Final ID:
Indoxyl Sulfate Suppresses GAS6 and Impairs Anti-Atherogenic Macrophage Function: A Novel Mechanism Driving Accelerated Atherosclerosis in Chronic Kidney Disease
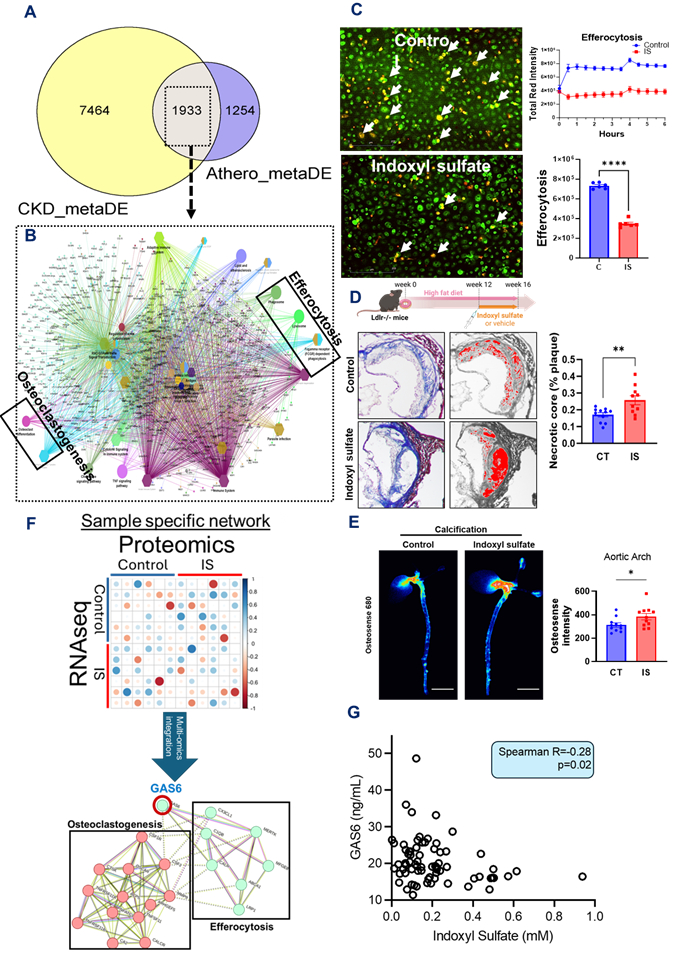
Methods & Results: Meta-analysis of gene expression datasets from CKD (n=102) and atherosclerosis (n=136) identified 1,933 shared differentially expressed genes. Pathway analysis highlighted impaired efferocytosis and osteoclastogenesis as shared mechanisms (Fig. A, B). IS exposure impairs efferocytosis, crucial for apoptotic cell clearance, and osteoclastogenesis, which mitigates vascular calcification, both in vitro and in vivo.
Clinically relevant IS levels (1 mM) suppressed efferocytosis (P=<0.0001, Fig. C) and osteoclastogenesis (>50% reduction, P=0.002) in human primary macrophages (n=6 PBMC donors). In vivo, IS administration (100 mg/kg/day for 4 weeks) in hyperlipidemic Ldlr-/- mice impaired efferocytosis, increasing necrotic core area in plaques (n=10/group, P=0.007, Fig. D). IS also inhibited osteoclastogenesis, promoting aortic calcification in mouse plaques (n=10/group, P=0.04, Fig. E).
Multi-omics integration of transcriptomics and proteomics data from IS-treated human macrophages (n=6 PBMC donors) identified growth arrest-specific protein 6 (GAS6), essential for macrophage-apoptotic cell interaction, as a key target (Fig. F). IS-treated macrophages and mouse plaques demonstrated a >50% reduction in GAS6 mRNA and protein. Mechanistic studies revealed that IS suppresses GAS6 via STAT6 signaling. In macrophage-specific Gas6 knock-in mice, efferocytosis and osteoclastogenesis were restored despite IS exposure. Clinical validation showed a significant inverse correlation (P=0.02) between GAS6 levels and IS in CKD patients on hemodialysis (n=74, Fig. G).
Conclusions: IS suppresses GAS6 through STAT6 signaling, repressing efferocytosis and osteoclastogenesis, leading to high-risk plaque features. These findings elucidate CKD-associated atherogenesis and identify GAS6 as a therapeutic target to reduce cardiovascular risk in CKD.
- Jha, Prabhash ( Brigham and Womens Hospital, Harvard Medical School , Boston , Massachusetts , United States )
- Kasai, Taku ( Brigham and Women's Hospital , Boston , Massachusetts , United States )
- Vromman, Amelie ( Brigham and Women's Hospital , Boston , Massachusetts , United States )
- Libby, Peter ( BRIGHAM AND WOMENS HOSPITAL , Boston , Massachusetts , United States )
- Tabas, Ira ( Columbia Univ. Medical Center , New York , New York , United States )
- Holden, Rachel ( Queen's University , Kingston , Ontario , Canada )
- Singh, Sasha ( BRIGHAM AND WOMEN'S HOSPITAL , Boston , Massachusetts , United States )
- Aikawa, Elena ( BRIGHAM WOMANS HOSPITAL , Boston , Massachusetts , United States )
- Aikawa, Masanori ( Brigham and Women's Hospital , Boston , Massachusetts , United States )
- Lupieri, Adrien ( Brigham and Women's Hospital , Boston , Massachusetts , United States )
- Chelvanambi, Sarvesh ( Brigham And Womens Hospital , Brighton , Massachusetts , United States )
- Sonawane, Abhijeet ( Brigham and Women's Hospital , Boston , Massachusetts , United States )
- Le, Thanh-dat ( Brigham and Women's Hospital , Boston , Massachusetts , United States )
- Turner, Mandy ( Brigham and Women's Hospital , Boston , Massachusetts , United States )
- Becker-greene, Dakota ( Brigham and Women's Hospital , Boston , Massachusetts , United States )
- Nakamura, Yuto ( Brigham and Women's Hospital , Boston , Massachusetts , United States )
- Passos, Livia Silva ( Brigham and Women's Hospital , Boston , Massachusetts , United States )
Meeting Info:
Session Info:
Wednesday, 04/23/2025 , 03:30PM - 05:00PM
Oral
More abstracts on this topic:
Kala Petr, Miklovic Matus, Molnar Matej, Mikula Jan, Skaroupkova Petra, Gawrys Olga, Ostadal Petr, Melenovsky Vojtech, Cervenka Ludek
Computational Model Predicts Mechanisms of Low-density Lipoprotein Receptor-related Protein 1 Cardioprotection through the RISK PathwayNgo Lavie, Saquing Jamie, Abbate Antonio, Toldo Stefano, Saucerman Jeffrey
More abstracts from these authors:
Jha Prabhash, Kasai Taku, Vromman Amelie, Holden Rachel, Libby Peter, Tabas Ira, Singh Sasha, Aikawa Elena, Aikawa Masanori, Lupieri Adrien, Sonawane Abhijeet, Le Thanh-dat, Becker-greene Dakota, Chelvanambi Sarvesh, Turner Mandy, Nakamura Yuto, Passos Livia
Characterization of NIMA-related kinase 7 (NEK7)-NLRP3 inflammasome complex in macrophages by combining CRISPR/Cas9 gene-editing with comprehensive proteomicNakamura Yuto, Chelvanambi Sarvesh, Kasai Taku, Whelan Mary, Sasaki Yusuke, Singh Sasha, Aikawa Elena, Aikawa Masanori