Final ID: MDP981
Invasive CPET-based hemodynamic correlates of abnormal peak VO2 and VE/VCO2 in HFpEF and pre-capillary Pulmonary Hypertension
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Pulmonary hypertension (PH) is a heterogeneous disease characterized by impaired gas exchange (CO2, O2) in the pulmonary circulation, leading to dyspnea and exercise intolerance. We hypothesize that specific hemodynamic metrics correlate with poor gas exchange in PH phenotypes, which can be leveraged to define therapeutically relevant hemodynamic targets.
Aim: This study aims to define hemodynamic correlates of poor gas exchange (peak VO2, VE/VCO2 slope) in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) and pre-capillary PH.
Methods: We retrospectively analyzed 170 participants with invasive cardiopulmonary exercise testing: HFpEF (n=91), pre-capillary PH (n=54), and non-cardiac dyspnea (NCD, n=25). Linear regression models, adjusted for patient groups with interaction, were used to assess the association of peak VO2 and VE/VCO2 slope with predictors (pulmonary vascular resistance [PVR], distensibility, and pulmonary arterial compliance [PAC]).
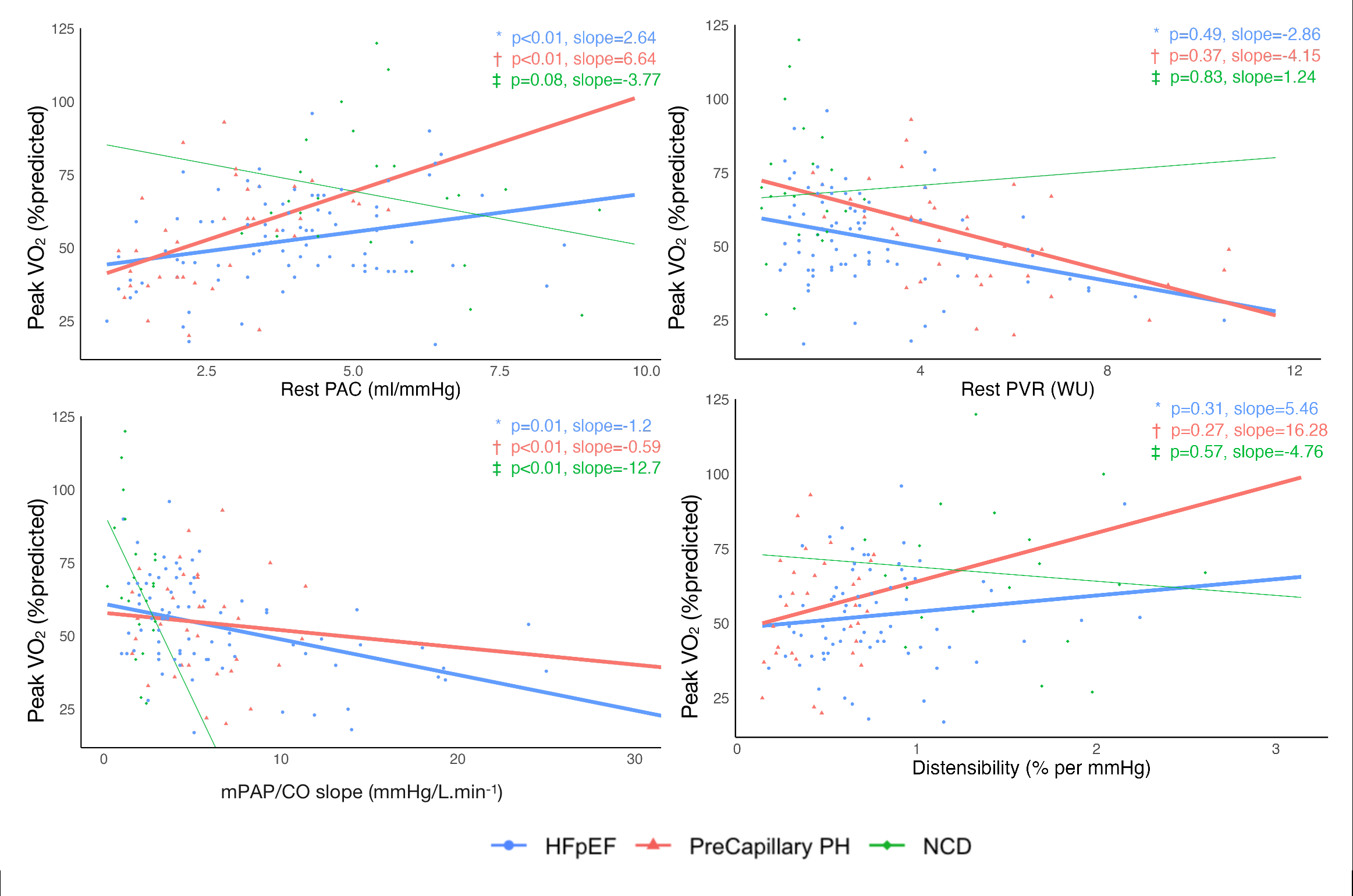
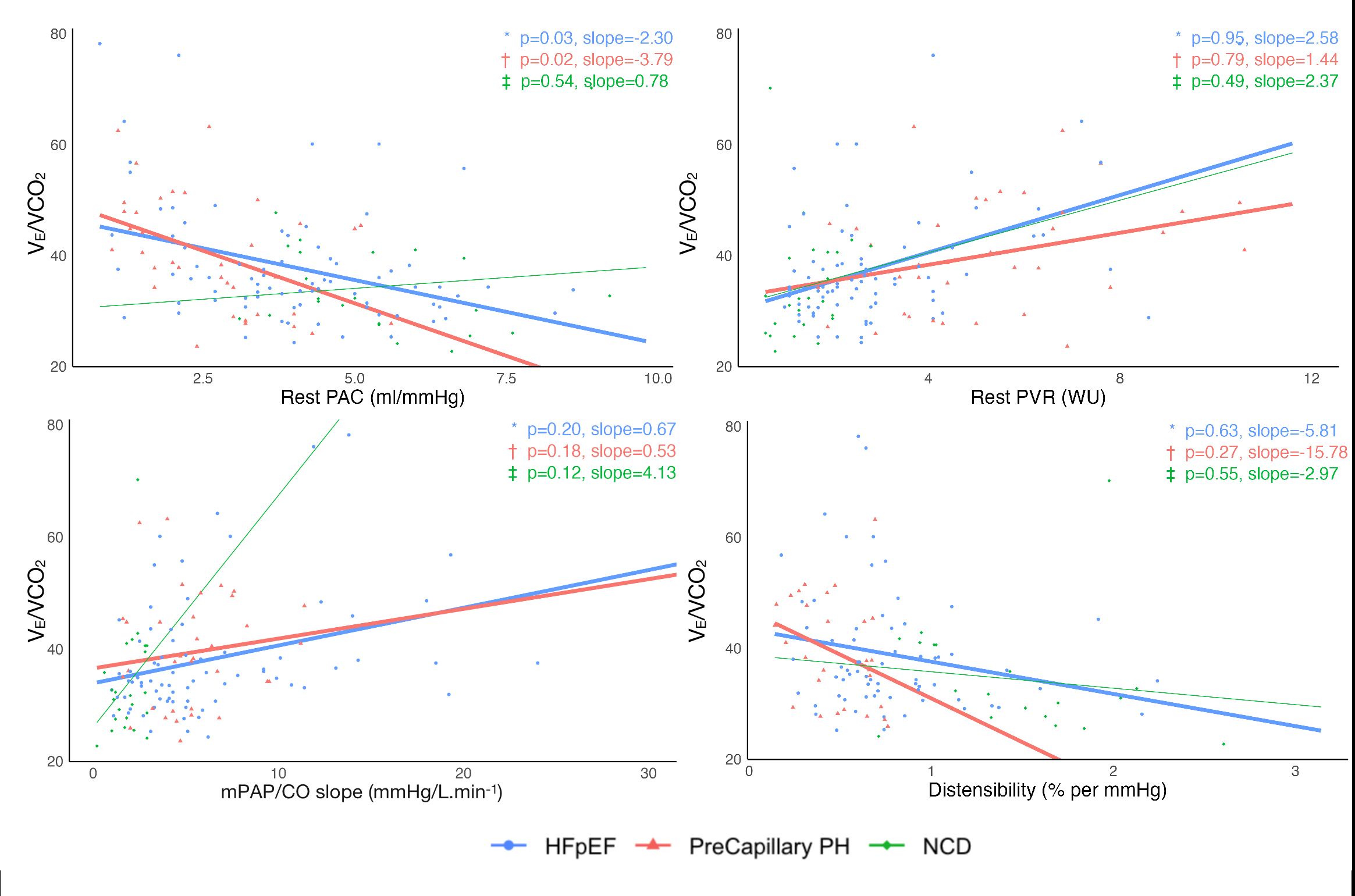
Results: In the order of NCD vs. HFpEF vs. pre-capillary PH, rest PAC (5.5±1.6 vs 3.8±1.7 vs 2.6±1.3 mL/mmHg), rest PVR (1.4±0.6 vs 3.2±2.0 vs 5.7±3.0 Woods unit), and distensibility (1.5±0.5 vs 0.8±0.4 vs 0.5±0.2 % per mmHg). In comparison to a non-significant correlation with rest PVR and distensibility, peak VO2 (%predicted) showed significant correlation with rest PAC (p<0.01) with significantly positive slope of +6 in HFpEF and +10 in pre-capillary PH. Similarly, significant slopes were noted with rest PAC and VE/VCO2 relationship (p<0.01) in HFpEF (-3) and pre-capillary PH (-4).
Conclusion: Pulmonary arterial compliance (PAC) is the best correlate of poor gas exchange. Improving rest PAC by 1.0 mL/mmHg can lead to improvement in peak VO2 predicted (+10% in pre-capillary PH, +6% in HFpEF), and VE/VCO2 slope (-4 in pre-capillary PH, and -3 in HFpEF). In comparison to pre-capillary PH, more limited improvement in HFpEF is likely due to multi-organ dysfunction leading to exercise intolerance.
Aim: This study aims to define hemodynamic correlates of poor gas exchange (peak VO2, VE/VCO2 slope) in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) and pre-capillary PH.
Methods: We retrospectively analyzed 170 participants with invasive cardiopulmonary exercise testing: HFpEF (n=91), pre-capillary PH (n=54), and non-cardiac dyspnea (NCD, n=25). Linear regression models, adjusted for patient groups with interaction, were used to assess the association of peak VO2 and VE/VCO2 slope with predictors (pulmonary vascular resistance [PVR], distensibility, and pulmonary arterial compliance [PAC]).
Results: In the order of NCD vs. HFpEF vs. pre-capillary PH, rest PAC (5.5±1.6 vs 3.8±1.7 vs 2.6±1.3 mL/mmHg), rest PVR (1.4±0.6 vs 3.2±2.0 vs 5.7±3.0 Woods unit), and distensibility (1.5±0.5 vs 0.8±0.4 vs 0.5±0.2 % per mmHg). In comparison to a non-significant correlation with rest PVR and distensibility, peak VO2 (%predicted) showed significant correlation with rest PAC (p<0.01) with significantly positive slope of +6 in HFpEF and +10 in pre-capillary PH. Similarly, significant slopes were noted with rest PAC and VE/VCO2 relationship (p<0.01) in HFpEF (-3) and pre-capillary PH (-4).
Conclusion: Pulmonary arterial compliance (PAC) is the best correlate of poor gas exchange. Improving rest PAC by 1.0 mL/mmHg can lead to improvement in peak VO2 predicted (+10% in pre-capillary PH, +6% in HFpEF), and VE/VCO2 slope (-4 in pre-capillary PH, and -3 in HFpEF). In comparison to pre-capillary PH, more limited improvement in HFpEF is likely due to multi-organ dysfunction leading to exercise intolerance.
More abstracts on this topic:
Effect of Medical-Grade Mask Use on Exercise Physiology in Healthy Adults: A Randomized Crossover Study
Lee Ju-hee, Lee Goo Joo, Kang Mingyu, Eom Sang Yong
A Novel EMR-Based Algorithm with the Virtual Echocardiography Screening Tool (VEST) to Screen Patients for Pulmonary Arterial HypertensionNarowska Gabriela, Anand Suneesh, Gangireddy Chethan, Enevoldsen John, Keane Martin, Edmundowicz Daniel, Forfia Paul, Vaidya Anjali