Final ID: MDP707
Derivation and internal validation of a nomogram for bleeding risk prediction in patients with atrial fibrillation and acute coronary syndrome or undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Standard scoring system for bleeding risk assessment has not been developed in patients with atrial fibrillation (AF) and acute coronary syndrome (ACS) or undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). This study aims to develop a practical nomogram for bleeding risk evaluation in patients with AF and ACS or undergoing PCI who received both oral anticoagulant (OAC) and antiplatelet therapy (APT).
Methods: A total of 930 patients with AF and ACS/PCI receiving both OAC and APT were consecutively recruited and followed up for 1 year. The primary endpoint was defined according to the bleeding academic research consortium (BARC) criteria as major bleeding (BARC 3a, 3b, 3c, and 5). Potential prognostic variables of the primary endpoint were selected by the LASSO method and incorporated in a multivariable logistic regression model. A nomogram visualizing the logistic regression model was then generated. Discrimination was evaluated and compared by the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves and c-indexes. Calibration was assessed by the Hosmer-Lemeshow tests, Brier scores and calibration plots.
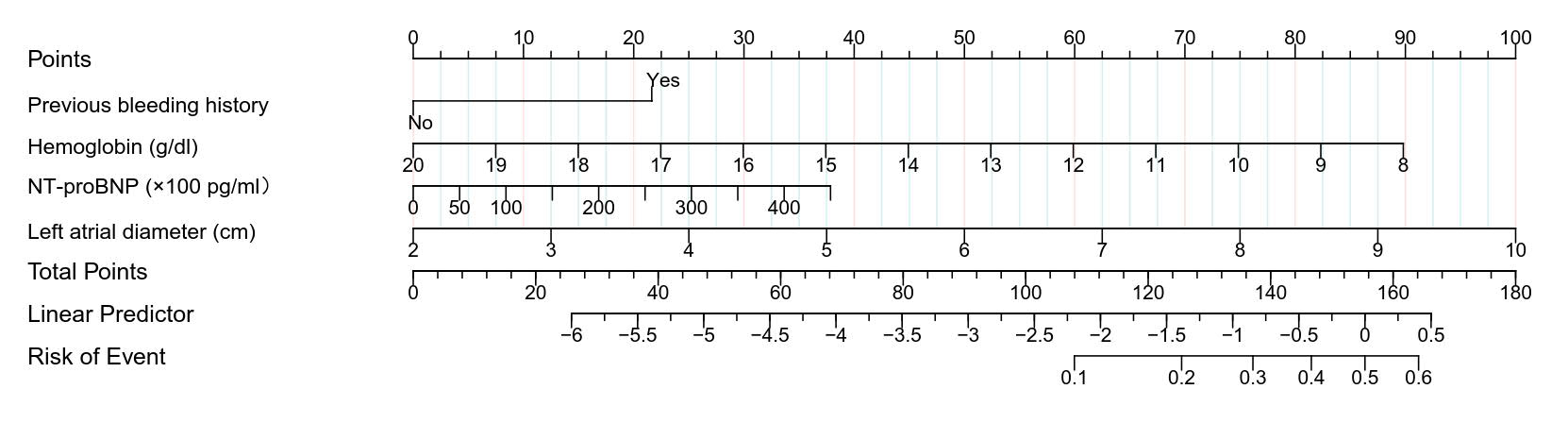
Results: During 1-year follow-up, BARC type 3 or 5 bleeding occurred in 36 patients (3.9%). Four key predictors of the primary endpoint (previous bleeding history, hemoglobin, N-terminal pro-B type natriuretic peptide, and left atrial diameter) were selected by the LASSO method and integrated to construct a nomogram for bleeding risk prediction. This nomogram displayed good discrimination with a c-index of 0.740 (95% CI: 0.639-0.841). Bootstrap resampling was undertaken for internal validation and the bias-corrected c-index was 0.726. Compared to the HAS-BLED score, the nomogram displayed a significant improvement in bleeding risk prediction (c-statistics: 0.740 vs. 0.575, p<0.001). According to the Hosmer-Lemeshow test and the Brier score, the calibration of this nomogram was good.
Conclusion: In patients with AF and ACS or undergoing PCI who received both OAC and APT, a simple 4-variable nomogram provide a practical tool for 1-year BARC type 3 or 5 bleeding prediction.
Methods: A total of 930 patients with AF and ACS/PCI receiving both OAC and APT were consecutively recruited and followed up for 1 year. The primary endpoint was defined according to the bleeding academic research consortium (BARC) criteria as major bleeding (BARC 3a, 3b, 3c, and 5). Potential prognostic variables of the primary endpoint were selected by the LASSO method and incorporated in a multivariable logistic regression model. A nomogram visualizing the logistic regression model was then generated. Discrimination was evaluated and compared by the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves and c-indexes. Calibration was assessed by the Hosmer-Lemeshow tests, Brier scores and calibration plots.
Results: During 1-year follow-up, BARC type 3 or 5 bleeding occurred in 36 patients (3.9%). Four key predictors of the primary endpoint (previous bleeding history, hemoglobin, N-terminal pro-B type natriuretic peptide, and left atrial diameter) were selected by the LASSO method and integrated to construct a nomogram for bleeding risk prediction. This nomogram displayed good discrimination with a c-index of 0.740 (95% CI: 0.639-0.841). Bootstrap resampling was undertaken for internal validation and the bias-corrected c-index was 0.726. Compared to the HAS-BLED score, the nomogram displayed a significant improvement in bleeding risk prediction (c-statistics: 0.740 vs. 0.575, p<0.001). According to the Hosmer-Lemeshow test and the Brier score, the calibration of this nomogram was good.
Conclusion: In patients with AF and ACS or undergoing PCI who received both OAC and APT, a simple 4-variable nomogram provide a practical tool for 1-year BARC type 3 or 5 bleeding prediction.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Comparative Analysis of Esophageal Cooling for Preventing Esophageal Injury Post Atrial Fibrillation Catheter Ablation: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Ibrahim Momen Mohamed, Al Hennawi Hussam, Tanas Yousef, Abourady Youmna, Sewedan Nourhan, Hashem Ahmed Magdy, Motawea Karam R.
A novel deep learning framework identified associated genes and Interpretable deep learning translation of GWAS findings for drug repurposing in Atrial FibrillationTonegawa-kuji Reina, Xu Jielin, Guntupalli Suman, Barnard John, Chung Mina, Cheng Feixiong