Final ID: MDP929
Cardiomyocyte resilience to Doxorubicin with NAD+ supplementation in cardiotoxicity
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Doxorubicin (DOX) is a potent chemotherapy drug that carries a significant risk of cardiotoxicity leading tso heart failure by presenting a notable challenge in cancer treatment. Despite being characterized by oxidative stress and inflammation, fully understanding Doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity (DIC) mechanisms remains elusive. Ongoing research emphasizes the promising role of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) and its precursors in cardiovascular health. Therefore, we sought to evaluate the effectiveness of NAD+ in preventing or reducing DIC.
Methods: H9c2 rat cardiomyocytes were pre-treated with NAD+ 100uM for 48 hours, subsequently exposed to DOX 500nM for 24 hours, and received a follow-up NAD+ 100uM treatment for an additional 48 hours. Cell viability was evaluated via the MTT assay. Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) production was measured using the MitoSOX assay. The expression of genes crucial for cardiac cell development and function was analyzed through quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR). Furthermore, Western blotting (WB) was conducted to detect changes in the expression of proteins associated with oxidative stress and apoptosis, thus providing an in-depth assessment of NAD+'s potential therapeutic effects against anthracycline-induced cardiac complications.
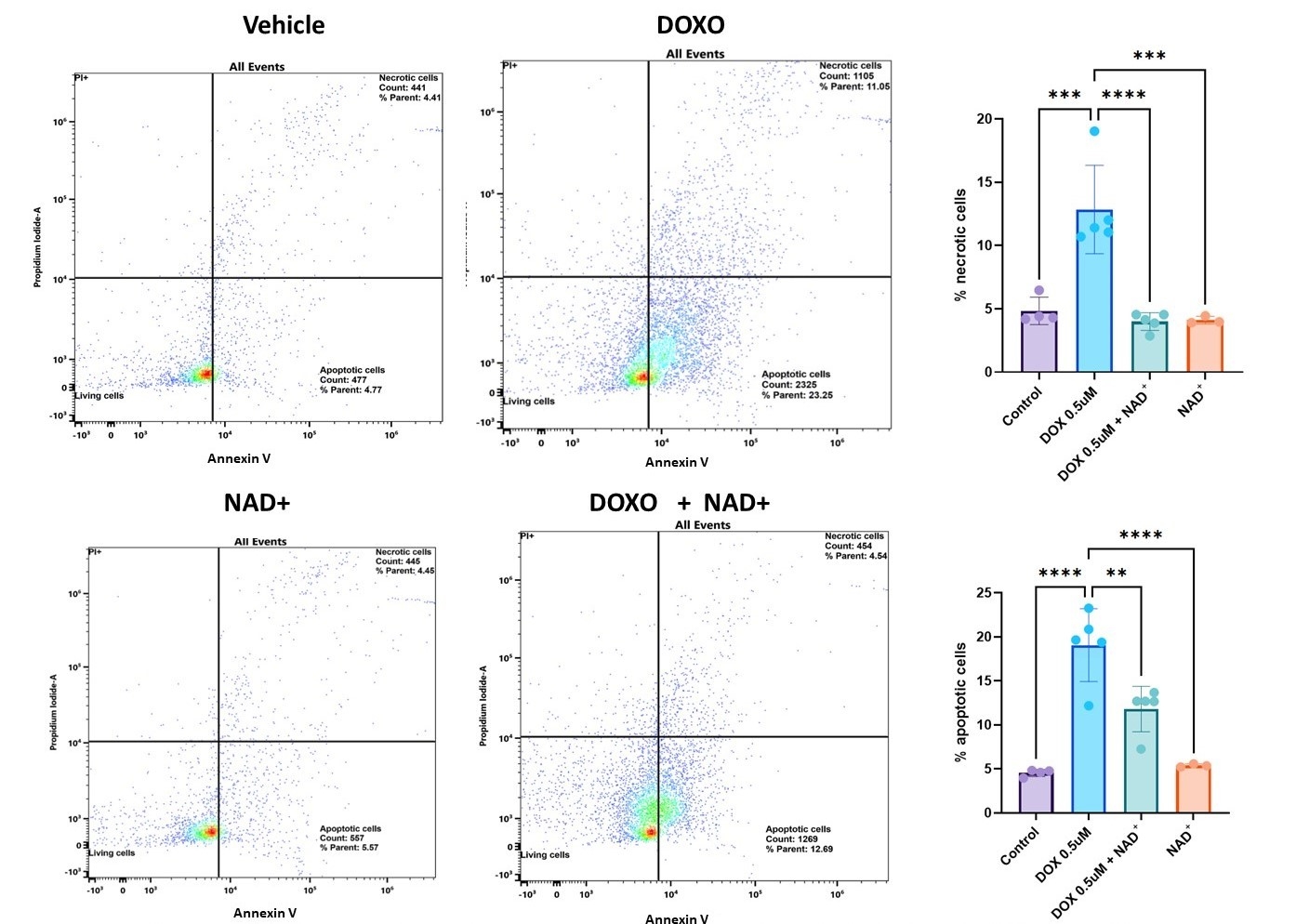
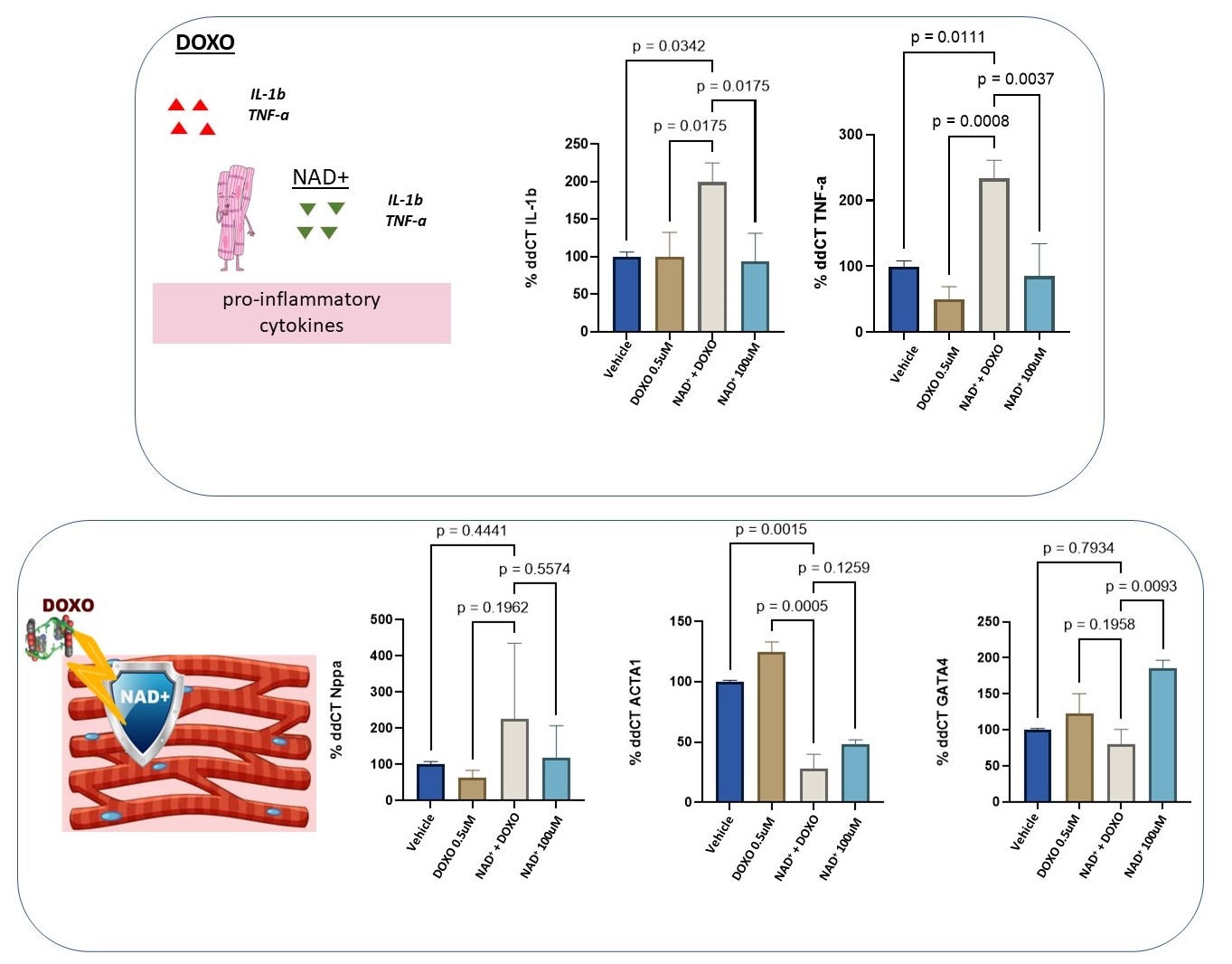
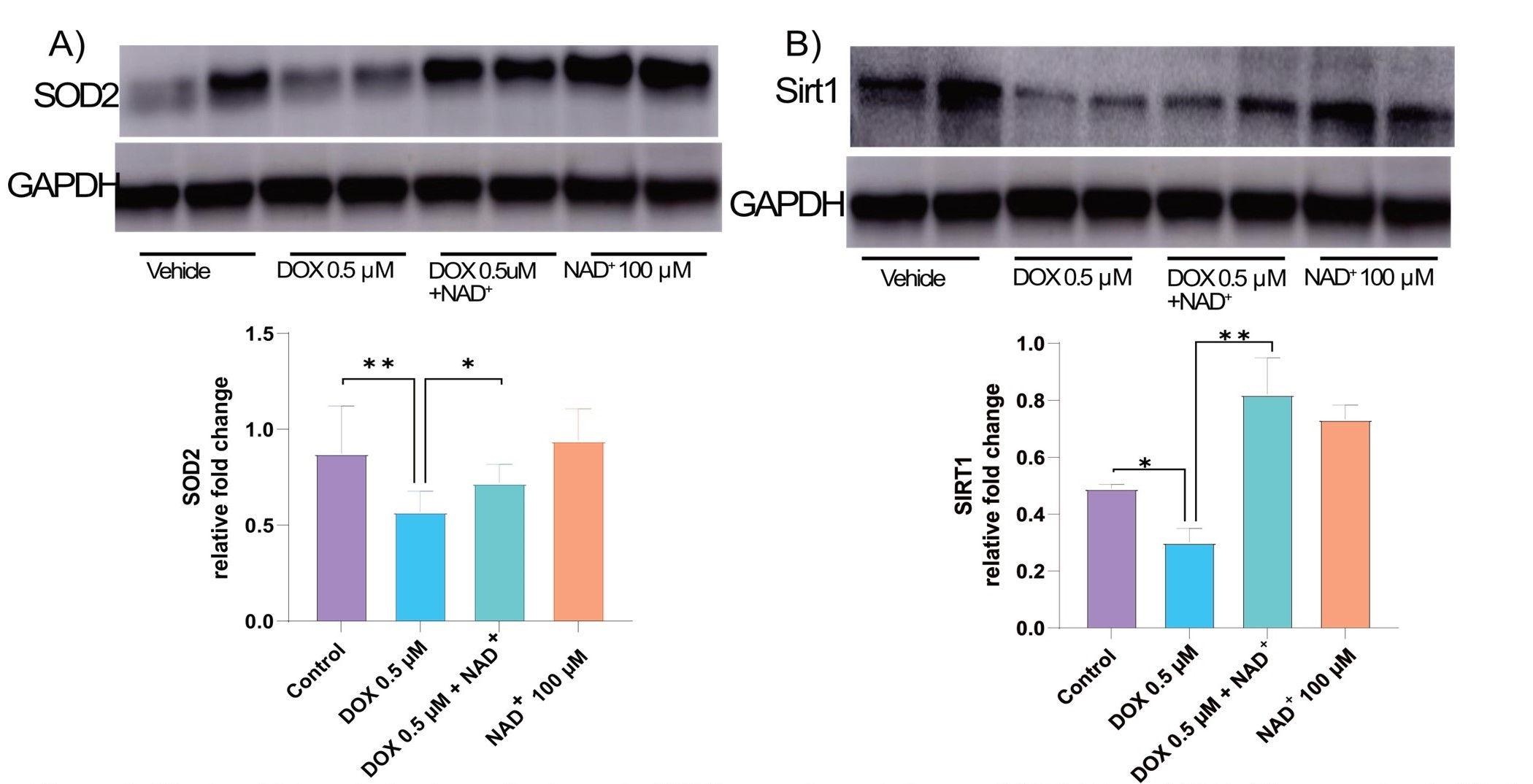
Results: NAD+ treatment maintained myocardial cell viability in the presence of DOX and modulated gene expression beneficial for cardiac function, including downregulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL1b and TNF-a. Furthermore, it reduced oxidative stress markers, decreased levels of pro-apoptotic Caspase 3, and increased levels of the antioxidant SOD2 via Sirt1 pathway regulation.
Conclusion: Our findings highlight the critical importance of a multidisciplinary research approach to elucidate the cardioprotective capacity of NAD+ against DIC, potentially paving the way for new targeted strategies in oncological therapies.
Methods: H9c2 rat cardiomyocytes were pre-treated with NAD+ 100uM for 48 hours, subsequently exposed to DOX 500nM for 24 hours, and received a follow-up NAD+ 100uM treatment for an additional 48 hours. Cell viability was evaluated via the MTT assay. Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) production was measured using the MitoSOX assay. The expression of genes crucial for cardiac cell development and function was analyzed through quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR). Furthermore, Western blotting (WB) was conducted to detect changes in the expression of proteins associated with oxidative stress and apoptosis, thus providing an in-depth assessment of NAD+'s potential therapeutic effects against anthracycline-induced cardiac complications.
Results: NAD+ treatment maintained myocardial cell viability in the presence of DOX and modulated gene expression beneficial for cardiac function, including downregulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL1b and TNF-a. Furthermore, it reduced oxidative stress markers, decreased levels of pro-apoptotic Caspase 3, and increased levels of the antioxidant SOD2 via Sirt1 pathway regulation.
Conclusion: Our findings highlight the critical importance of a multidisciplinary research approach to elucidate the cardioprotective capacity of NAD+ against DIC, potentially paving the way for new targeted strategies in oncological therapies.
More abstracts on this topic:
Apelin Signaling Protects Against Experimental Pulmonary Hypertension-Induced Right Ventricular Remodeling Through Regulation of the Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone System
Bharti Manisha, Yakubov Bakhtiyor, Zagorski John, Albrecht Marjorie, Fisher Amanda, Cook Todd, Frump Andrea
A Novel Cardioprotective Mechanism in Myocardial Reperfusion Injury: Dual Neutrophil Modulation and ROS/HOCl Scavenging by an Atypical ChemokineZwissler Leon, Bernhagen Juergen, Cabrera-fuentes Hector Alejandro, Hernandez Resendiz Sauri, Yap En Ping, Schindler Lisa, Zhang Zhishen, Dickerhof Nina, Hampton Mark, Liehn Elisa, Hausenloy Derek