Final ID: WP123
Exploring Myasthenia Gravis as a Potential Contributor to Post-Stroke Fatigue: A Prospective Case-Control Study
Post-stroke fatigue is a common and debilitating issue, often linked to depression or neural damage. Emerging evidence suggests that myasthenia gravis (MG) may also play a role in post-stroke fatigue, offering a new perspective on patient management and long-term disability reduction.
Objectives:
This study aims to assess the incidence of de novo MG in stroke survivors following motor recovery over 18 to 24 months and compare findings with a healthy control group.
Methods:
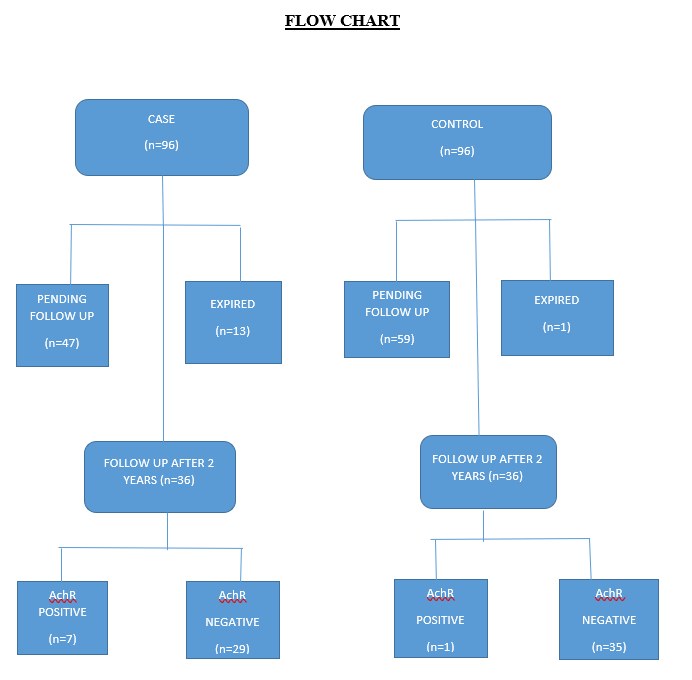
Conducted at a tertiary care institution over two years, this prospective case-control study included ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke patients. Participants were recruited during the acute stroke phase and underwent evaluations for neuromuscular weakness and autoimmune disorders. They were monitored in a specialized stroke clinic for two years. Key variables included demographics, comorbidities, autoimmune disorders, stroke subtype, time since onset of stroke, and muscle fatigability. Age and sex-matched controls were assessed concurrently. Baseline and two-year follow-up measurements of acetylcholine receptor (AChR) antibodies were performed, and new antibodies were monitored. Participants with significant fatigability were tested for MG, and if confirmed, treated with cholinergic drugs.
Results:
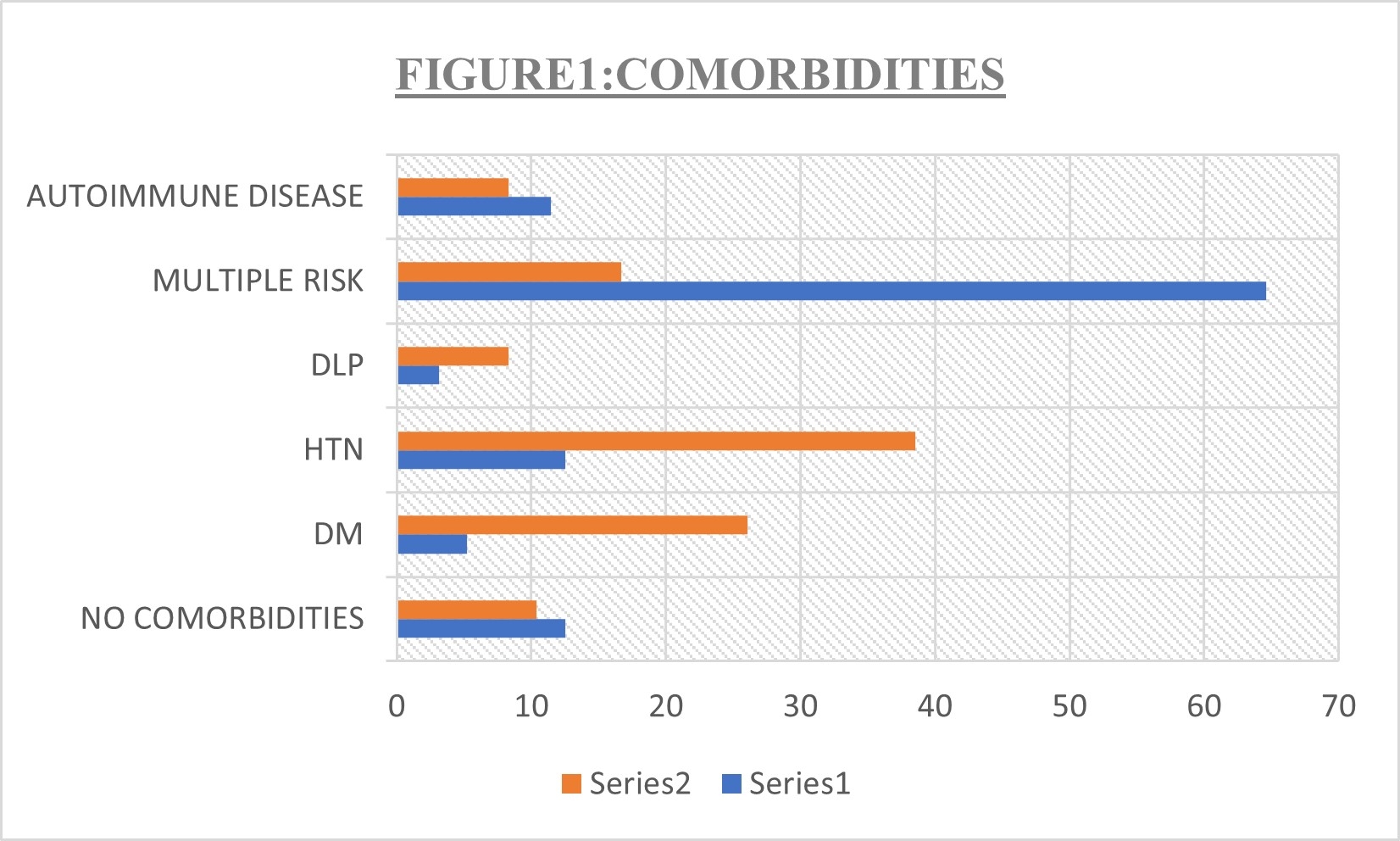
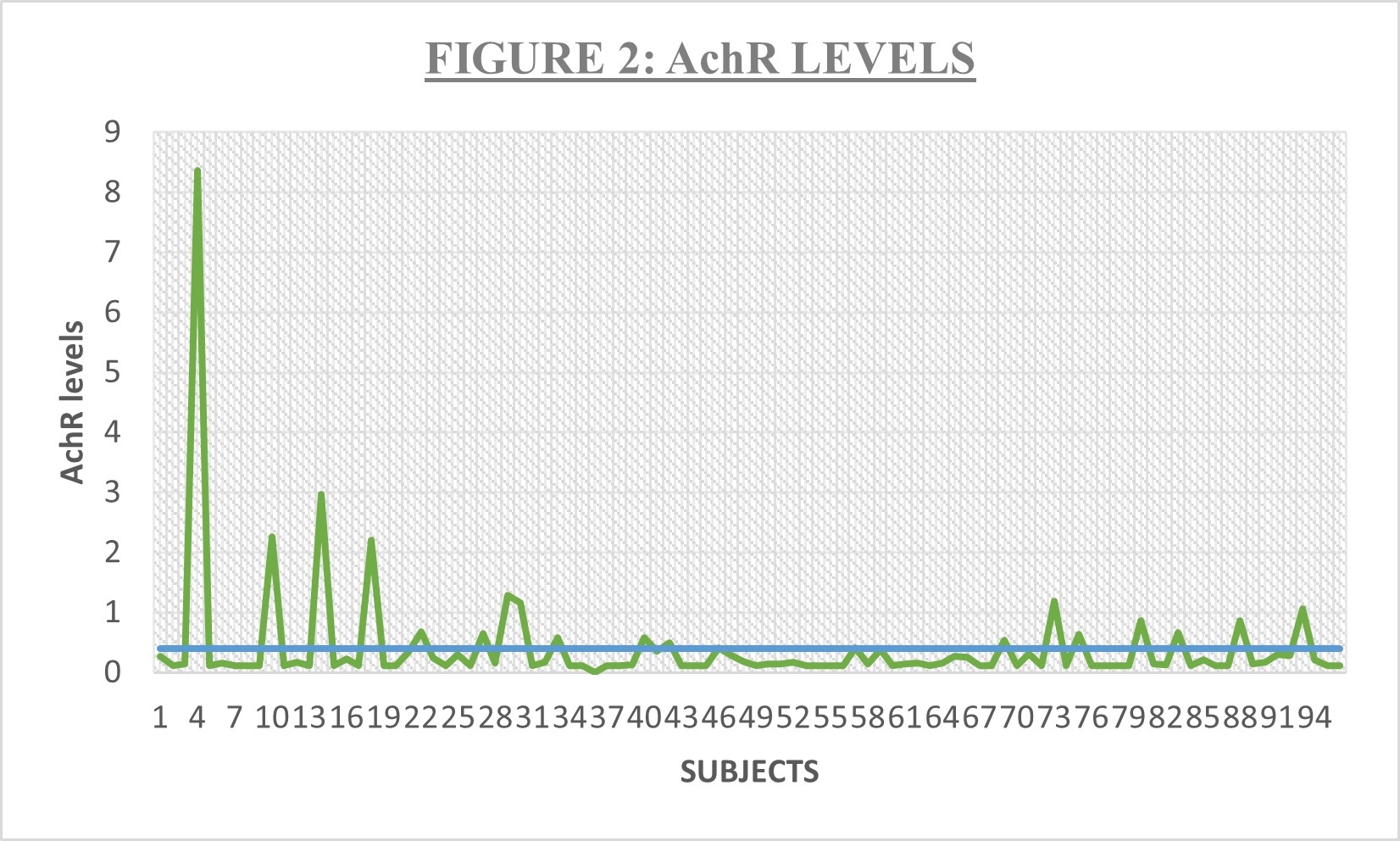
The study involved 96 participants with a mean age of 60.45 years, predominantly male (63.86%). Ischemic stroke was most common (93.75%). Major risk factors included hypertension (12.5%), diabetes (5.20%), and dyslipidemia (3.12%), with 11.45% having autoimmune disorders. Of the 96 participants, 74 (77.08%) reported fatigability an average of 23.2 months post-stroke. Types of fatigability included neck (34.37%), proximal arm (11.46%), grip (19.80%), speech (5.21%), and eye (6.25%). Among 36 stroke patients with post-stroke fatigability and 36 controls re-evaluated at follow-up, 7 stroke patients tested positive for AChR antibodies compared to 1 control. Fisher’s Exact test showed a significant association between stroke and AChR-Ab positivity (p = 0.001), with an odds ratio of 7, suggesting a potential link between post-stroke fatigue and MG.
Conclusion:
The study highlights MG as a potential underrecognized factor in post-stroke fatigue. These findings may improve diagnostic and therapeutic strategies for stroke survivors and pave the way for further research into post-stroke immune alterations and MG development.
More abstracts on this topic:
Krieger Katherine, Rossi Camilla, Rahouma Mohamed, Gaudino Mario, Hameed Irbaz, Quer Giorgio, Mack Charles, Savic Marco, Mantaj Polina, Hirofuji Aina, Gregg Alexander, Soletti Giovanni
Does Knowledge of Anti-Ro Antibody Status Before Pregnancy Affect Diagnosis of Fetal Cardiac Neonatal Lupus? A Fetal Heart Society Research Collaborative StudyKaplinski Michelle, Krishnan Anita, Hogan Whitnee, Sharma Kavita, Ikemba Catherine, Levasseur Stephanie, Owens Sonal, Deweert Katherine, Kohari Katherine, Copel Joshua, Bucholz Emily, Kaizer Alexander, Gilbert Lisa, Srinivasan Shardha, Samples Stefani, Patel Angira, Phoon Colin, Srinivasan Ranjini, Mcintosh Amanda, Kiaffas Maria, Geiger Miwa, Mcfarland Carol, Cuneo Bettina, Pinto Nelangi, Arya Bhawna, Doan Tam, Moreno Jamine, Lindblade Chris, Gropler Melanie, Buyon Jill, Killen Stacy, Moon-grady Anita, Nunez Gallegos Flora, Hornberger Lisa, Howley Lisa, Paul Erin, Donofrio Mary
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.