Final ID: TP371
Effects of Empagliflozin on Ischemic Stroke in a Rat Model: Time-Frequency Electroencephalogram Features and Cerebral Infarction Size
Abstract Body: Background: Emerging evidence suggests that empagliflozin (EMPA) may offer additional benefits beyond its primary use in diabetes. Ischemic stroke is known to cause distinctive alterations in EEG signals. However, the influences of EMPA on the stroke-induced EEG changes has not been investigated. Here, we study such influences via EEG time-frequency features using the Hilbert-Huang Transform (HHT) and examine how these features correlate with the cerebral infarction.
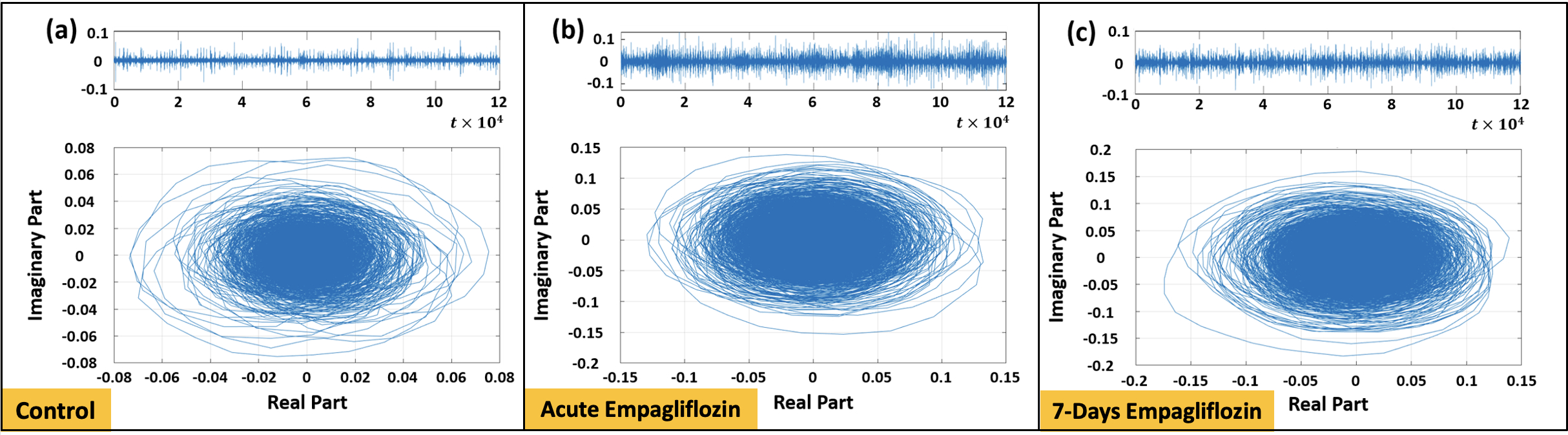
Methods: n= 47 male SD rats were randomized into 3 groups: 1] Control (n = 16, regular diet); 2] Acute EMPA treatment (n = 16, EMPA 10 mg/kg, IV given at 10 mins prior to middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) and 1 min prior to reperfusion); 3] Chronic EMPA treatment (n = 15, EMPA by food, 20 mg/kg for 7 days before MCAO). To induce ischemic stroke, standard MCAO was performed for 1 hour followed by 3 hours of reperfusion. Post-surgery, triphenyltetrazolium chloride (TTC) staining was used to measure volume of cerebral infarction. EEG signals were continuously recorded throughout the procedure. We applied the Hilbert-Huang Transform (HHT) to analyze the EEG signals. HHT includes 2 steps: 1] empirical mode decomposition (EMD) to decompose the EEG signal into a set of intrinsic mode functions (IMFs); 2] the Hilbert Transform is applied to each IMF to compute analytic signals. Such analytic signals are represented in the complex plane, where they often form circular or elliptical contours (Fig. 1). The area of these contours in the complex plane contains unique information about variations in the signal properties. We computed the HHT area metric for the first four IMFs by using EEG recordings at 3 hours post-reperfusion (duration: 2 minute).
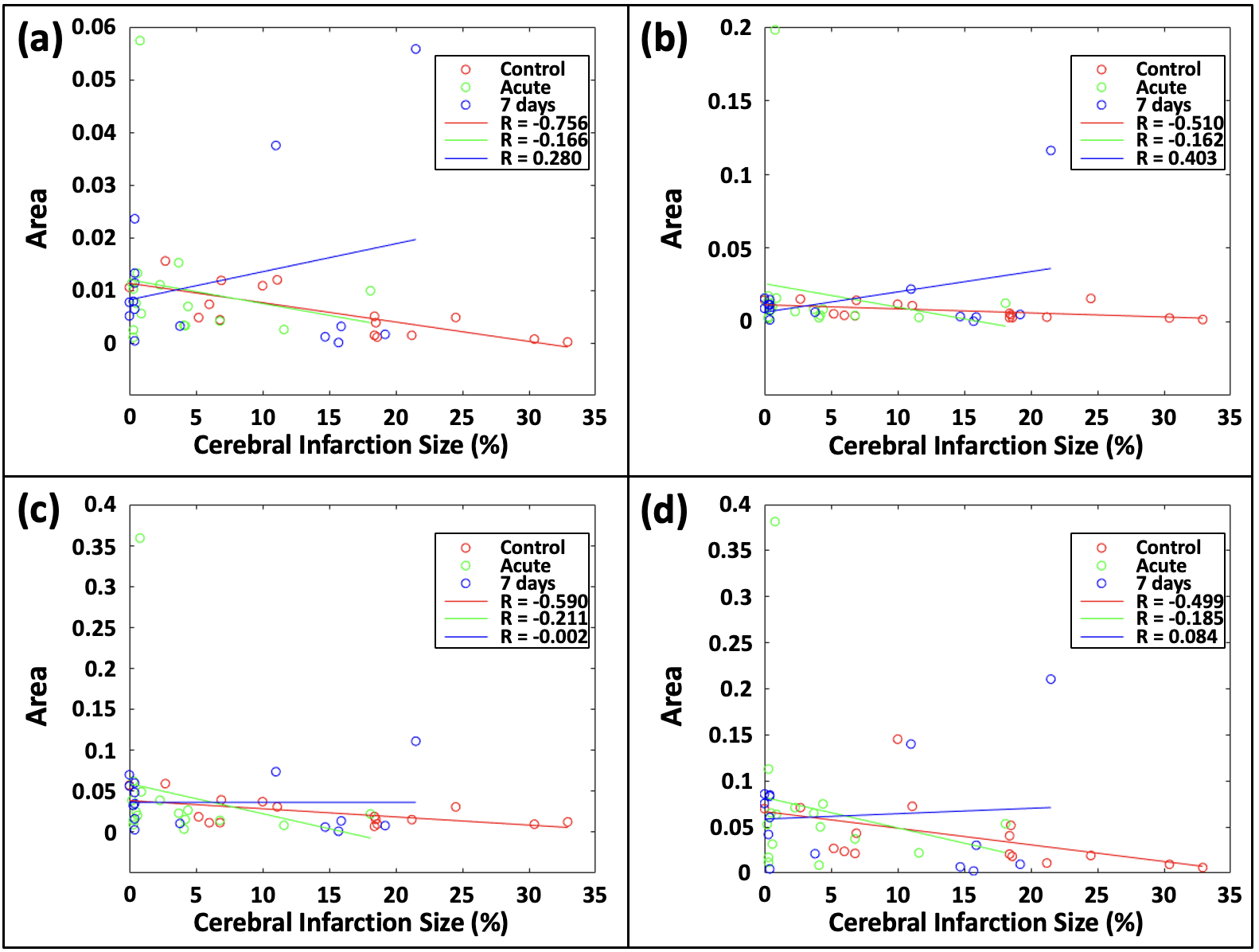
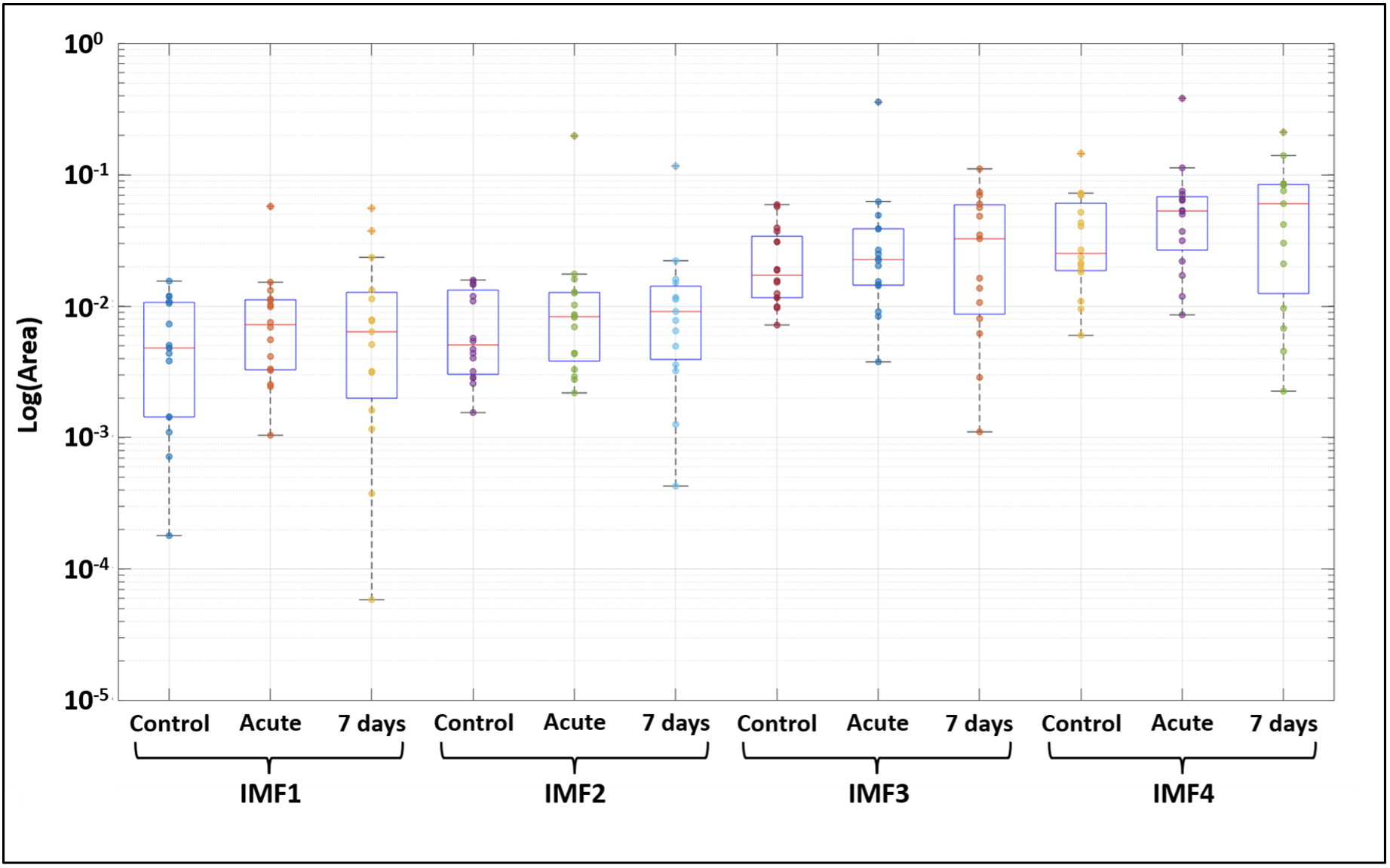
Results and Conclusions: Our results showed the control group demonstrates higher correlations between the HHT area metric and the cerebral infarction size, compared to acute or chronic EMPA treatments (Fig. 2), with an especially significant correlation for IMF1in controls (R= -0.76). No significant difference was found in the HHT area metric between control, acute, and chronic EMPA (Fig. 3). It revealed that while EMPA treatments do not alter the EEG time-frequency features compared to controls, control group exhibits a stronger correlation between EEG features and cerebral infarction size. This indicates that EMPA's neuroprotective effects might not be directly reflected in EEG changes, highlighting the need for further investigation of its mechanisms.
Methods: n= 47 male SD rats were randomized into 3 groups: 1] Control (n = 16, regular diet); 2] Acute EMPA treatment (n = 16, EMPA 10 mg/kg, IV given at 10 mins prior to middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) and 1 min prior to reperfusion); 3] Chronic EMPA treatment (n = 15, EMPA by food, 20 mg/kg for 7 days before MCAO). To induce ischemic stroke, standard MCAO was performed for 1 hour followed by 3 hours of reperfusion. Post-surgery, triphenyltetrazolium chloride (TTC) staining was used to measure volume of cerebral infarction. EEG signals were continuously recorded throughout the procedure. We applied the Hilbert-Huang Transform (HHT) to analyze the EEG signals. HHT includes 2 steps: 1] empirical mode decomposition (EMD) to decompose the EEG signal into a set of intrinsic mode functions (IMFs); 2] the Hilbert Transform is applied to each IMF to compute analytic signals. Such analytic signals are represented in the complex plane, where they often form circular or elliptical contours (Fig. 1). The area of these contours in the complex plane contains unique information about variations in the signal properties. We computed the HHT area metric for the first four IMFs by using EEG recordings at 3 hours post-reperfusion (duration: 2 minute).
Results and Conclusions: Our results showed the control group demonstrates higher correlations between the HHT area metric and the cerebral infarction size, compared to acute or chronic EMPA treatments (Fig. 2), with an especially significant correlation for IMF1in controls (R= -0.76). No significant difference was found in the HHT area metric between control, acute, and chronic EMPA (Fig. 3). It revealed that while EMPA treatments do not alter the EEG time-frequency features compared to controls, control group exhibits a stronger correlation between EEG features and cerebral infarction size. This indicates that EMPA's neuroprotective effects might not be directly reflected in EEG changes, highlighting the need for further investigation of its mechanisms.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Novel Imaging Biomarker to Make Precise Outcome Predictions for Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke
Mallavarapu Monica, Kim Hyun Woo, Iyyangar Ananya, Salazar-marioni Sergio, Yoo Albert, Giancardo Luca, Sheth Sunil, Jeevarajan Jerome
A Retrospective Analysis of the Association of Rehab Time on Discharge Disposition and Length of Stay in Hospitalized Patients with Ischemic Stroke or Intracerebral HemorrhageEperjesi Sarah, Yutrzenka Kayla, Marginean Horia, Crawford Erin, Lesko Alexandra, Clark Diane
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.
Rate this abstract
(Maximum characters: 500)