Final ID: Su507
Occurrence of Fibrillation in Out-of-hospital Cardiac Arrest Patients Presenting in a Non-shockable Rhythm when Treated with an Automated External Defibrillator
Abstract Body: Background: Most out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA) patients who are initially treated with an automated external defibrillator (AED) and present in a non-shockable rhythm never receive a shock. This analysis reports on patients who presented in a non-shockable rhythm when the AED was initially applied and later transitioned into a shockable rhythm.
Methods: Data from a convenience group of OHCA patients treated with a Philips HeartStart Home, Onsite or FRx AED were included. The AEDs were the first defibrillator on scene either in home, in public access or by a BLS team. Application of any medication during AED use was unlikely. Each patient’s heart rhythms were reviewed by an expert. All patients whose initial rhythm was non-shockable but later received at least one shock were identified and the rhythms were analyzed.
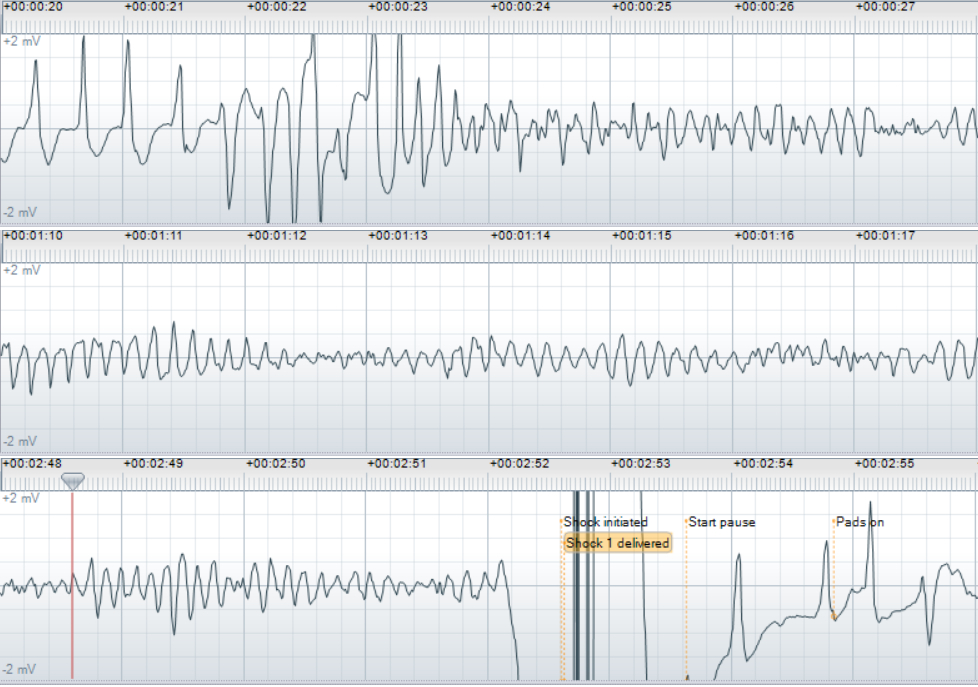
Results: Out of 876 patients, 322 (36.8%) received at least one shock, of which five patients (1.6%) presented in a non-shockable rhythm and were later shocked. Three patients presented in an organized rhythm. The first patient degraded into Torsade de Pointe as shown in Figure 1; the post-shock rhythm was organized. The second patient received no CPR and A-V pacing was observed in the ECG recording. The pacing stopped when the rhythm transitioned into VF and restarted post shock. The third patient transitioned into VF during chest compressions and the post-shock rhythm was asystole. The remaining two patients presented in asystole and the rhythm evolved to fine VF after receiving chest compressions. After defibrillation, their rhythms returned to asystole.
Conclusions: For OHCA patients treated with an AED, presenting in a non-shockable rhythm and later transitioning into a shockable rhythm is rare but possible. Lay-responder CPR may play a role in rhythm evolvement. The impact of rhythm changes on survivability of these patients is unknown.
Methods: Data from a convenience group of OHCA patients treated with a Philips HeartStart Home, Onsite or FRx AED were included. The AEDs were the first defibrillator on scene either in home, in public access or by a BLS team. Application of any medication during AED use was unlikely. Each patient’s heart rhythms were reviewed by an expert. All patients whose initial rhythm was non-shockable but later received at least one shock were identified and the rhythms were analyzed.
Results: Out of 876 patients, 322 (36.8%) received at least one shock, of which five patients (1.6%) presented in a non-shockable rhythm and were later shocked. Three patients presented in an organized rhythm. The first patient degraded into Torsade de Pointe as shown in Figure 1; the post-shock rhythm was organized. The second patient received no CPR and A-V pacing was observed in the ECG recording. The pacing stopped when the rhythm transitioned into VF and restarted post shock. The third patient transitioned into VF during chest compressions and the post-shock rhythm was asystole. The remaining two patients presented in asystole and the rhythm evolved to fine VF after receiving chest compressions. After defibrillation, their rhythms returned to asystole.
Conclusions: For OHCA patients treated with an AED, presenting in a non-shockable rhythm and later transitioning into a shockable rhythm is rare but possible. Lay-responder CPR may play a role in rhythm evolvement. The impact of rhythm changes on survivability of these patients is unknown.
More abstracts on this topic:
Clinical Characteristic-Driven Machine Learning Models for the Prediction of Stroke Subtypes and Eligibility of Endovascular Thrombectomy
Yoshie Tomohide, Minematsu Kazuo, Iihara Koji, Toyoda Kazunori, Koga Masatoshi, Yoshimura Sohei, Sakuraba Makino, Wada Shinichi, Miwa Kaori, Miyamoto Yoshihiro, Miyazaki Junji, Yazawa Yukako, Kamiyama Kenji
A Comparative Analysis of Esophageal Cooling for Preventing Esophageal Injury Post Atrial Fibrillation Catheter Ablation: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysisIbrahim Momen Mohamed, Al Hennawi Hussam, Tanas Yousef, Abourady Youmna, Sewedan Nourhan, Hashem Ahmed Magdy, Motawea Karam R.