Final ID: Su1305
Survival and Neurological Function with a Novel Trapezoidal Compression-Decompression CPR Waveform during Automated Head-Up CPR in a Porcine Model of Cardiac Arrest
Abstract Body: Background: Automated head-up cardiopulmonary resuscitation (AHUP-CPR), a combination of automated head/thorax elevation, active compression-decompression (ACD) CPR, and an impedance threshold device, improves neurological survival in pre-clinical studies and is associated with improved clinical outcomes compared to conventional (C) CPR in the flat position. An optimal ACD waveform during AHUP-CPR is unknown.
Aim: This AHUP-CPR study compared hemodynamics, survival rates, and neurological function with a rectilinear ACD waveform with 1 cm of active lift above the neutral chest position (RWF-1cm) versus a novel trapezoidal ACD waveform with 3 cm of active lift (TWF-3cm).
Methods: Male and female ~40 kg farm pigs (n=19) were anesthetized, ventilated, and hemodynamics were continuously measured. After ventricular fibrillation (VF), pigs were randomized to either RWF-1cm or TWF-3cm. After 10 min of untreated VF, automated CPR was initiated in both groups with sinusoidal waveform mimicking C-CPR: the device compressed to 22% of the antero-postero diameter, at 100 beats/min, with a cloth under the suction cup on the piston to prevent active lift. After 2 min of C-CPR, AHUP-CPR was performed for 18 minutes with either RWF-1cm or TWF-3cm. Ventilations (10ml/kg) with O2 supplementation were delivered 10 times/min. Pigs received intravenous epinephrine (0.5mg) and amiodarone (50mg) after 19 minutes of CPR, and were defibrillated 60 sec later. Outcomes included coronary perfusion pressure (CorPP), sustained return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC), 24-hour survival rates and neurological function. A Neurological Deficit Score (NDS; 0= no deficits and 260 = dead) was used. Data were expressed as mean ± SD. Statistical significance was determined by student’s T test, Fisher’s exact, log-rank, and Mann-Whitney U test.
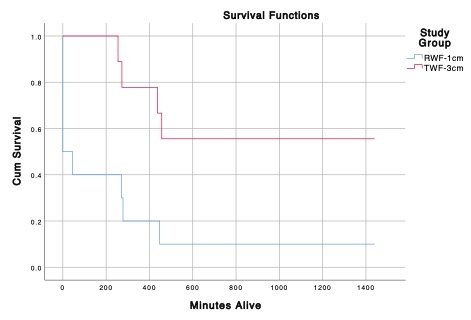
Results: The RWF-1cm CorPP after 19 minutes of CPR was 31.9 ± 26.0 vs 54.8 ± 14.6 in the TWF-3cm group (p=0.037). With RWF-1cm 5/10 pigs had ROSC vs 9/9 with TWF-3cm (p=0.03), and 24-hour survival rates were 10% vs 56%, respectively (p=0.008)(see Figure). The NDS was 241 ± 19 with RWF-1cm vs 152 ± 36 with TWF-3cm (p=0.04).
Conclusion: AHUP-CPR with a novel trapezoidal ACD-CPR waveform with 3 cm of active lift resulted in significantly higher CorPP and 24-hr neurologically favorable survival rates versus a rectilinear ACD-CPR waveform with 1 cm of active lift. These findings emphasize the need for, and importance of, an optimal automated AHUP-CPR waveform.
Aim: This AHUP-CPR study compared hemodynamics, survival rates, and neurological function with a rectilinear ACD waveform with 1 cm of active lift above the neutral chest position (RWF-1cm) versus a novel trapezoidal ACD waveform with 3 cm of active lift (TWF-3cm).
Methods: Male and female ~40 kg farm pigs (n=19) were anesthetized, ventilated, and hemodynamics were continuously measured. After ventricular fibrillation (VF), pigs were randomized to either RWF-1cm or TWF-3cm. After 10 min of untreated VF, automated CPR was initiated in both groups with sinusoidal waveform mimicking C-CPR: the device compressed to 22% of the antero-postero diameter, at 100 beats/min, with a cloth under the suction cup on the piston to prevent active lift. After 2 min of C-CPR, AHUP-CPR was performed for 18 minutes with either RWF-1cm or TWF-3cm. Ventilations (10ml/kg) with O2 supplementation were delivered 10 times/min. Pigs received intravenous epinephrine (0.5mg) and amiodarone (50mg) after 19 minutes of CPR, and were defibrillated 60 sec later. Outcomes included coronary perfusion pressure (CorPP), sustained return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC), 24-hour survival rates and neurological function. A Neurological Deficit Score (NDS; 0= no deficits and 260 = dead) was used. Data were expressed as mean ± SD. Statistical significance was determined by student’s T test, Fisher’s exact, log-rank, and Mann-Whitney U test.
Results: The RWF-1cm CorPP after 19 minutes of CPR was 31.9 ± 26.0 vs 54.8 ± 14.6 in the TWF-3cm group (p=0.037). With RWF-1cm 5/10 pigs had ROSC vs 9/9 with TWF-3cm (p=0.03), and 24-hour survival rates were 10% vs 56%, respectively (p=0.008)(see Figure). The NDS was 241 ± 19 with RWF-1cm vs 152 ± 36 with TWF-3cm (p=0.04).
Conclusion: AHUP-CPR with a novel trapezoidal ACD-CPR waveform with 3 cm of active lift resulted in significantly higher CorPP and 24-hr neurologically favorable survival rates versus a rectilinear ACD-CPR waveform with 1 cm of active lift. These findings emphasize the need for, and importance of, an optimal automated AHUP-CPR waveform.
More abstracts on this topic:
Improving Bystander CPR Knowledge and Preparedness Among Secondary School Students and Healthcare Workers in Ikare-Akoko, Nigeria.
Oturoko Mayowa, Chang Mary
A Hospital-Wide Multidimensional Approach to Pediatric In-Hospital Cardiac Arrest Review: Early Identification and PreventionLoeb Daniel, Collins Kelly, Ortega Karina, Dewan Maya