Final ID: MDP1106
Exercise Pulmonary Vascular Mechanics and cardiac MRI prospective study to define Low vs. High-risk HFpEF phenotypes with Right Ventricular Failure in HFpEF
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here):
Background: Highly precise definition of high-risk features associated with HFpEF may guide targeted treatments and inform biological studies. The aim of this two-step study is to 1) define a high risk HFpEF cluster with unsupervised machine learning approach using cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR), 2) define novel pulmonary vascular mechanics at rest and with exercise in low- vs. high-risk phenotypes. Vascular mechanics defines vessel- and cardiac cycle-specific flow dynamics in pulmonary circulation.
Methods: 48 HFpEF participants underwent CMR and invasive cardiopulmonary exercise testing. With unsupervised K-means clustering analyses using CMR data, two specific clusters were identified with different survival outcomes at 12-months (mortality and heart failure hospitalizations): HR=5.4 (CI:1.7-17.4), log-rank p<0.01. Within this cohort (n=48), additional flow data (right ventricular outflow tract pulse wave doppler) was acquired in 13 participants at rest and 25 watts exercise, to obtain simultaneous pressure (pulmonary artery)-flow data for vascular mechanics analyses in time domain.
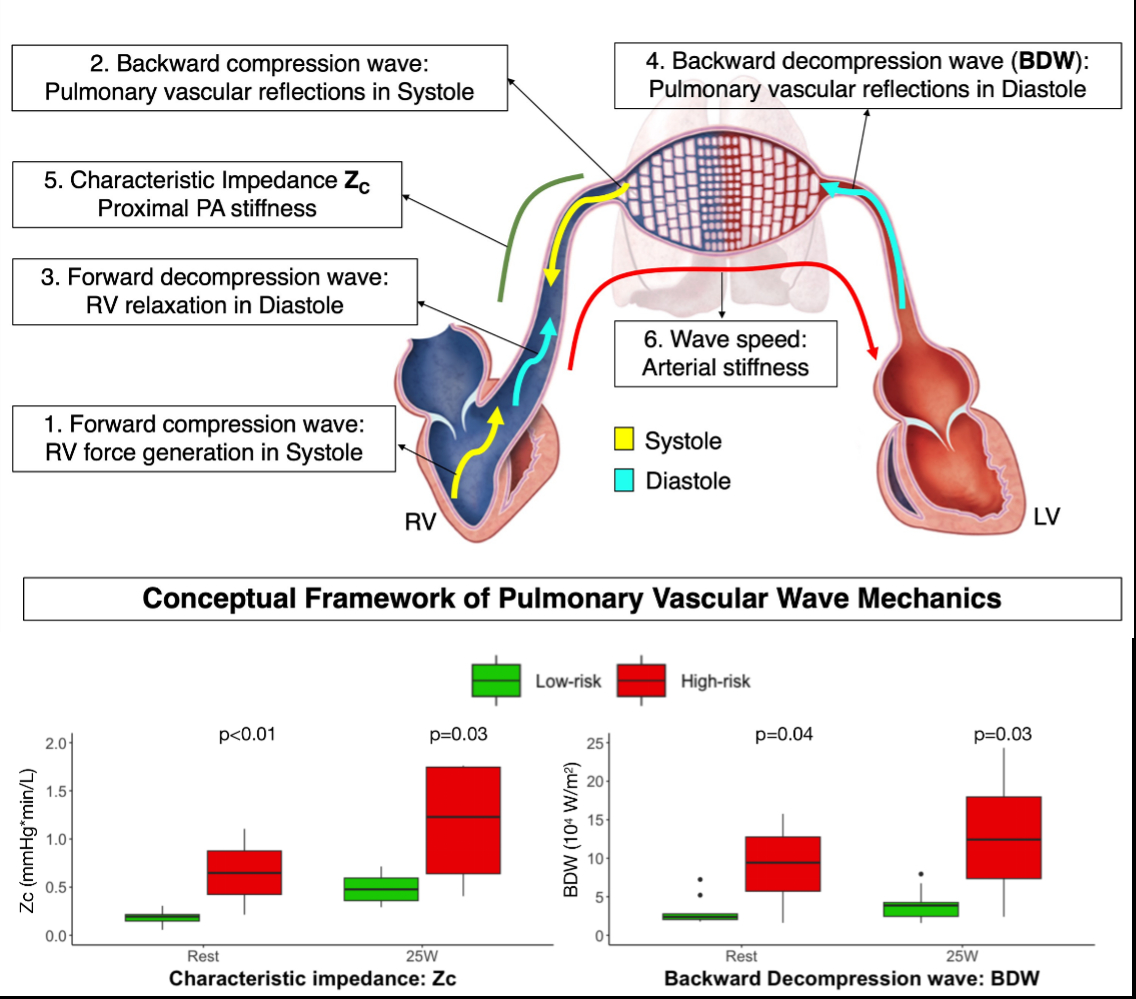
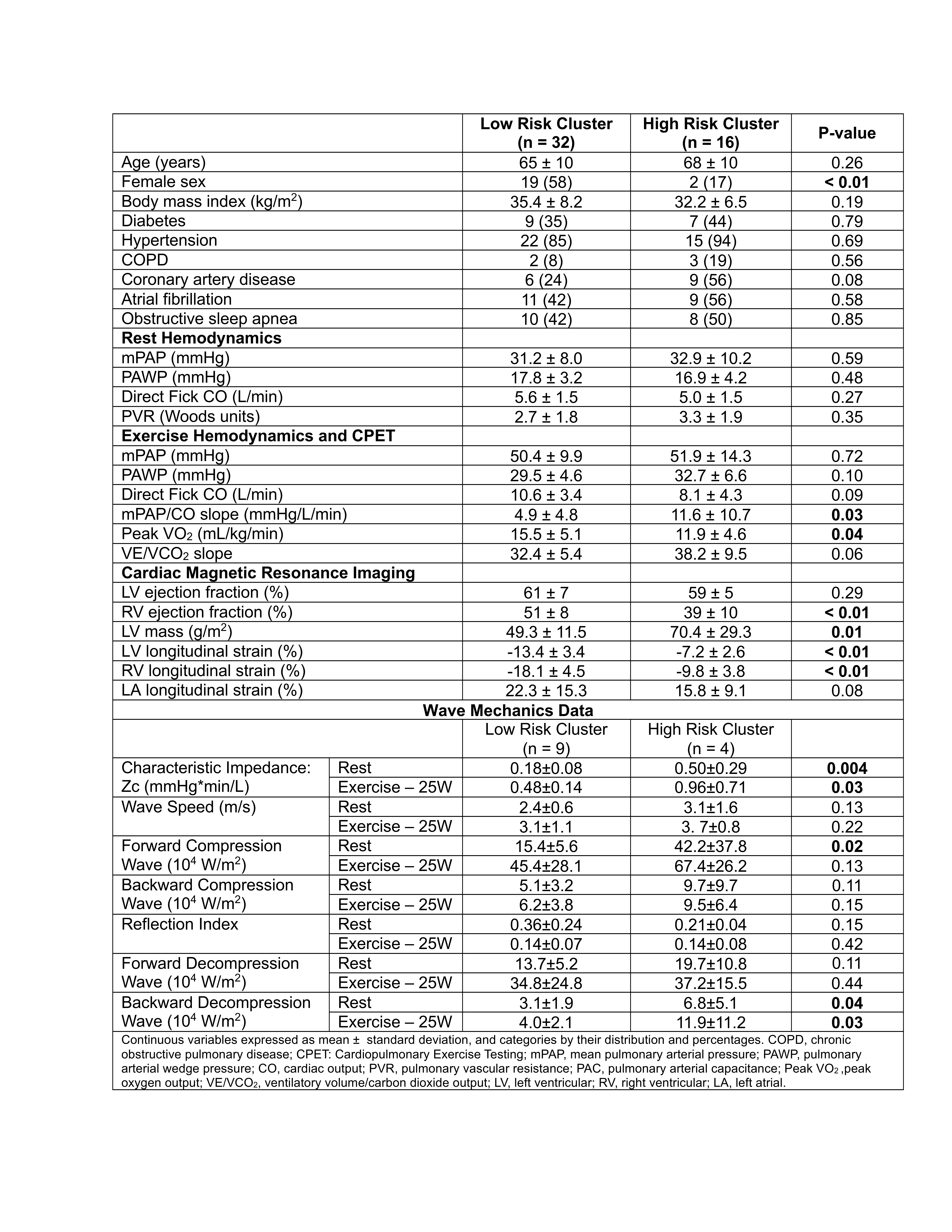
Results: Features of low- (n=32) and high-risk (n=16) clusters are summarized in Table. High-risk cluster displayed decreased right ventricular ejection fraction and worse biventricular longitudinal strain. Among wave mechanics, characteristic impedance (proximal pulmonary artery stiffness) and backward decompression wave (pulmonary vascular reflections in diastole) were elevated in high-risk HFpEF phenotype.
Conclusions: We report a high-risk HFpEF phenotype with reduced RV ejection fraction and biventricular strain, indicating myocardial limitations. Vascular mechanics revealed proximal pulmonary artery stiffness and increased wave reflections in diastole as key features in high-risk HFpEF, indicating pulmonary vascular limitations. These multimodal methods reveal that mechanism of RV failure in HFpEF likely involves both pulmonary vascular and intrinsic myocardial abnormalities.
Background: Highly precise definition of high-risk features associated with HFpEF may guide targeted treatments and inform biological studies. The aim of this two-step study is to 1) define a high risk HFpEF cluster with unsupervised machine learning approach using cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR), 2) define novel pulmonary vascular mechanics at rest and with exercise in low- vs. high-risk phenotypes. Vascular mechanics defines vessel- and cardiac cycle-specific flow dynamics in pulmonary circulation.
Methods: 48 HFpEF participants underwent CMR and invasive cardiopulmonary exercise testing. With unsupervised K-means clustering analyses using CMR data, two specific clusters were identified with different survival outcomes at 12-months (mortality and heart failure hospitalizations): HR=5.4 (CI:1.7-17.4), log-rank p<0.01. Within this cohort (n=48), additional flow data (right ventricular outflow tract pulse wave doppler) was acquired in 13 participants at rest and 25 watts exercise, to obtain simultaneous pressure (pulmonary artery)-flow data for vascular mechanics analyses in time domain.
Results: Features of low- (n=32) and high-risk (n=16) clusters are summarized in Table. High-risk cluster displayed decreased right ventricular ejection fraction and worse biventricular longitudinal strain. Among wave mechanics, characteristic impedance (proximal pulmonary artery stiffness) and backward decompression wave (pulmonary vascular reflections in diastole) were elevated in high-risk HFpEF phenotype.
Conclusions: We report a high-risk HFpEF phenotype with reduced RV ejection fraction and biventricular strain, indicating myocardial limitations. Vascular mechanics revealed proximal pulmonary artery stiffness and increased wave reflections in diastole as key features in high-risk HFpEF, indicating pulmonary vascular limitations. These multimodal methods reveal that mechanism of RV failure in HFpEF likely involves both pulmonary vascular and intrinsic myocardial abnormalities.
More abstracts on this topic:
Integrin α5β1 represents a novel therapeutic target to improve vascular remodeling in pulmonary arterial hypertension
Lemay Sarah-eve, Theberge Charlie, Martineau Sandra, Lippa Blaise, Goodwin Bryan, Lin Albert, Wang Hua, Dowling James, Lu Min, Qiao Qi, Mcteague T. Andrew, Montesinos Monica, Moy Terence I., Potus Francois, Provencher Steeve, Boucherat Olivier, Bonnet Sebastien, Grobs Yann, Yokokawa Tetsuro, Shimauchi Tsukasa, Romanet Charlotte, Sauvaget Melanie, Breuils Bonnet Sandra, Bourgeois Alice
5-oxoproline/ OPLAH Axis Alleviates Doxorubicin-induced Cardiomyopathy By Inhibiting FerroptosisJiang Meng, Guo Xinning