Final ID: Sa308
Augmentation of Intraventricular Stroke Volume during Head Up Position CPR: Implications for Clinical Outcomes
Abstract Body: Background: Active compression-decompression (ACD) cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR), an impedance threshold device (ITD) and controlled, gradual, automated head and thorax elevation, collectively termed automated Head Up Position (AHUP) CPR, increases cerebral perfusion pressure (CerPP), brain blood flow, coronary perfusion pressure (CorPP), end tidal CO2 (ETCO2) and cerebral oximetry (rSO2) in animal models when compared with conventional (C) CPR. AHUP-CPR in patients is associated with increased neurologically favorable survival versus C-CPR. This study tested the hypothesis that AHUP CPR will increase cardiac stroke volume (SV) and other hemodynamics compared with C-CPR in a porcine model of cardiac arrest.
Methods: Farm pigs (n=15) were sedated, anesthetized, and ventilated. Hemodynamics, including intracardiac conductance catheter based biventricular (BiV) pressure-volume (PV) loops, were continuously measured and recorded. After 10 minutes of untreated ventricular fibrillation, C-CPR was performed for 2 minutes in the supine position using an automated CPR device designed for pigs at a rate of 100 compressions/minute, depth of 21% of the chest antero-postero diameter, a 50% duty cycle, and no active decompression. ACD+ITD was then performed with 3 cm of active decompression for 2 minutes, followed by AHUP-CPR, where the head and thorax were initially raised to 10 cm and 8 cm for a 2-minute priming phase, followed by elevation over the next 2 minutes to 24 cm and 9 cm. A linear mixed-effects model with a random intercept for individual pigs was used for statistical analysis.
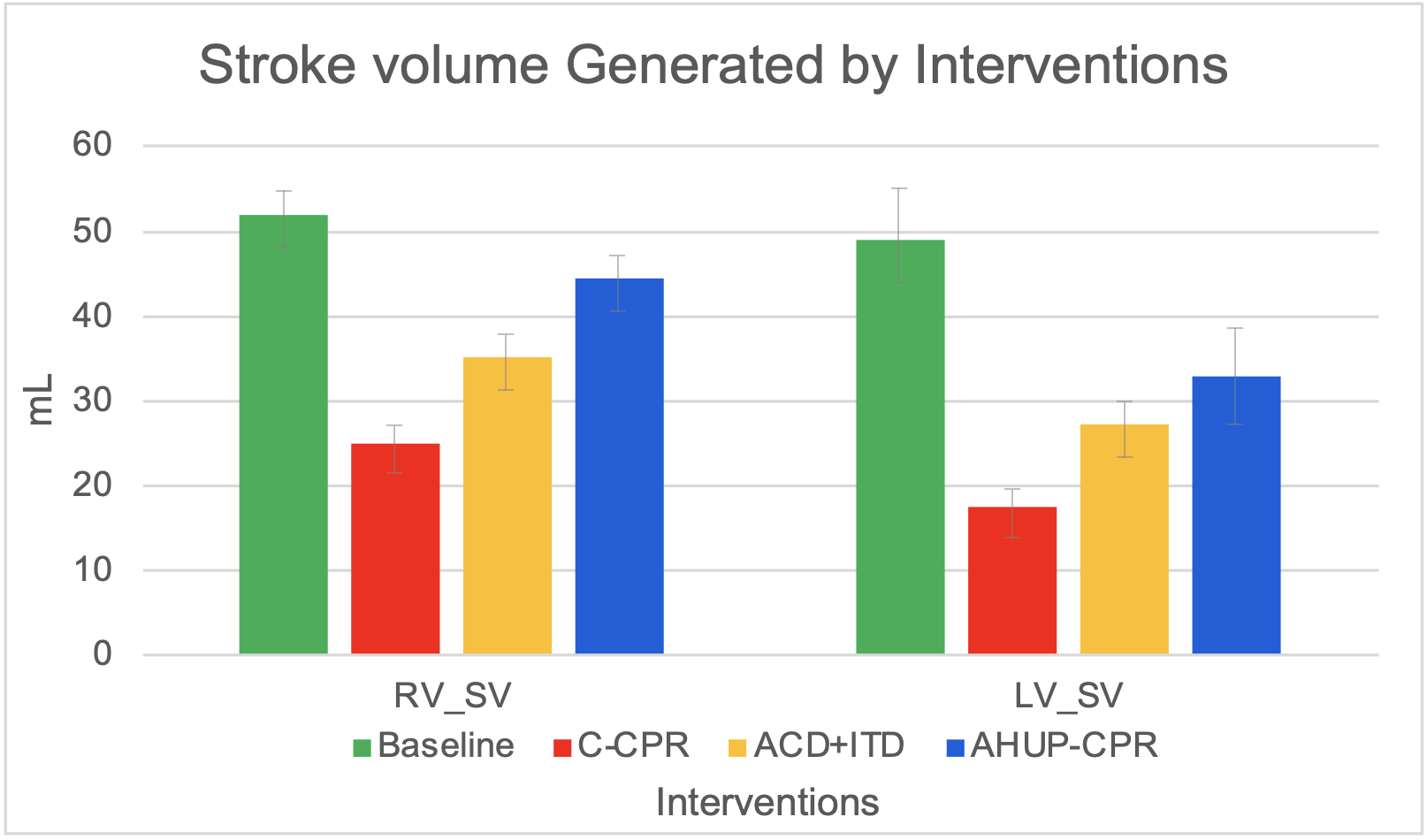
Results: CerPP, CorPP, ETCO2, and rSO2, as well as BiV SV and cardiac output, increased progressively and significantly with implementation of AHUP-CPR (p<0.05). C-CPR generated a right ventricular (RV) SV of 25.0 mL (48% of baseline pre-VF) and left ventricular (LV) SV of 17.5 mL (39% of baseline). ACD+ITD significantly increased RV and LV SV by an average of ~ 48% versus C-CPR; AHUP-CPR further increased BiV SV by an average of ~ 83%, reaching 85% and 75% of RV and LV pre-VF values, respectively. (Figure 1)
Conclusion: This study demonstrated biventricular stroke volume is significantly augmented with AHUP-CPR versus C-CPR or ACD+ITD in the flat position. These findings, together with AHUP-enhanced higher ETCO2, rSO2, and CerPP values versus C-CPR or ACD-CPR in the flat position, help explain the improved clinical outcomes associated with early use of AHUP-CPR.
Methods: Farm pigs (n=15) were sedated, anesthetized, and ventilated. Hemodynamics, including intracardiac conductance catheter based biventricular (BiV) pressure-volume (PV) loops, were continuously measured and recorded. After 10 minutes of untreated ventricular fibrillation, C-CPR was performed for 2 minutes in the supine position using an automated CPR device designed for pigs at a rate of 100 compressions/minute, depth of 21% of the chest antero-postero diameter, a 50% duty cycle, and no active decompression. ACD+ITD was then performed with 3 cm of active decompression for 2 minutes, followed by AHUP-CPR, where the head and thorax were initially raised to 10 cm and 8 cm for a 2-minute priming phase, followed by elevation over the next 2 minutes to 24 cm and 9 cm. A linear mixed-effects model with a random intercept for individual pigs was used for statistical analysis.
Results: CerPP, CorPP, ETCO2, and rSO2, as well as BiV SV and cardiac output, increased progressively and significantly with implementation of AHUP-CPR (p<0.05). C-CPR generated a right ventricular (RV) SV of 25.0 mL (48% of baseline pre-VF) and left ventricular (LV) SV of 17.5 mL (39% of baseline). ACD+ITD significantly increased RV and LV SV by an average of ~ 48% versus C-CPR; AHUP-CPR further increased BiV SV by an average of ~ 83%, reaching 85% and 75% of RV and LV pre-VF values, respectively. (Figure 1)
Conclusion: This study demonstrated biventricular stroke volume is significantly augmented with AHUP-CPR versus C-CPR or ACD+ITD in the flat position. These findings, together with AHUP-enhanced higher ETCO2, rSO2, and CerPP values versus C-CPR or ACD-CPR in the flat position, help explain the improved clinical outcomes associated with early use of AHUP-CPR.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Synthetic Small Molecule Efficiently Sequesters Carbon Monoxide from Hemoglobin and Red Blood Cells In Vitro
Correnti Jacob, Ai Yong, Gladwin Mark, Xue Fengtian, Rose Jason, Demartino Anthony
A novel approach for LV delay evaluation: non-invasive QLV measurement using UHF ECGPoviser Lukas, Stros Petr, Vesela Jana, Curila Karol