Final ID: MDP537
Machine Learning Identifies Predictors of Poor Outcomes in Patients with Heart Failure Presenting to the Emergency Department for Chest Pain
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Heart failure (HF) is associated with unique comorbidities and sequelae, which can affect clinical presentation and patient outcomes. This is specifically challenging when patients are evaluated for suspected acute coronary syndrome (ACS). We sought to compare the most important predictors of poor outcomes in patients with and without HF seen in the emergency department (ED) for ACS.
Methods: This was a secondary analysis of a prospective observational cohort study of consecutive patients seen for symptoms suggestive of ACS, such as chest pain (CP) and dyspnea, in the EDs of three UPMC-affiliated tertiary care hospitals (NCT04237688, clinicaltrials.gov). Primary outcome was 30-day major adverse cardiac events (MACE), adjudicated by two independent reviewers. Clinical data were collected form charts and we used KNN to impute missing data for features, most of which had less than 12.5% missingness. For features with greater than 12.5% missingness (i.e., BNP, Mg), binary indicators were added to flag missing values. Data were normalized using the Euclidean norm. Two random forest (RF) classifiers were trained using 10-fold cross validation with 71 manually selected features available early in the ED course (i.e., vital signs, labs, past medical history, ECG), and tested on patients with and without known HF. Model performance was evaluated using AUROC, and top features were identified with SHAP values.
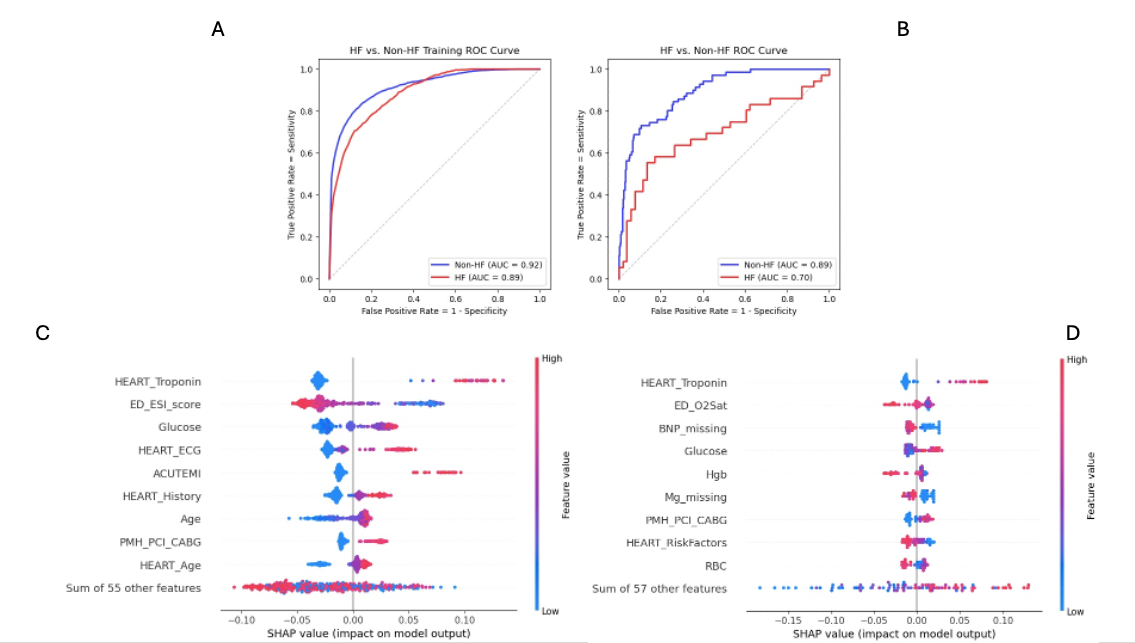
Results: The sample included 2400 patients (age 59 ± 16 years; 47% female, 41% Black, 15.9% ACS), of whom 438 had HF (age 66 ± 14 years; 45% female, 49% Black, 15.1% ACS). Individuals with HF were more likely to experience MACE (38% vs 23%, p<.001). The model had higher classification performance in patients without HF (AUC 0.89 vs 0.70). Figure 1 shows top MACE predictors for patients with and without HF.
Conclusion: The RF model performed sub-optimally among patients with HF, who were more likely to have poor outcomes moderated by characteristics such as low pulse oximetry, BNP measurement, and anemia, which are related to pathophysiology of HF. Current routine ED assessment tools for CP (i.e., HEART score) do not translate well to patients with HF, which requires more elaborate diagnostic testing.
Methods: This was a secondary analysis of a prospective observational cohort study of consecutive patients seen for symptoms suggestive of ACS, such as chest pain (CP) and dyspnea, in the EDs of three UPMC-affiliated tertiary care hospitals (NCT04237688, clinicaltrials.gov). Primary outcome was 30-day major adverse cardiac events (MACE), adjudicated by two independent reviewers. Clinical data were collected form charts and we used KNN to impute missing data for features, most of which had less than 12.5% missingness. For features with greater than 12.5% missingness (i.e., BNP, Mg), binary indicators were added to flag missing values. Data were normalized using the Euclidean norm. Two random forest (RF) classifiers were trained using 10-fold cross validation with 71 manually selected features available early in the ED course (i.e., vital signs, labs, past medical history, ECG), and tested on patients with and without known HF. Model performance was evaluated using AUROC, and top features were identified with SHAP values.
Results: The sample included 2400 patients (age 59 ± 16 years; 47% female, 41% Black, 15.9% ACS), of whom 438 had HF (age 66 ± 14 years; 45% female, 49% Black, 15.1% ACS). Individuals with HF were more likely to experience MACE (38% vs 23%, p<.001). The model had higher classification performance in patients without HF (AUC 0.89 vs 0.70). Figure 1 shows top MACE predictors for patients with and without HF.
Conclusion: The RF model performed sub-optimally among patients with HF, who were more likely to have poor outcomes moderated by characteristics such as low pulse oximetry, BNP measurement, and anemia, which are related to pathophysiology of HF. Current routine ED assessment tools for CP (i.e., HEART score) do not translate well to patients with HF, which requires more elaborate diagnostic testing.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Novel Classification of Heart Failure Derived from the Nationwide JROADHF Cohort Using Unsupervised Machine Learning
Kyodo Atsushi, Tsutsui Hiroyuki, Hikoso Shungo, Nakada Yasuki, Nogi Kazutaka, Ishihara Satomi, Ueda Tomoya, Tohyama Takeshi, Enzan Nobuyuki, Matsushima Shouji, Ide Tomomi
30-day and one-year outcomes of patients with severe aortic stenosis after TAVI using Myval : A Meta-analysisHasabo Elfatih A., Sultan Sherif, Soliman Osama, A. Aboali Amira, Hemmeda Lina, Salah Alaa, Alrawa Salma S., Elgadi Ammar, Abdalmotalib Malaz, Yasir H Eissa Abdullatif, Mahmmoud Fadelallah Eljack Mohammed