Final ID:
Targeting leucine metabolism in macrophages as a novel therapeutic strategy in atherosclerosis.
Abstract Body: Background: Despite numerous improvements in treatment and prevention, cardiovascular disease (CVD) remains one of the leading causes of morbidity and mortality in the world. Nutrients such as lipids have long been linked to CVD pathogenesis. However, the role of other nutrients such as amino acids remains poorly defined. Recently, we implicated amino acids in the stimulation of pathogenic mTOR signaling in macrophages to drive atherosclerosis. More importantly, we identified leucine as the predominant activator of this signaling pathway that solely explains the atherosclerosis phenotype. Therefore, selective inhibition of leucine-mediated mTORC1 activation in macrophages appears to be a highly promising therapeutic approach in CVD.
Methods: We utilize two independent approaches to target leucine metabolism in macrophages by inhibiting its uptake and stimulating its catabolism in order to reduce pathogenic mTOR signaling. Both murine and human primary macrophages in vitro and genetic and pharmacological approaches in vivo are used to conduct this work.
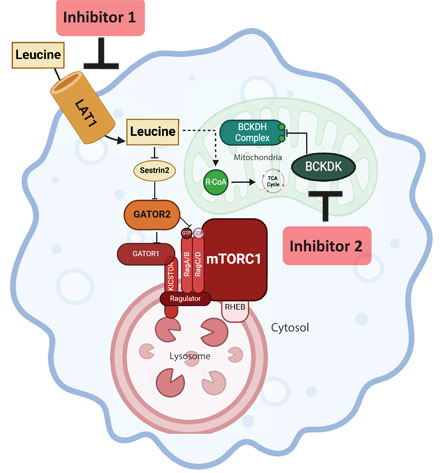
Results: First, we found leucine to be particularly enriched in lesional macrophages using PET/CT imaging of plaques via an F18-leucine analog. Immunofluorescence staining and scRNAseq profiling of murine and human plaques revealed concomitant increase in the major leucine transporter, LAT1/SLC7a5, as well as the critical inhibitor of leucine catabolism, BCKDK. Genetic or transcriptional silencing of either LAT1 or BCKDK were equally effective in reducing macrophage mTOR signaling which ameliorated mitochondrial dysfunction, apoptosis, and ROS generation via protective autophagy/mitophagy signaling. These data were recapitulated using pharamacological inhibitors of LAT1 and BCKDK in primary macrophages, circulating monocytes, and plaques of atherogenic ApoE-null mice. Utilizing macrophage-specific LAT1-null mice (on ApoE-null background) we observed significant reductions in plaque size and complexity. The pharmacological inhibition of LAT1 also abrogated leucine uptake in ApoE-null mice resulting in atheroprotection mirroring our genetic data.
Conclusions: Our study is the first to demonstrate that modulation of leucine metabolism in macrophages is a highly effective approach to suppress mTORC1 signaling and atherosclerosis with implications in CVD therapeutics.
Methods: We utilize two independent approaches to target leucine metabolism in macrophages by inhibiting its uptake and stimulating its catabolism in order to reduce pathogenic mTOR signaling. Both murine and human primary macrophages in vitro and genetic and pharmacological approaches in vivo are used to conduct this work.
Results: First, we found leucine to be particularly enriched in lesional macrophages using PET/CT imaging of plaques via an F18-leucine analog. Immunofluorescence staining and scRNAseq profiling of murine and human plaques revealed concomitant increase in the major leucine transporter, LAT1/SLC7a5, as well as the critical inhibitor of leucine catabolism, BCKDK. Genetic or transcriptional silencing of either LAT1 or BCKDK were equally effective in reducing macrophage mTOR signaling which ameliorated mitochondrial dysfunction, apoptosis, and ROS generation via protective autophagy/mitophagy signaling. These data were recapitulated using pharamacological inhibitors of LAT1 and BCKDK in primary macrophages, circulating monocytes, and plaques of atherogenic ApoE-null mice. Utilizing macrophage-specific LAT1-null mice (on ApoE-null background) we observed significant reductions in plaque size and complexity. The pharmacological inhibition of LAT1 also abrogated leucine uptake in ApoE-null mice resulting in atheroprotection mirroring our genetic data.
Conclusions: Our study is the first to demonstrate that modulation of leucine metabolism in macrophages is a highly effective approach to suppress mTORC1 signaling and atherosclerosis with implications in CVD therapeutics.
More abstracts on this topic:
ApoB-100 peptide nanoparticles inhibit established atherosclerosis progression in female HLA-A*0201 transgenic mice
Zhou Jianchang, Zhao Xiaoning, Dimayuga Paul, Lio Nicole, Cercek Bojan, Trac Noah, Chung Eun Ji, Shah Prediman, Chyu Kuang-yuh
A hepatic steatosis-mediated metabolite reprograms macrophage lipid metabolism and aggravates atherosclerosisLong Ting, Feng Ruijia, Feng Weiqi, Peng Guiyan, Yang Wenchao, Li Zilun, Huang Kan, Chang Guangqi