Final ID: MDP1065
Decline In Treatment, Testing and Control of Lipids Amongst Diabetic Patients, a Population-Level Analysis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: In patients with diabetes mellitus (DM), lipid-lowering therapy (LLT) with statins +/- adjuvant LLT are recognised treatment approaches. It is unknown what proportion of patients with DM are prescribed LLT, have documented low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels, or achieve guideline LDL-C targets.
Aims: To document population trends in (i) the incidence and prevalence of DM, (ii) prescribing of LLT, and (iii) testing and achievement of LDL-C targets in patients with or without atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD).
Methods: We conducted a retrospective, population-level, observational study using linked anonymised health record data amongst 269,735 diabetic patients in Wales (UK). Associations between patient characteristics and (i) statin prescription and (ii) achievement of LDL-C target of (<1.8 mmol/L) were evaluated.
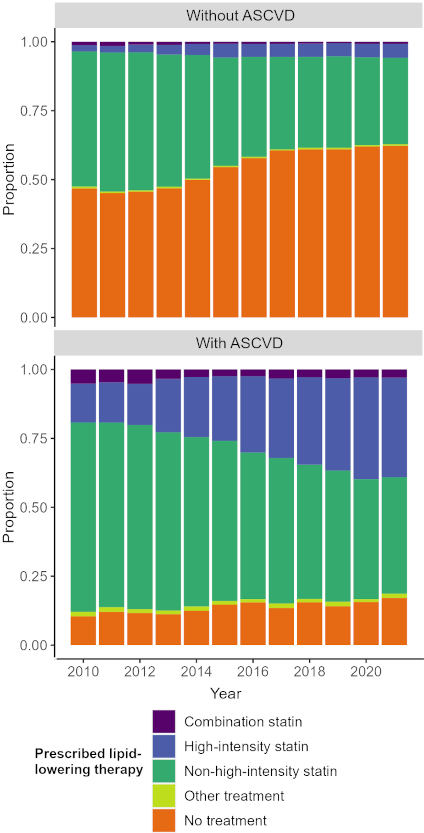
Results: The prevalence of DM increased from 6,519 to 8,128 per 100k, and incidence increased from 543 to 633 per 100k per year (2010-21). The proportion of patients prescribed any LLT decreased from 89.5% to 82.9% in those with ASCVD and from 53.2% to 37.8% without. An increasing and greater proportion of patients with ASCVD were prescribed high-intensity statin therapy (14.1% to 36.1%) over the study period, compared to those without (2.3% to 5.1%; Figure 1).
The proportion of patients with documented LDL-C decreased (from 68.1% to 52.3% in those with ASCVD and 64.7% to 48.3% without) over the study period. A greater proportion of those with ASCVD achieved an LDL-C <1.8 mmol/L (43.1% to 45.4%) than those without (22.2% to 22.0%). In a multivariate logistic regression, presence of ASCVD and history of hypertension were associated with prescription of statin therapy (ORs = 4.01, 1.75, respectively; both p < 0.01). Male sex and presence of ASCVD were associated with achievement of LDL-C target (ORs = 1.25, 8.15; both p < 0.01).
Conclusions: The incidence and prevalence of DM is increasing over time, but the overall quality of lipid management is decreasing, as evidenced by documented testing, treatment and control of LDL-C. In order to realise the full evidence-based benefit from LLT, improvement in the implementation of guideline-recommended care is required.
Aims: To document population trends in (i) the incidence and prevalence of DM, (ii) prescribing of LLT, and (iii) testing and achievement of LDL-C targets in patients with or without atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD).
Methods: We conducted a retrospective, population-level, observational study using linked anonymised health record data amongst 269,735 diabetic patients in Wales (UK). Associations between patient characteristics and (i) statin prescription and (ii) achievement of LDL-C target of (<1.8 mmol/L) were evaluated.
Results: The prevalence of DM increased from 6,519 to 8,128 per 100k, and incidence increased from 543 to 633 per 100k per year (2010-21). The proportion of patients prescribed any LLT decreased from 89.5% to 82.9% in those with ASCVD and from 53.2% to 37.8% without. An increasing and greater proportion of patients with ASCVD were prescribed high-intensity statin therapy (14.1% to 36.1%) over the study period, compared to those without (2.3% to 5.1%; Figure 1).
The proportion of patients with documented LDL-C decreased (from 68.1% to 52.3% in those with ASCVD and 64.7% to 48.3% without) over the study period. A greater proportion of those with ASCVD achieved an LDL-C <1.8 mmol/L (43.1% to 45.4%) than those without (22.2% to 22.0%). In a multivariate logistic regression, presence of ASCVD and history of hypertension were associated with prescription of statin therapy (ORs = 4.01, 1.75, respectively; both p < 0.01). Male sex and presence of ASCVD were associated with achievement of LDL-C target (ORs = 1.25, 8.15; both p < 0.01).
Conclusions: The incidence and prevalence of DM is increasing over time, but the overall quality of lipid management is decreasing, as evidenced by documented testing, treatment and control of LDL-C. In order to realise the full evidence-based benefit from LLT, improvement in the implementation of guideline-recommended care is required.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Qualitative Study of Perspectives on South Asian Dietary Practices: Exploring a Framework for Culturally Tailored Food-is-Medicine Interventions
Kaloth Srivarsha, Fitzgerald Nurgul, Bacalia Karen Mae, Kalbag Aparna, Setoguchi Soko
A human cardiomyocyte model of CD36 haploinsufficiency uncovers fatty acid oxidation deficits driving dilated cardiomyopathyAl Sayed Zeina, Klattenhoff Carla, Aragam Krishna, Ellinor Patrick, Willcox Jon, Zheng Alice, Koledova Vera, Srivastava Salil, Yin Xiaofei, Chaffin Mark, Rigaud Vagner, Kovacs-bogdan Erika