Final ID: MDP131
Scoring System-Based Approach for Identifying Patients With Positive Intracoronary Acetylcholine Provocation Tests: The Original and Modified ABCD Score
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Although intracoronary acetylcholine (ACh) provocation testing is a guideline-recommended invasive standard for the diagnosis of vasospastic angina (VSA), ACh tests are largely underused in clinical practice globally. Recently, Rinaldi et al. developed a risk-scoring system, the ABCD score, to predict positive ACh test results. However, the ABCD score, consisting of clinical presentation, myocardial bridge, C-reactive protein, and dyslipidemia, has not been externally validated yet. We aimed to examine the diagnostic ability of the score and attempted to improve the predictivity for identifying patients with VSA.
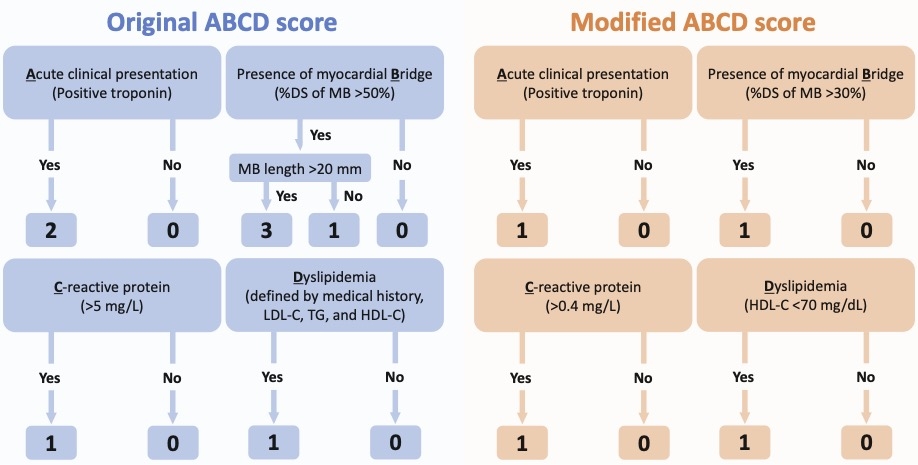
Methods: From May 2012 to September 2023, a total 1029 patients underwent ACh provocation test for diagnosing VSA. Patients without data on C-reactive protein and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and those who had a history of coronary artery bypass grafting and stenting in the left anterior descending artery were excluded. The original and modified ABCD score were calculated as shown in Figure 1. The positive ACh provocation test (i.e. VSA) was defined as significant angiographic vasospasm accompanied by chest pain and/or ischemic electrocardiographic changes.
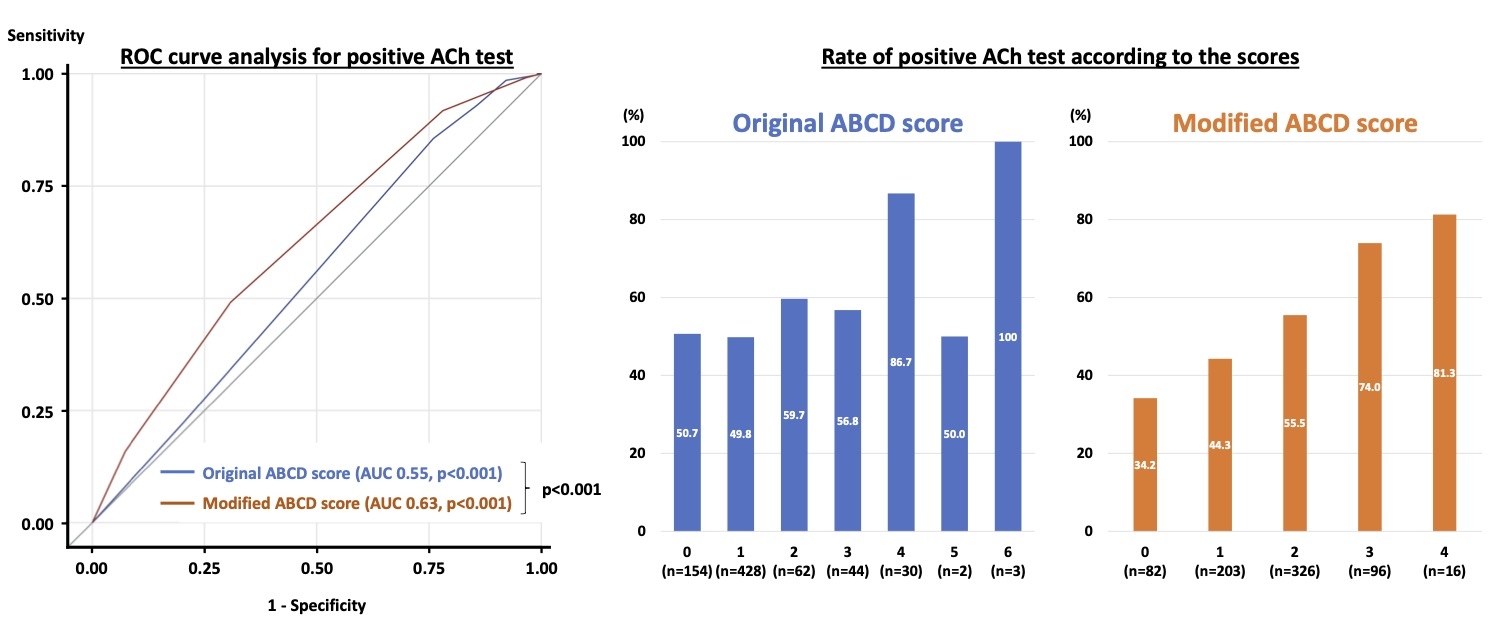
Results: Of the 723 patients included in this study, 383 (53.0%) had positive ACh provocation tests. The receiver operating characteristics curve analysis indicated that the original ABCD score was significantly predictive of VSA, but the diagnostic ability was modest (Figure 2). Using best cut-off values on receiver operating characteristics curve analyses, we developed the modified ABCD score (Figure 1), resulting in significantly greater diagnostic accuracy (Figure 2). The modified ABCD score better stratified positive ACh test results than the original score (Figure 2).
Conclusions: The original ABCD was predictive of VSA in this external validation study with modest diagnostic accuracy. The modified ABCD score achieved better predictivity for identifying patients with VSA.
Methods: From May 2012 to September 2023, a total 1029 patients underwent ACh provocation test for diagnosing VSA. Patients without data on C-reactive protein and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and those who had a history of coronary artery bypass grafting and stenting in the left anterior descending artery were excluded. The original and modified ABCD score were calculated as shown in Figure 1. The positive ACh provocation test (i.e. VSA) was defined as significant angiographic vasospasm accompanied by chest pain and/or ischemic electrocardiographic changes.
Results: Of the 723 patients included in this study, 383 (53.0%) had positive ACh provocation tests. The receiver operating characteristics curve analysis indicated that the original ABCD score was significantly predictive of VSA, but the diagnostic ability was modest (Figure 2). Using best cut-off values on receiver operating characteristics curve analyses, we developed the modified ABCD score (Figure 1), resulting in significantly greater diagnostic accuracy (Figure 2). The modified ABCD score better stratified positive ACh test results than the original score (Figure 2).
Conclusions: The original ABCD was predictive of VSA in this external validation study with modest diagnostic accuracy. The modified ABCD score achieved better predictivity for identifying patients with VSA.
More abstracts on this topic:
Exploring Myasthenia Gravis as a Potential Contributor to Post-Stroke Fatigue: A Prospective Case-Control Study
Nambiar Vivek, Pt Karthika, Kannoth Sudheeran, Mathai Annamma, V U Anaghakrishna, Chandran Divyasree, S Midhun, Tu Athira
Association Between the Severity of Coronary Artery Stenosis with the Minimum Responsive Dose of Intracoronary Acetylcholine Provocation TestRha Seung-woon, Park Chang Gyu, Oh Dong, Ahn Woo Jin, Hyun Sujin, Cha Jinah, Choi Se Yeon, Choi Byoung Geol, Sinurat Markz, Park Soohyung, Choi Cheol Ung