Final ID: 150
Racial and Ethnic Disparities in Post-stroke Quality of Life: A Post-Hoc Analysis of the SHINE Trial
Abstract Body: Background and Purpose
Stroke is a leading cause of long-term disability, often resulting in functional and cognitive impairments that significantly reduce quality of life. While racial and ethnic differences in clinical outcomes after stroke are well-documented, the impact of post-stroke disability on patient-centered outcome measures, which account for physical, emotional, and sociocultural factors, remains insufficiently understood. This study aimed to investigate racial and ethnic differences in post-stroke quality of life among participants in the SHINE trial.
Methods
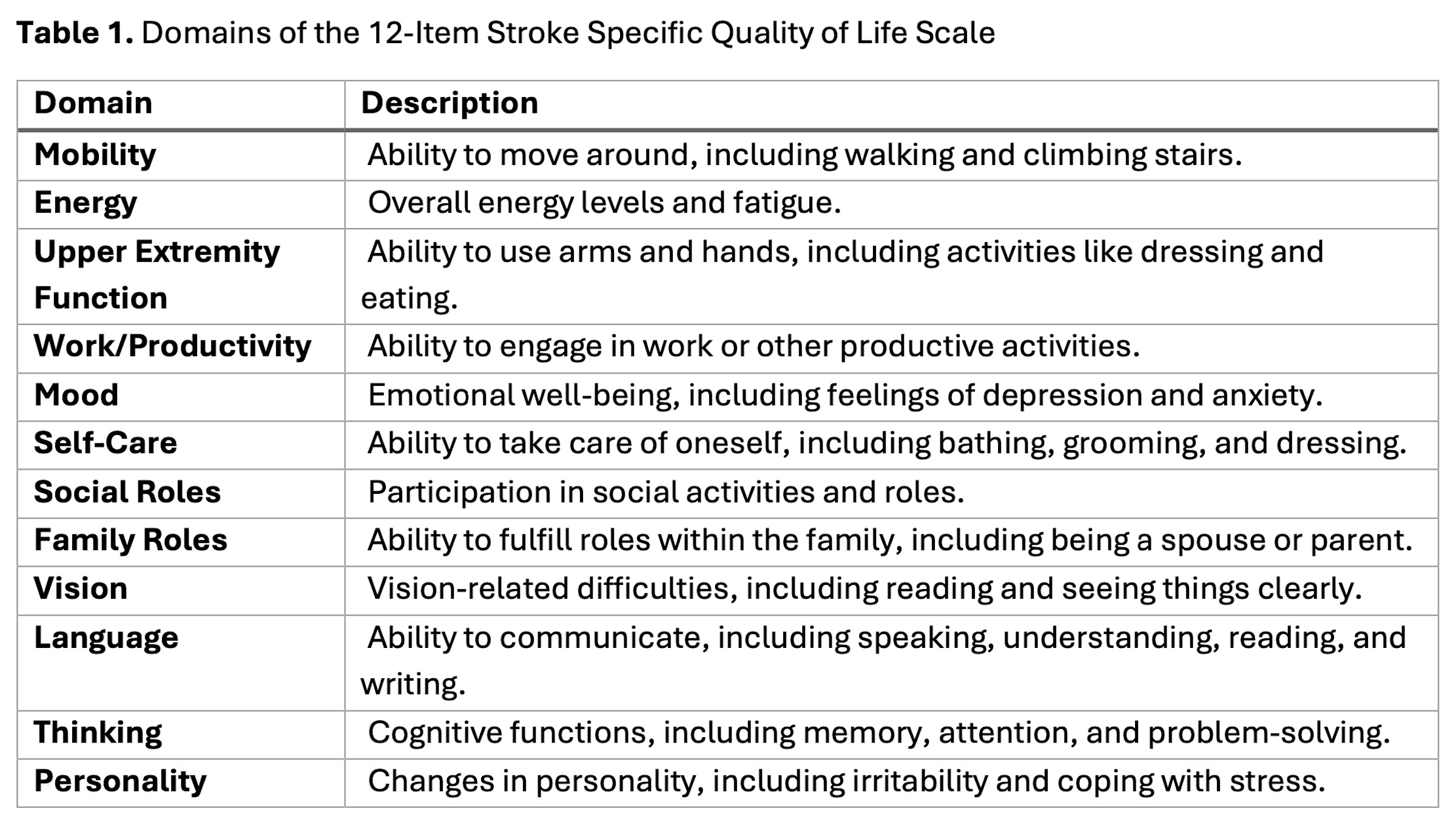
This is a post-hoc analysis of the Stroke Hyperglycemia Insulin Network Effort (SHINE) trial. Self-reported race, ethnicity, and the 12-item Stroke Specific Quality of Life (SSQOL) Scale at 90-day follow-up were used for correlation analyses, adjusted for age, sex, hypertension, diabetes, stroke size, recurrent stroke, and 90-day modified Rankin Scale. The SSQOL is a patient-centered outcome measure that assesses health-related quality of life specific to stroke survivors across 12 domains (Table 1).
Results
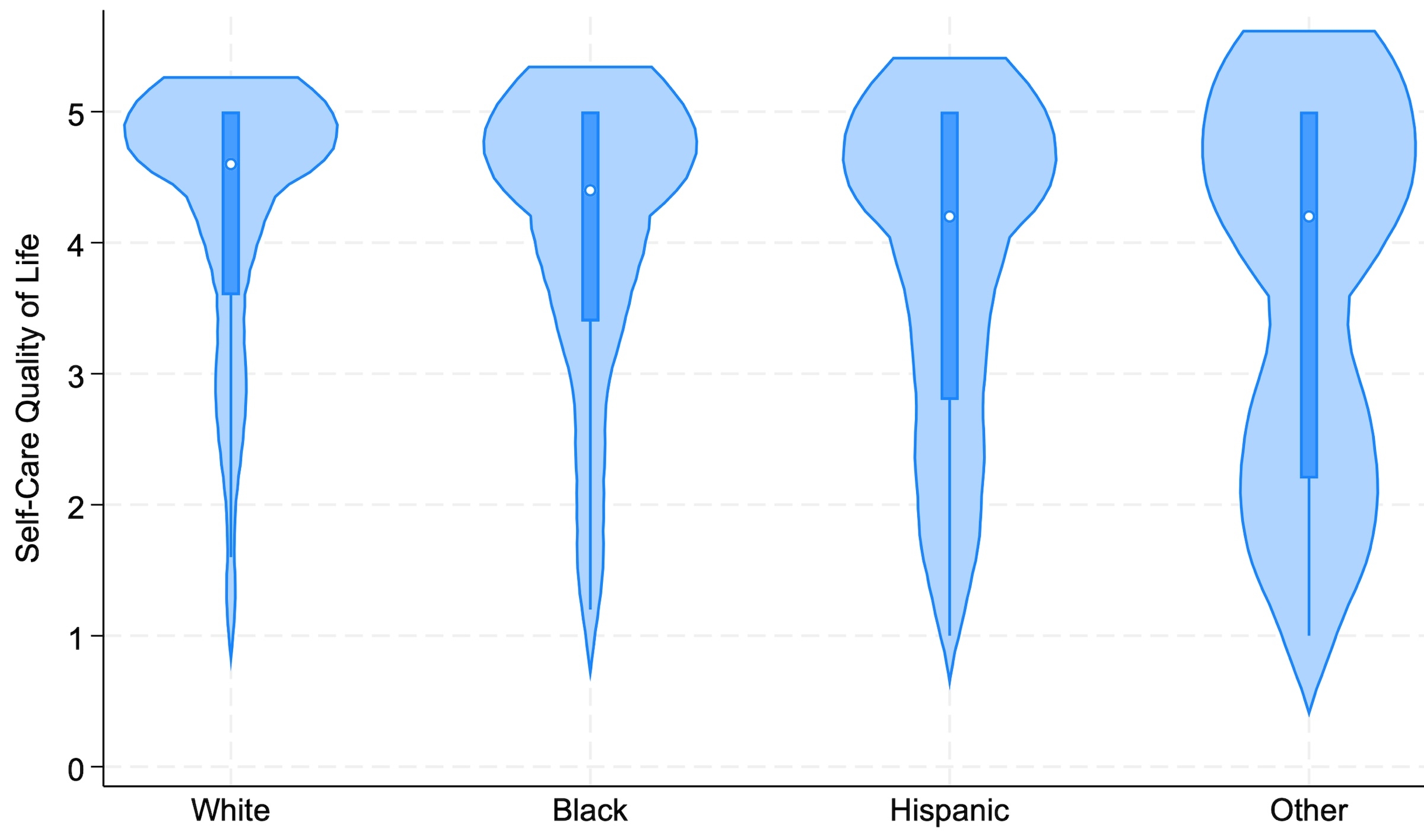
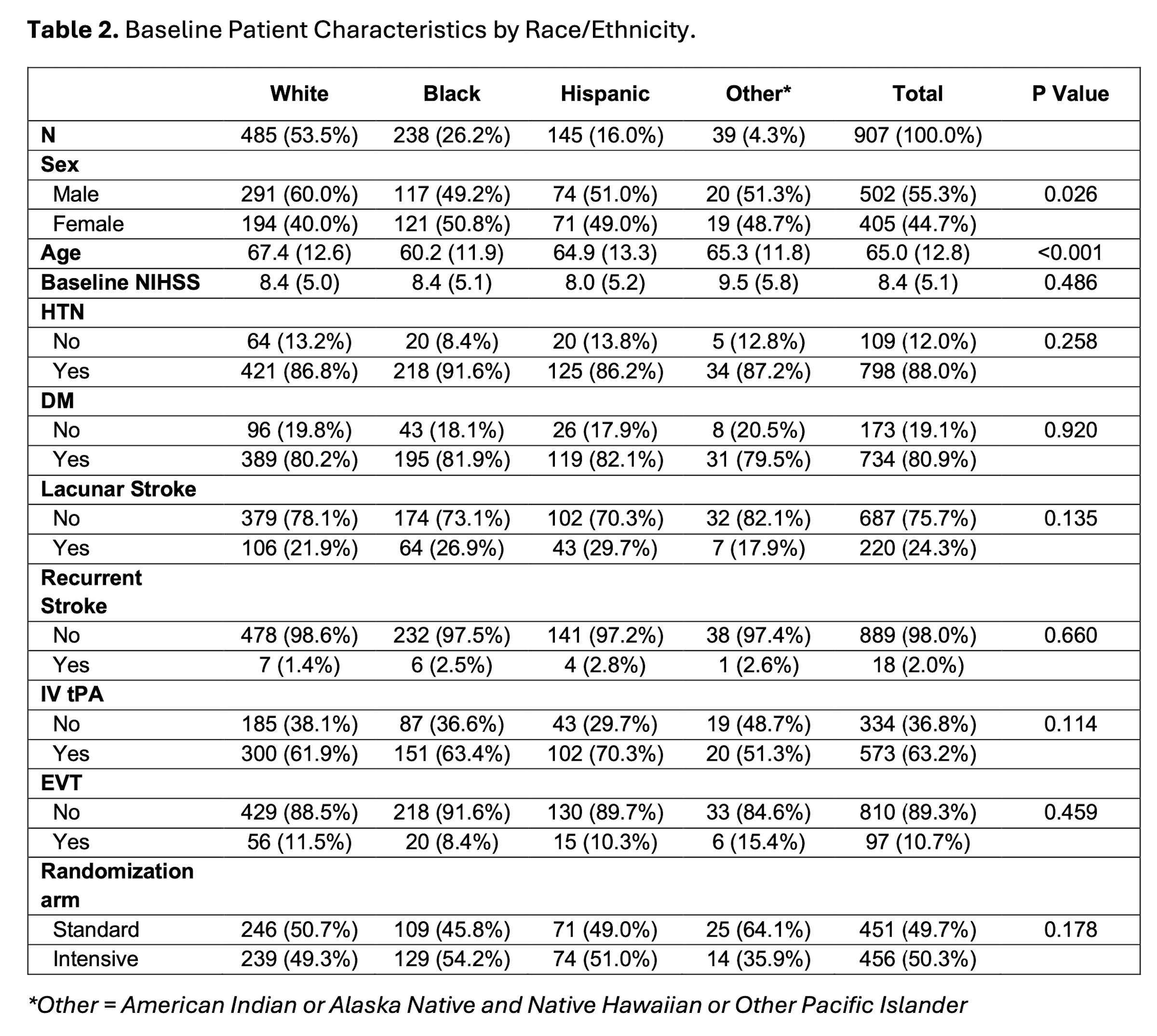
A total of 907 ischemic stroke patients with hyperglycemia (mean age 65±12.8, 44.7% female, 80.9% with diabetes) were included in this study. At 90-day follow-up, no significant differences were found in overall SSQOL summary scores by race/ethnicity. However, Hispanic patients reported significantly lower scores in self-care (p < .0001) (Figure 1), vision (p = .015), and upper extremity function (p = .007), while Black patients reported lower energy (p = 0.012).
Discussion
These findings indicate that Hispanic and Black stroke survivors experience lower quality of life in specific domains after adjusting for stroke severity and other potential confounders. In addition to clinical outcomes, it is crucial to understand stroke survivors’ perceptions of their quality of life which can inform more culturally competent care. Future research should validate these associations and examine the role of socio-economic factors in shaping post-stroke quality of life to promote effective and equitable care in line with the WHO 2030 Rehabilitation agenda.
Stroke is a leading cause of long-term disability, often resulting in functional and cognitive impairments that significantly reduce quality of life. While racial and ethnic differences in clinical outcomes after stroke are well-documented, the impact of post-stroke disability on patient-centered outcome measures, which account for physical, emotional, and sociocultural factors, remains insufficiently understood. This study aimed to investigate racial and ethnic differences in post-stroke quality of life among participants in the SHINE trial.
Methods
This is a post-hoc analysis of the Stroke Hyperglycemia Insulin Network Effort (SHINE) trial. Self-reported race, ethnicity, and the 12-item Stroke Specific Quality of Life (SSQOL) Scale at 90-day follow-up were used for correlation analyses, adjusted for age, sex, hypertension, diabetes, stroke size, recurrent stroke, and 90-day modified Rankin Scale. The SSQOL is a patient-centered outcome measure that assesses health-related quality of life specific to stroke survivors across 12 domains (Table 1).
Results
A total of 907 ischemic stroke patients with hyperglycemia (mean age 65±12.8, 44.7% female, 80.9% with diabetes) were included in this study. At 90-day follow-up, no significant differences were found in overall SSQOL summary scores by race/ethnicity. However, Hispanic patients reported significantly lower scores in self-care (p < .0001) (Figure 1), vision (p = .015), and upper extremity function (p = .007), while Black patients reported lower energy (p = 0.012).
Discussion
These findings indicate that Hispanic and Black stroke survivors experience lower quality of life in specific domains after adjusting for stroke severity and other potential confounders. In addition to clinical outcomes, it is crucial to understand stroke survivors’ perceptions of their quality of life which can inform more culturally competent care. Future research should validate these associations and examine the role of socio-economic factors in shaping post-stroke quality of life to promote effective and equitable care in line with the WHO 2030 Rehabilitation agenda.
More abstracts on this topic:
Aerobic Physical Activity, Resistance Exercise, and Sedentary Times of Stroke Survivors
Lee Eung-joon, Kim Seung Jae, Bae Jeonghoon, Jeong Haebong
APOL1 Risk Variants and Risk of Incident Atrial Fibrillation in Systolic Blood Pressure Intervention Trial (SPRINT)Ahmad Muhammad, Kazibwe Richard, Mostafa Mohamed, Naeem Rimsha, Singh Sanjay, Bansal Nisha, Soliman Elsayed
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.
Rate this abstract
(Maximum characters: 500)