Final ID: TP314
Health and Coverage: How Co-Morbidities and Insurance Status Affect Post-Stroke Blood Pressure Control
Objective: To analyze the relationship between insurance type, comorbidities and post-stroke BP control among patients within a regional health system.
Methods: This report is an observational cohort study. Patients were admitted between 2013-2021 for ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke and had seen a PCP/PCAPP (primary care physician/primary care advance practice provider) in a regional health system or affiliated outpatient clinics using the EPIC electronic health record. We excluded patients who died during hospitalization, were lost to follow-up, or were on dialysis.
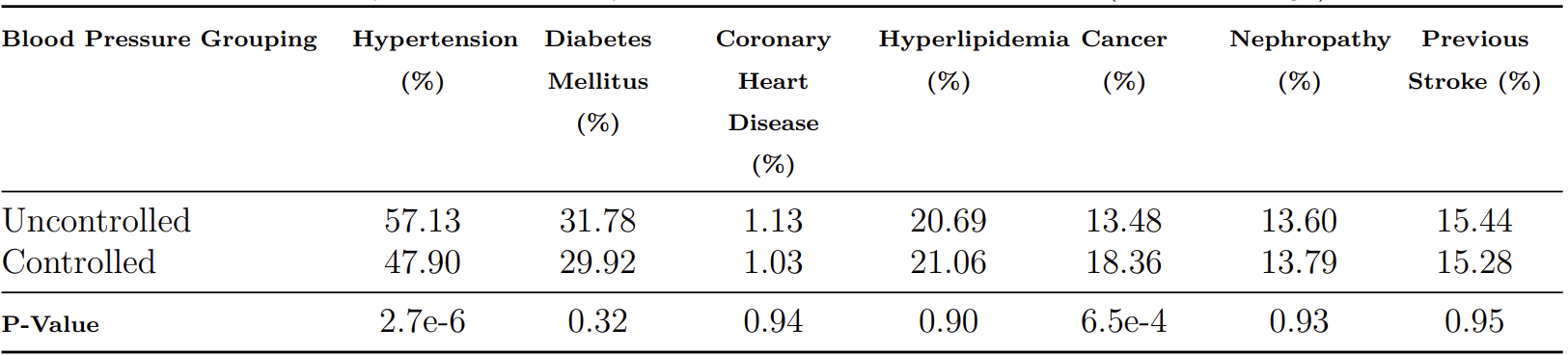
Results: The analysis included 2,750 patients. Six months after hospital discharge, the insurance coverage among stroke survivors with uncontrolled BP (>130/80 mm Hg) was 61.1% for public, 35.8% for private, 1.9% for other/unknown, and 1.3% for self-pay. In comparison, among those with controlled BP (<130/80 mm Hg), the coverage was 63.0% for public, 33.6% for private, 1.9% for other/unknown, and 1.6% for self-pay; a chi-square test showed a non-statistically significant difference (p=0.6026). The comorbidities with a statistically significant difference for BP control were hypertension for the uncontrolled BP group (p=0.0000027) and cancer for the controlled BP group (p=0.00065).
Conclusions: We found that type of insurance is not associated with post-stroke BP control as we did not find a statistically significant difference in the proportion of stroke survivors with uncontrolled versus controlled BP for insurance types. There is a strong association between hypertension and uncontrolled BP suggesting that patients with hypertension are significantly more likely to have uncontrolled BP. Additionally, there is a significant association between cancer and BP control indicating that patients with cancer are more likely to have controlled BP. To the best of our knowledge, this study is the first to analyze insurance type and co-morbidities affecting post-stroke BP control from a regional health system that is not solely self-insured or operating under a global budget.
More abstracts on this topic:
Wu Hongguang, Hu Juda, Li Peiyao, Li Xiaoyan, Chen Jing, Yanqiu Ou
A First-In-Human Phase 1 Study of the Safety, Tolerability, and Pharmacodynamics of REGN7544, a Novel Natriuretic Peptide Receptor 1–Blocking Monoclonal AntibodyAhmed Mohsin, Morton Lori, Olenchock Benjamin, Herman Gary, Wynne Chris, Marin Ethan, Tuckwell Katie, Xu Meng, Cheng Xiping, Redington Emily, Koyani Bharatkumar, Mateo Katrina, Thakur Mazhar, Devalaraja-narashimha Kishor
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.