Final ID: Su203
Development of Bioimpedance for the Measurement of Ventilation During Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation
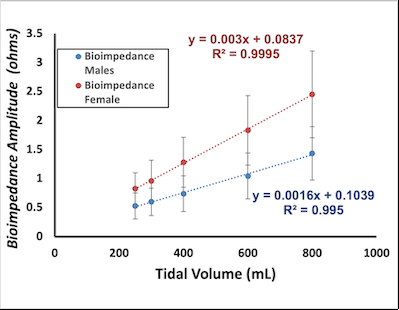
Abstract Body: Introduction: Previous studies have shown that ventilation during cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) produces better patient outcomes. However, research regarding ventilation during the early stages of basic life support CPR is limited. Prior studies showed that thoracic bioimpedance, recorded by the LifePak 12 defibrillator device, can be used to count ventilations with a tidal volume at least 250 mL during CPR. However, the relationship between thoracic bioimpedance and tidal volume has yet to be studied for the Phillips MRx device, excluding a large data set from ventilation studies. Hypothesis: Bioimpedance, measured by the Phillips MRx device has a linear relationship with tidal volume. Aims: To determine the relationship between bioimpedance measured by the Phillips MRx device and tidal volume in males and females. Methods: We conducted the study in a respiratory laboratory at a University Hospital. We asked 27 volunteers to breathe fixed volumes (250 mL, 300 mL, 400 mL, 600 mL, and 800 mL) delivered by a mechanical ventilator while recording bioimpedance simultaneously with the Philips MRx monitor-defibrillator through electrode pads placed on the chest. Six measurements of bioimpedance waveform amplitudes (Ohms) were taken at each tidal volume. Results: Of 27 volunteers, 11 were female and 16 were male. In the female sample set, a linear equation of y=0.003x + 0.837 with an R^2 value of 0.9995 was calculated. In the male sample set, a linear equation of Y=0.0016x +0.1039 with a R^2 value of 0.995 was calculated. Females had a higher median bioimpedance amplitude than men at each tidal volume, and a steeper linear regression slope. At the minimum threshold tidal volume used for counting ventilations (250 mL), the median bioimpedance amplitude was 0.5 (0.4, 0.6) ohm for males and the median bioimpedance amplitude was 0.8 (0.6, 1) ohm for females. Conclusion: As measured and recorded with the Philips MRx monitor-defibrillator, there is a linear relationship between tidal volume and thoracic bioimpedance. The linear models created in this study can be used in future studies to count ventilations during CPR using the Philips MRx device.
More abstracts on this topic:
Capnoraphy and Thoracic Impedance Ventilation Quality During Cardiac Resuscitation
Nassal Michelle, Idris Ahamed, Wang Henry, Jaureguibeitia Xabier, Aramendi Elisabete, Ania Imanol, Elola Andoni, Moeller Kim, Murphy Andrew, Lowe Robert, Panchal Ashish
Association of Emergency Medical Services Utility and Outcomes of Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest in Young Adults and PediatricChen Szu Han, Chiang Wen-chu, Tseng Wei-chieh, Lee Meng-chang, Wang Po-yuan, Chu Yen-ju, Liu Hsin-ming, Wu Jhong-lin, Lin Haoyang, Hsieh Ming-ju, Ma Matthew Huei-ming