Final ID: Tu0046a
Red Blood Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Type 2 Diabetes Induce Endothelial Dysfunction Through Transfer of Arginase-1 to the Endothelium
Abstract Body: Background: Recently, we have demonstrated that red blood cells (RBCs) from individuals with type 2 diabetes (T2D-RBCs) induce endothelial dysfunction via upregulation of arginase-1 in RBCs. However, the mechanism by which RBCs communicate with the vessel is unknown. Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are actively secreted by practically all cell types, including RBCs, and represent a novel mechanism of intercellular communication. However, the involvement of EVs from RBCs in the development of endothelial dysfunction remains to be elucidated.
Purpose: This study was designed to test the hypothesis that EVs transfer arginase-1 protein to the vascular endothelium to induce endothelial dysfunction in T2D.
Methods: RBCs from T2D patients and age-matched healthy controls (H-RBCs) were incubated for 18h for EV release. The content of arginase-1 in RBC-derived EVs was determined. The EVs were co-incubated with mouse aortas from endothelial cell arginase-1 KO mice (Arg-1fl/fl/Tie2Cretg/–) and their littermates (Arg-1fl/fl/Tie2Cre–/–) to evaluate endothelium-dependent relaxation (EDR) and arginase-1 expression by immunohistochemistry. The functional involvement of arginase was investigated using pharmacological interventions and expression analyses.
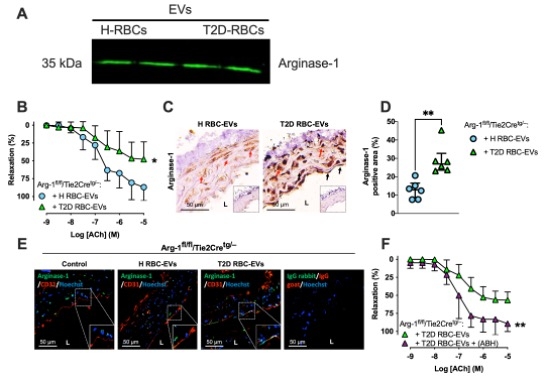
Results: Arginase-1 was detected in RBC-derived EVs (Fig. 1A). T2D RBC-EVs impaired EDR in vessels isolated from endothelial cell arginase-1 KO mice compared to those incubated with H RBC-EVs (Fig. 1B). Interestingly, incubation of aortas from endothelial cell arginase-1 KO mice with T2D RBC-EVs led to increased expression of arginase-1 in the vessel wall (Fig. 1C-D). Arginase-1 was co-expressed with CD31 in the aortas of Arg-1fl/fl/Tie2Cretg/– mice following incubation with T2D RBC-EVs (Fig. 1E), suggesting co-localization in the endothelium. Moreover, the impaired EDR induced by T2D RBC-EVs in aortas from endothelial cell arginase-1 KO mice was attenuated by the arginase inhibitor ABH in the vessel (Fig. 1F).
Conclusion: EVs derived from RBCs of individuals with T2D carry arginase-1 protein to induce endothelial dysfunctionthrough the delivery of arginase-1. EVs derived from T2D-RBCs transfer arginase-1 protein to endothelial cells, leading to endothelial dysfunction. Potential therapeutic strategies that interfere with the uptake of the cargo of the EVs, or the transfer of signaling molecules by RBC-derived EVs have the potential to prevent vascular injury in T2D.
Purpose: This study was designed to test the hypothesis that EVs transfer arginase-1 protein to the vascular endothelium to induce endothelial dysfunction in T2D.
Methods: RBCs from T2D patients and age-matched healthy controls (H-RBCs) were incubated for 18h for EV release. The content of arginase-1 in RBC-derived EVs was determined. The EVs were co-incubated with mouse aortas from endothelial cell arginase-1 KO mice (Arg-1fl/fl/Tie2Cretg/–) and their littermates (Arg-1fl/fl/Tie2Cre–/–) to evaluate endothelium-dependent relaxation (EDR) and arginase-1 expression by immunohistochemistry. The functional involvement of arginase was investigated using pharmacological interventions and expression analyses.
Results: Arginase-1 was detected in RBC-derived EVs (Fig. 1A). T2D RBC-EVs impaired EDR in vessels isolated from endothelial cell arginase-1 KO mice compared to those incubated with H RBC-EVs (Fig. 1B). Interestingly, incubation of aortas from endothelial cell arginase-1 KO mice with T2D RBC-EVs led to increased expression of arginase-1 in the vessel wall (Fig. 1C-D). Arginase-1 was co-expressed with CD31 in the aortas of Arg-1fl/fl/Tie2Cretg/– mice following incubation with T2D RBC-EVs (Fig. 1E), suggesting co-localization in the endothelium. Moreover, the impaired EDR induced by T2D RBC-EVs in aortas from endothelial cell arginase-1 KO mice was attenuated by the arginase inhibitor ABH in the vessel (Fig. 1F).
Conclusion: EVs derived from RBCs of individuals with T2D carry arginase-1 protein to induce endothelial dysfunctionthrough the delivery of arginase-1. EVs derived from T2D-RBCs transfer arginase-1 protein to endothelial cells, leading to endothelial dysfunction. Potential therapeutic strategies that interfere with the uptake of the cargo of the EVs, or the transfer of signaling molecules by RBC-derived EVs have the potential to prevent vascular injury in T2D.
More abstracts on this topic:
37,500 man-years of clinical expertise validate the cardio-metabolic benefits of empagliflozin-linagliptin in type 2 diabetes: findings from the amplified consensus
Nair Tiny, Jabbar P, Ray Saumitra, Hazra Prakash, Gupta Sushil, Joshi Ameya, Shaikh Shehla, B Jayagopal, Pandit Kaushik, Sharma D, Seshadri Krishna, S Sridhar
A Multimodal Artificial Intelligence Signature of Advanced Cardiac and Vascular Aging Defines Elevated Risk of Cardiovascular DiseasePerera Sudheesha, Biswas Dhruva, Dhingra Lovedeep, Aminorroaya Arya, Coppi Andreas, Khera Rohan