Final ID: 4141227
Characterization of NIMA-related kinase 7 (NEK7)-NLRP3 inflammasome complex in macrophages by combining CRISPR/Cas9 gene-editing with comprehensive proteomic
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: The aberrant activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome in macrophages promotes chronic inflammation in cardiovascular disease (CVD). NEK7 is essential to the NLRP3 inflammasome’s function, however, its role in inflammasome-mediated macrophage activation has yet to be elucidated.
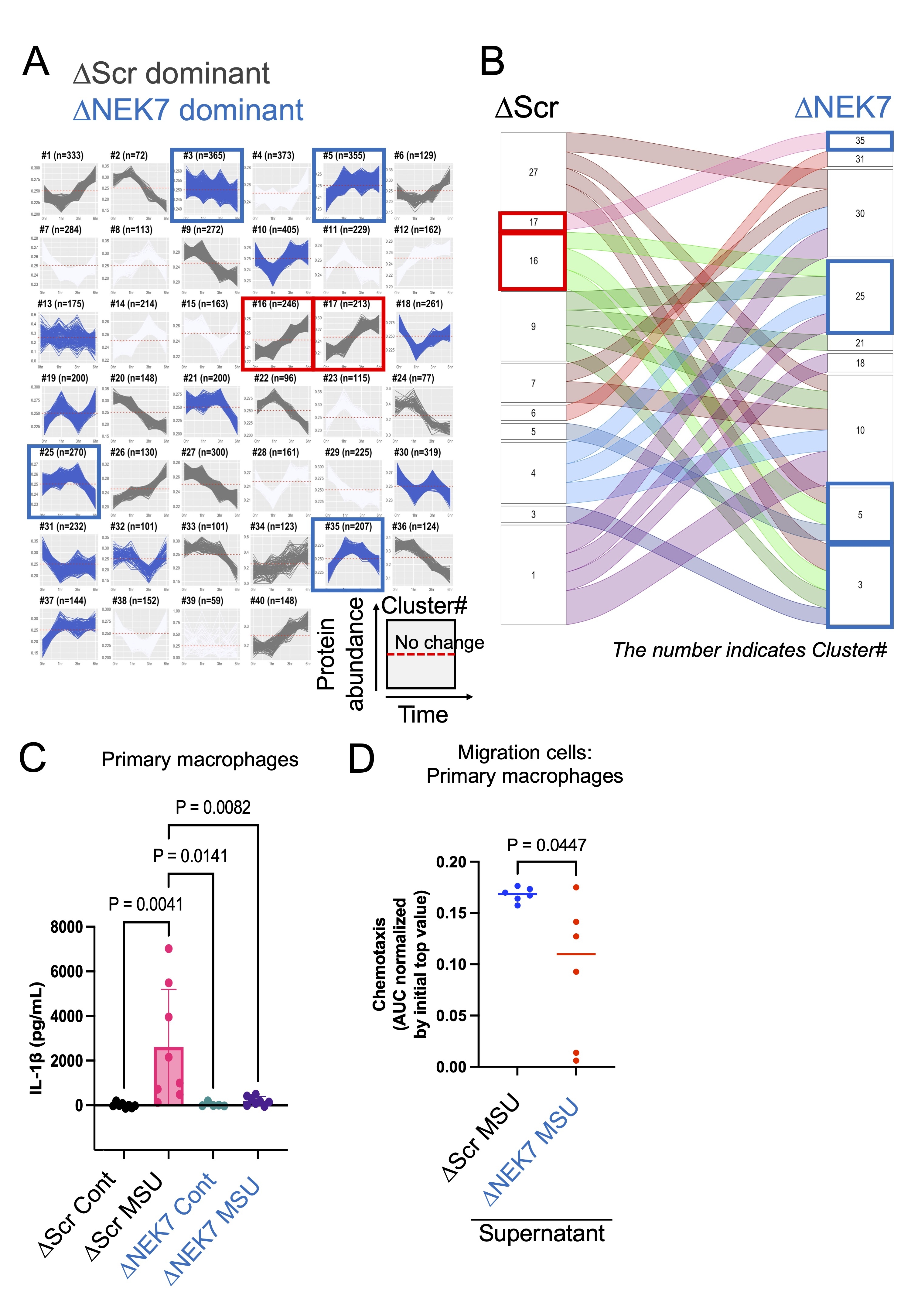
Methods & Results: We employed CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing to delete NEK7 in human primary macrophage cells (PBMCs) and in a macrophage-like cell line (THP-1). First, we employed mass spectrometry-based proteomics to monitor the response of Scramble control (ΔScr) or NEK7-null (ΔNEK7)-THP-1 cells to monosodium urate crystal (MSU). We quantified 4,030 proteins representing ΔNEK7-THP-1 and ΔScr-THP-1 conditions, analyzed at 4 timepoints (0hr, 1hr, 3hr, 6hr; MSU treamtent). NEK7 was identified in ΔScr but not in ΔNEK7 cells. In order to identify proteins whose abundances were suppressed by ΔNEK7, we performed a multiplexed high-dimensional clustering and network analysis using our custom made software (XINA, Fig.A). Specifically, we identified NOD-like receptor and Interleukin-1 (IL-1) signaling in clusters 16 and 17, that a) increased steadily over the timepoints and b) were overrepresented by proteins from the ΔScr condition (Fig.A, red rectangles). Whereas in ΔNEK7, these proteins migrated to either clusters 3, 5, 25, or 35 (Fig.B, alluvial plot), indicating their suppression (Fig.A, blue rectangles). In ΔNEK7-PBMCs, IL-1β secretion decreased in response to MSU compared to ΔScr-PBMCs (Fig.C, n=8); and less chemotaxis as determined by high-content imaging that monitored PBMC migration (Fig.D, n=6). Finally, we confirmed that small molecule inhibitor of the NLRP3-NEK7 complex itself decreased IL-1β secretion in an MSU-elicited peritonitis mouse model (C57BL/6J, n= 8, Control: PBS, p<0.05).
Conclusions: NEK7 itself is sufficient as a therapeutic target to suppress inflammasome-mediated macrophage activation; providing molecular bases for the development of new therapies for CVD.
Methods & Results: We employed CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing to delete NEK7 in human primary macrophage cells (PBMCs) and in a macrophage-like cell line (THP-1). First, we employed mass spectrometry-based proteomics to monitor the response of Scramble control (ΔScr) or NEK7-null (ΔNEK7)-THP-1 cells to monosodium urate crystal (MSU). We quantified 4,030 proteins representing ΔNEK7-THP-1 and ΔScr-THP-1 conditions, analyzed at 4 timepoints (0hr, 1hr, 3hr, 6hr; MSU treamtent). NEK7 was identified in ΔScr but not in ΔNEK7 cells. In order to identify proteins whose abundances were suppressed by ΔNEK7, we performed a multiplexed high-dimensional clustering and network analysis using our custom made software (XINA, Fig.A). Specifically, we identified NOD-like receptor and Interleukin-1 (IL-1) signaling in clusters 16 and 17, that a) increased steadily over the timepoints and b) were overrepresented by proteins from the ΔScr condition (Fig.A, red rectangles). Whereas in ΔNEK7, these proteins migrated to either clusters 3, 5, 25, or 35 (Fig.B, alluvial plot), indicating their suppression (Fig.A, blue rectangles). In ΔNEK7-PBMCs, IL-1β secretion decreased in response to MSU compared to ΔScr-PBMCs (Fig.C, n=8); and less chemotaxis as determined by high-content imaging that monitored PBMC migration (Fig.D, n=6). Finally, we confirmed that small molecule inhibitor of the NLRP3-NEK7 complex itself decreased IL-1β secretion in an MSU-elicited peritonitis mouse model (C57BL/6J, n= 8, Control: PBS, p<0.05).
Conclusions: NEK7 itself is sufficient as a therapeutic target to suppress inflammasome-mediated macrophage activation; providing molecular bases for the development of new therapies for CVD.
More abstracts on this topic:
Age Associated T cells (TAA cells) expressing Granzyme k are novel cell types in Atherosclerotic plaques.
Patil Mallikarjun, Tyrrell Daniel, Ali Md Akkas, Siam Md Hasanul Banna, Brazell James
A major uremic toxin indoxyl sulfate impairs macrophage efferocytosis and accelerates atherogenesis: a potential mechanism for cardiovascular risk in chronic kidney diseaseJha Prabhash, Kasai Taku, Vromman Amelie, Holden Rachel, Libby Peter, Tabas Ira, Singh Sasha, Aikawa Elena, Aikawa Masanori, Lupieri Adrien, Sonawane Abhijeet, Le Thanh-dat, Becker-greene Dakota, Chelvanambi Sarvesh, Turner Mandy, Nakamura Yuto, Passos Livia