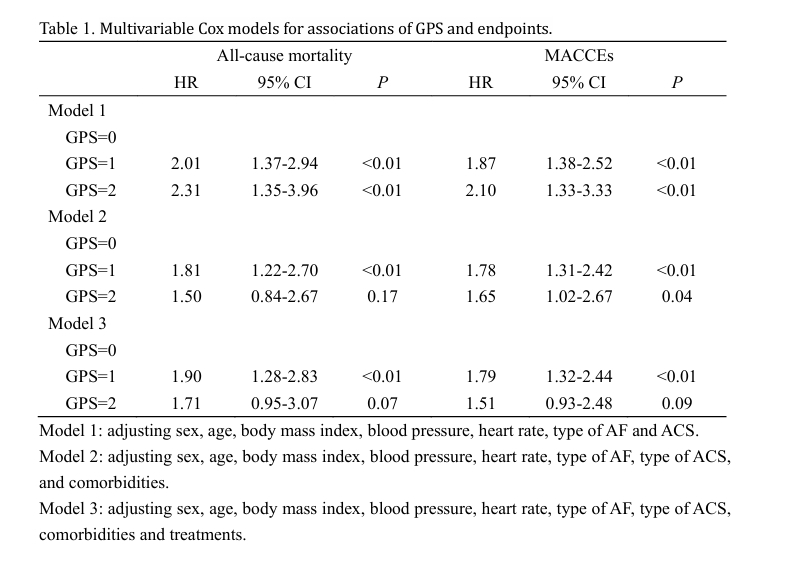
Results: Patients were divided into 3 groups: GPS=0 (c-reactive protein≤10mg/L and albumin ≥35g/L, n=812), GPS=1 (c-reactive protein >10mg/L or albumin <35g/L, n=264), GPS=2 (c-reactive protein >10mg/L and albumin <35g/L, n=77). During a median follow-up of 34.0 months, log-rank analysis showed that higher GPS was associated with decreased overall survival (P<0.001, Figure 1A) and a higher incidence of MACCEs (P<0.001, Figure 1B). After adjustment for confounders including demographics, comorbidities, and treatments, multivariable Cox models showed that GPS=1 was independently associated with increased risk of all-cause mortality and MACCEs (Table 1).
Conclusions: Hypoalbuminemia or elevated c-reactive protein is independently associated with worse prognosis in patients with ACS and AF, suggesting that inflammatory status plays an important role in the prognostic assessment of ACS patients with AF.
Methods: We conducted a prospective observational study and consecutively recruited 1153 patients with AF combined with ACS. The primary endpoint was all-cause mortality and the secondary endpoint was major adverse cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events (MACCEs). Three multivariable adjusted Cox proportional hazards models were performed to evaluate the associations between GPS and endpoints.
Results: Patients were divided into 3 groups: GPS=0 (c-reactive protein≤10mg/L and albumin ≥35g/L, n=812), GPS=1 (c-reactive protein >10mg/L or albumin <35g/L, n=264), GPS=2 (c-reactive protein >10mg/L and albumin <35g/L, n=77). During a median follow-up of 34.0 months, log-rank analysis showed that higher GPS was associated with decreased overall survival (P<0.001, Figure 1A) and a higher incidence of MACCEs (P<0.001, Figure 1B). After adjustment for confounders including demographics, comorbidities, and treatments, multivariable Cox models showed that GPS=1 was independently associated with increased risk of all-cause mortality and MACCEs (Table 1).
Conclusions: Hypoalbuminemia or elevated c-reactive protein is independently associated with worse prognosis in patients with ACS and AF, suggesting that inflammatory status plays an important role in the prognostic assessment of ACS patients with AF.
More abstracts on this topic:
Assessing Coronary Artery Disease Severity: Leveraging Inflammatory Markers As a Prognostic Indicators
Turnbull Scott, Dugal Jasmine, Gill Randeep, Wang Shawn, Cross Chad, Mubder Mohamad
A Comparative Analysis of Esophageal Cooling for Preventing Esophageal Injury Post Atrial Fibrillation Catheter Ablation: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysisIbrahim Momen Mohamed, Al Hennawi Hussam, Tanas Yousef, Abourady Youmna, Sewedan Nourhan, Hashem Ahmed Magdy, Motawea Karam R.