Final ID: MP1516
Leveraging Noise-adapted Deep Learning Algorithm to Detect Structural Heart Disease from 1-lead ECGs Acquired with KardiaMobile 6L Device: The ACCESS-SHD Study
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here):
BACKGROUND: Portable devices that capture 1-lead ECG, coupled with AI tools, hold the potential to scale screening for structural heart disease (SHD) in communities. We previously developed ADAPT-HEART, a noise-adapted, 1-lead AI-ECG algorithm to detect SHD that could be scaled to portable devices.
AIM: In this investigator-initiated and independent ACCESS-SHD Study, we prospectively evaluated ADAPT-HEART in detecting SHD from 1-lead ECGs obtained with a real-world portable device, the AliveCor KardiaMobile 6L device.
METHODS: We prospectively enrolled 600 participants receiving a transthoracic echocardiogram (TTE) as part of their clinical care at Yale New Haven Hospital. Consenting participants captured a 30-second, 1-lead ECG using the KardiaMobile 6L device in the echo laboratory. We accessed the 1-lead data via an automated application programming interface (API) and deployed ADAPT-HEART. The model's output probability represented the risk of SHD, defined as a composite of LVEF <40%, severe left-sided valvular disease, or severe LVH (IVSd >15 mm + moderate or severe LV diastolic dysfunction) on TTE. The output probability of SHD was used to calculate the model’s AUROC for detecting SHD.
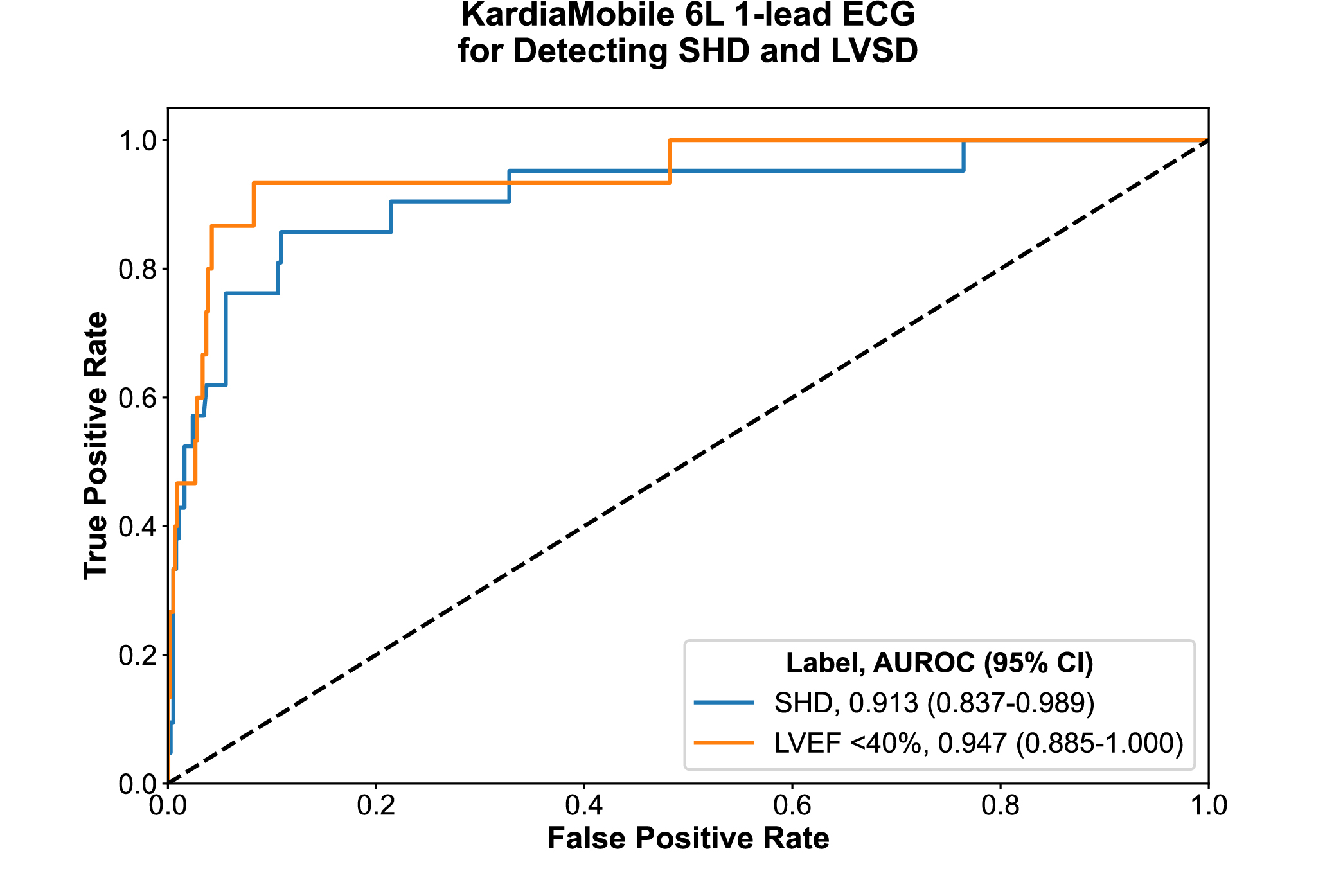
RESULTS: Of 600 participants, 597 (99.5%) successfully recorded a portable ECG and were included in the analysis. The median age was 62 years [IQR, 46–71], and 309 (51.8%) were women. There were 21 (5.3%) participants with SHD, including 15 (2.6%) with LVEF <40%, 5 (1.0%) with severe valvular disease, and 1 (0.2%) with severe LVH. ADAPT-HEART demonstrated an AUROC of 0.913 (95% CI, 0.837–0.989) for detecting SHD from 1-lead ECGs obtained with the KardiaMobile 6L. The AI-ECG model had a sensitivity of 85.7% and a specificity of 88.4% in detecting SHD. With a SHD prevalence of 5.3% in the study population, the model demonstrated a PPV of 29.0%, thereby enhancing the yield of TTE in identifying individuals with SHD by more than 5-fold.
CONCLUSIONS: ADAPT-HEART, a noise-adapted AI model for 1-lead ECGs, can detect a broad range of SHDs using a 30-second, 1-lead ECG obtained with the KardiaMobile 6L portable device. The portability of these devices, coupled with a validated and accurate SHD detection algorithm, can enable large-scale screening for SHDs in the community.
BACKGROUND: Portable devices that capture 1-lead ECG, coupled with AI tools, hold the potential to scale screening for structural heart disease (SHD) in communities. We previously developed ADAPT-HEART, a noise-adapted, 1-lead AI-ECG algorithm to detect SHD that could be scaled to portable devices.
AIM: In this investigator-initiated and independent ACCESS-SHD Study, we prospectively evaluated ADAPT-HEART in detecting SHD from 1-lead ECGs obtained with a real-world portable device, the AliveCor KardiaMobile 6L device.
METHODS: We prospectively enrolled 600 participants receiving a transthoracic echocardiogram (TTE) as part of their clinical care at Yale New Haven Hospital. Consenting participants captured a 30-second, 1-lead ECG using the KardiaMobile 6L device in the echo laboratory. We accessed the 1-lead data via an automated application programming interface (API) and deployed ADAPT-HEART. The model's output probability represented the risk of SHD, defined as a composite of LVEF <40%, severe left-sided valvular disease, or severe LVH (IVSd >15 mm + moderate or severe LV diastolic dysfunction) on TTE. The output probability of SHD was used to calculate the model’s AUROC for detecting SHD.
RESULTS: Of 600 participants, 597 (99.5%) successfully recorded a portable ECG and were included in the analysis. The median age was 62 years [IQR, 46–71], and 309 (51.8%) were women. There were 21 (5.3%) participants with SHD, including 15 (2.6%) with LVEF <40%, 5 (1.0%) with severe valvular disease, and 1 (0.2%) with severe LVH. ADAPT-HEART demonstrated an AUROC of 0.913 (95% CI, 0.837–0.989) for detecting SHD from 1-lead ECGs obtained with the KardiaMobile 6L. The AI-ECG model had a sensitivity of 85.7% and a specificity of 88.4% in detecting SHD. With a SHD prevalence of 5.3% in the study population, the model demonstrated a PPV of 29.0%, thereby enhancing the yield of TTE in identifying individuals with SHD by more than 5-fold.
CONCLUSIONS: ADAPT-HEART, a noise-adapted AI model for 1-lead ECGs, can detect a broad range of SHDs using a 30-second, 1-lead ECG obtained with the KardiaMobile 6L portable device. The portability of these devices, coupled with a validated and accurate SHD detection algorithm, can enable large-scale screening for SHDs in the community.
More abstracts on this topic:
A peptoid derivative of alpha-calcitonin gene related peptide improves cardiac function in pressure-overload heart failure mice
Kumar Ambrish, Deloach Sarah, Dipette Donald, Potts Jay
A Cross-scale Causal Machine Learning Framework Pinpoints Mgl2+ Macrophage Orchestrators of Balanced Arterial GrowthHan Jonghyeuk, Kong Dasom, Schwarz Erica, Takaesu Felipe, Humphrey Jay, Park Hyun-ji, Davis Michael E