Final ID: Sa2016
Development and Validation of a Pediatric Cardiology-Specific Large Language Model Chat Interface using Retrieval Augmented Generation
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction:Generative Pretrained Transformers (GPTs) utilize extensively pre-trained large language models (LLMs) to generate text that resembles human language. Commercially available GPTs are not optimized for medical use and are prone to generating hallucinatory information. Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) is a novel technology that allows embedding of customized knowledge bases for more enhanced performance of GPTs in specific domains. We aimed to validate the performance of a novel RAG empowered specialized GPT in Pediatric Cardiology.
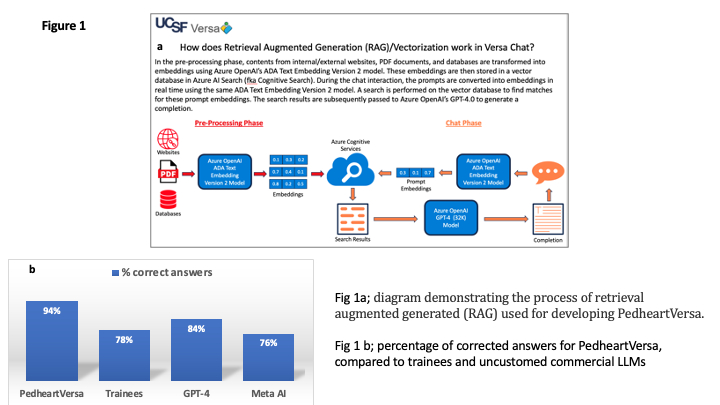
Methods:We developed "PedheartVersa," a pediatric cardiac disease-specific GPT, by using our institution's HIPAA-compliant text embedding and LLM platform, "Versa Chat". We conducted RAG on a custom knowledge base which we generated from 6 recent pediatric and fetal cardiology textbooks and 30 AHA/ACC guideline statements (Fig1). We applied prompt engineering through zero shot, few shot and chain of thought learning. We evaluated the performance of PedsheartVersa by comparing its outputs for 75 deidentified real-life fetal, pediatric and ACHD cases to those of trainees, OpenAI's ChatGPT 4, and Meta AI 2. Outputs were rated by expert pediatric Cardiologists on a detailed rubric (scientific consensus, reading comprehension, knowledge depth, reasoning, citation, hallucination, bias, and likelihood of harm).
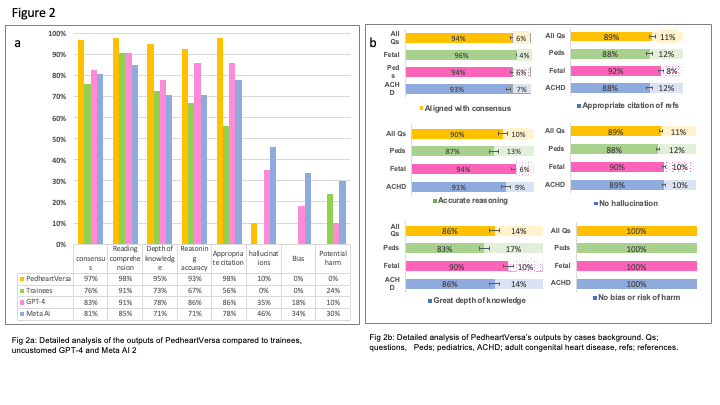
Results: 94% of the tested cases were correctly answered by PedsheartVersa vs 78% by trainees, 84% by ChatGPT 4 and 76% by Meta AI, P= 0.027(Fig 2). PedsheartVersa had significantly less demographic bias and likelihood of harm, and higher reading comprehension, reasoning, and depth of knowledge scores than trainees and rest of commercial unspecialized GPTs (Fig 2).
Conclusion: Our novel customized GPT demonstrated high performance on a wide range of pediatric cardiology-based problems. This lays a groundwork for future applications of customized models in pediatric cardiology education, training and overall decision making.
Methods:We developed "PedheartVersa," a pediatric cardiac disease-specific GPT, by using our institution's HIPAA-compliant text embedding and LLM platform, "Versa Chat". We conducted RAG on a custom knowledge base which we generated from 6 recent pediatric and fetal cardiology textbooks and 30 AHA/ACC guideline statements (Fig1). We applied prompt engineering through zero shot, few shot and chain of thought learning. We evaluated the performance of PedsheartVersa by comparing its outputs for 75 deidentified real-life fetal, pediatric and ACHD cases to those of trainees, OpenAI's ChatGPT 4, and Meta AI 2. Outputs were rated by expert pediatric Cardiologists on a detailed rubric (scientific consensus, reading comprehension, knowledge depth, reasoning, citation, hallucination, bias, and likelihood of harm).
Results: 94% of the tested cases were correctly answered by PedsheartVersa vs 78% by trainees, 84% by ChatGPT 4 and 76% by Meta AI, P= 0.027(Fig 2). PedsheartVersa had significantly less demographic bias and likelihood of harm, and higher reading comprehension, reasoning, and depth of knowledge scores than trainees and rest of commercial unspecialized GPTs (Fig 2).
Conclusion: Our novel customized GPT demonstrated high performance on a wide range of pediatric cardiology-based problems. This lays a groundwork for future applications of customized models in pediatric cardiology education, training and overall decision making.
More abstracts on this topic:
A ChatGLM-based stroke diagnosis and prediction tool
Song Xiaowei, Wang Jiayi, Ma Weizhi, Wu Jian, Wang Yueming, Gao Ceshu, Wei Chenming, Pi Jingtao
β1 integrins regulate cellular behavior and cardiomyocyte organization during ventricular wall formationMiao Lianjie, Schwartz Robert, R Burns Alan, Kumar Ashok, Dipersio C. Michael, Wu Mingfu, Lu Yangyang, Nusrat Anika, Zhao Luqi, Castillo Micah, Xiao Yongqi, Guo Hongyan, Liu Yu, Gunaratne Preethi