Final ID: Sa2163
Targeting Macrophage NCOR1 to Alleviate Inflammation in Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Inflammatory response is a key player in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction, however the underlying mechanisms remain unclear. Recent evidence indicates that macrophage inflammation driven by the transcriptional coregulatory protein NCOR1 could play a pivotal role in disease states.
Hypothesis: NCOR1 orchestrates macrophage inflammation and cardiac dysfunction in HFpEF.
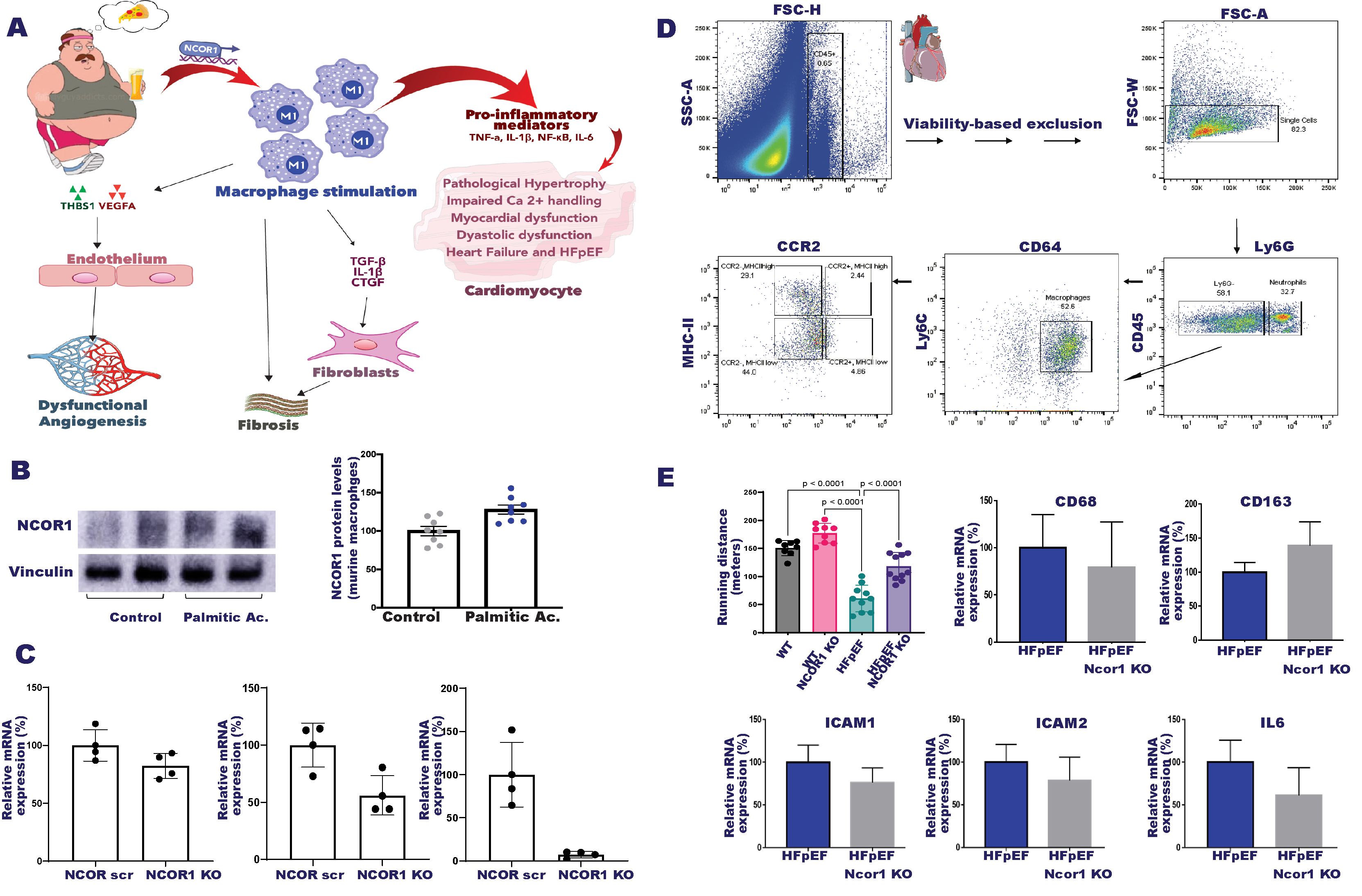
Methods: HFpEF was induced in mice using a validated model combining high-fat diet and L-NAME for 15 weeks. Cardiac function was assessed using high-resolution ultrasound imaging and LV samples were used to study macrophage polarization and inflammation by FACS. We generated myeloid-specific NCOR1-KO mice to investigate the in vivo effects of macrophage NCOR1 depletion on HFpEF. In vitro experiments included RAW 264.7 cells polarization and the assessment of macrophage phenotype switching in the presence or the absence of NCOR1. To study the crosstalk of macrophages with the surrounding cardiac cells, cardiomyocytes (H9c2) and endothelial cells (HAECS) were exposed to conditioned media from cultured RAW.
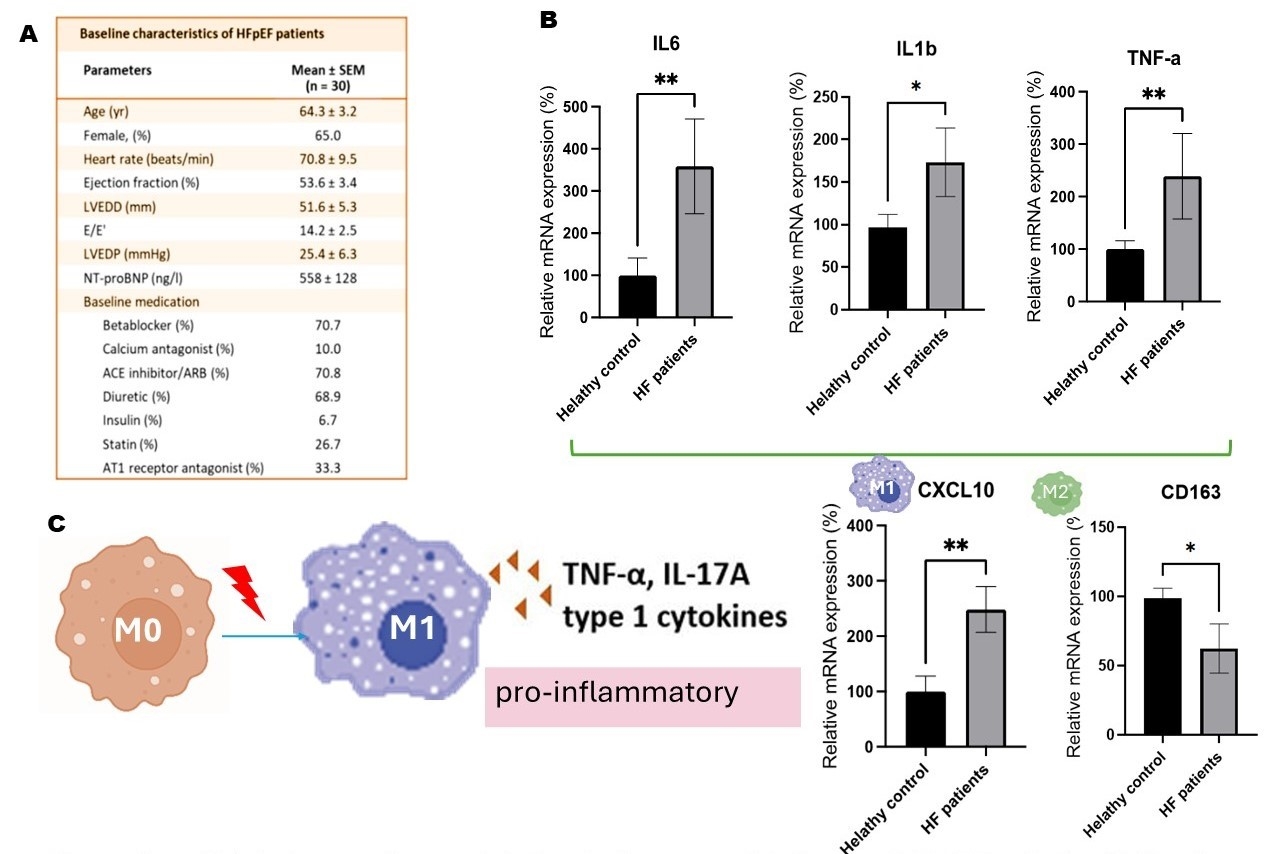
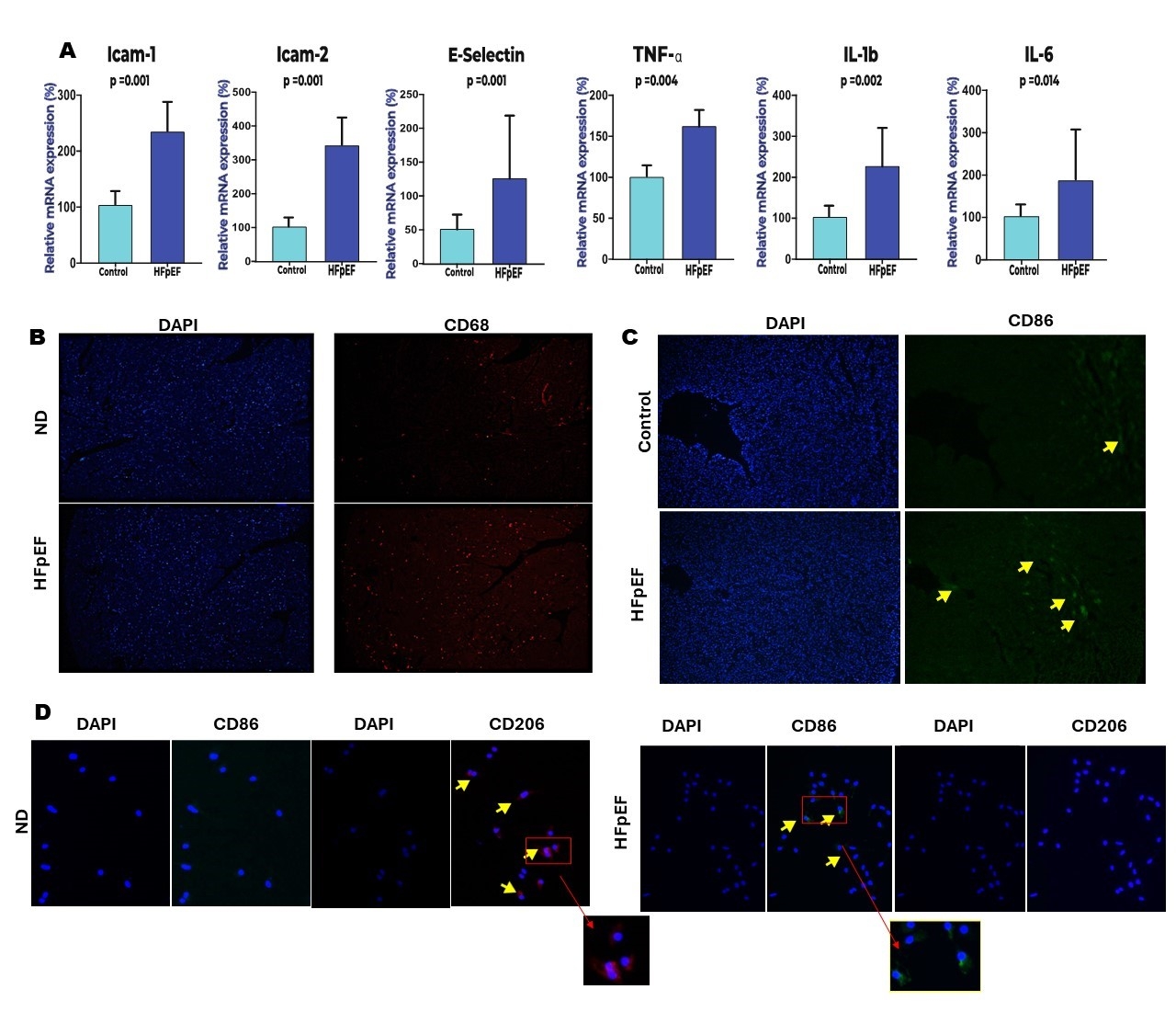
Results: The expression of macrophage markers in human LV specimens showed an increase in pro-inflammatory macrophages (M1) and a decrease in regulatory macrophages (M2) as compared to age-matched control mice. HFpEF mice showed increased expression of vascular adhesion molecules (ICAM1, ICAM2, E-selectin) and a significant recruitment of M1 macrophages as proved by qPCR, WB, and flow cytometry analysis. Of interest, diastolic dysfunction - assessed by E/A ratio and isovolumic relaxation time (IVRT) – and lung congestion were significantly reduced in mice with macrophage NCOR1 deletion as compared to WT littermates, while exercise tolerance was significantly improved. These findings were associated with a reduction of myocardial inflammation (TNF-a, IL6, IL-1b) in Ncor1-KO mice. In vitro assays showed that stimulation of macrophages with PA induced M1 type switch and increased NCOR1, TNF-a, IL-6, and IL-1b levels, whereas NCOR1 depletion prevented detrimental changes of macrophage conditional medium (Fig.1).
Conclusion: Targeting macrophage NCOR1 could represent a promising approach to blunt myocardial inflammation in HFpEF.
Hypothesis: NCOR1 orchestrates macrophage inflammation and cardiac dysfunction in HFpEF.
Methods: HFpEF was induced in mice using a validated model combining high-fat diet and L-NAME for 15 weeks. Cardiac function was assessed using high-resolution ultrasound imaging and LV samples were used to study macrophage polarization and inflammation by FACS. We generated myeloid-specific NCOR1-KO mice to investigate the in vivo effects of macrophage NCOR1 depletion on HFpEF. In vitro experiments included RAW 264.7 cells polarization and the assessment of macrophage phenotype switching in the presence or the absence of NCOR1. To study the crosstalk of macrophages with the surrounding cardiac cells, cardiomyocytes (H9c2) and endothelial cells (HAECS) were exposed to conditioned media from cultured RAW.
Results: The expression of macrophage markers in human LV specimens showed an increase in pro-inflammatory macrophages (M1) and a decrease in regulatory macrophages (M2) as compared to age-matched control mice. HFpEF mice showed increased expression of vascular adhesion molecules (ICAM1, ICAM2, E-selectin) and a significant recruitment of M1 macrophages as proved by qPCR, WB, and flow cytometry analysis. Of interest, diastolic dysfunction - assessed by E/A ratio and isovolumic relaxation time (IVRT) – and lung congestion were significantly reduced in mice with macrophage NCOR1 deletion as compared to WT littermates, while exercise tolerance was significantly improved. These findings were associated with a reduction of myocardial inflammation (TNF-a, IL6, IL-1b) in Ncor1-KO mice. In vitro assays showed that stimulation of macrophages with PA induced M1 type switch and increased NCOR1, TNF-a, IL-6, and IL-1b levels, whereas NCOR1 depletion prevented detrimental changes of macrophage conditional medium (Fig.1).
Conclusion: Targeting macrophage NCOR1 could represent a promising approach to blunt myocardial inflammation in HFpEF.
More abstracts on this topic:
Aberrant Trans- and De- Nitrosylation Underpins Nitrosative Stress in Cardiometabolic HFpEF
Li Zhen, Borch Jensen Martin, Vondriska Thomas, Lefer David, Gehred Natalie, Gromova Tatiana, Lapenna Kyle, Sharp Thomas, Chen Jingshu, Shambhu Smitha, Yu Xiaoman, Goodchild Traci
84 Immune checkpoint profiling in major aortic diseases leads to identification of potential roles of CD155-CD206 pathway in suppressing inflammation and immune responsesShao Ying, Saaoud Fatma, Xu Keman, Lu Yifan, Jiang Xiaohua, Wang Hong, Yang Xiaofeng