Final ID: WP382
New Insights from Time-Frequency Analysis of Electroencephalogram throughout Ischemic Stroke in Rats
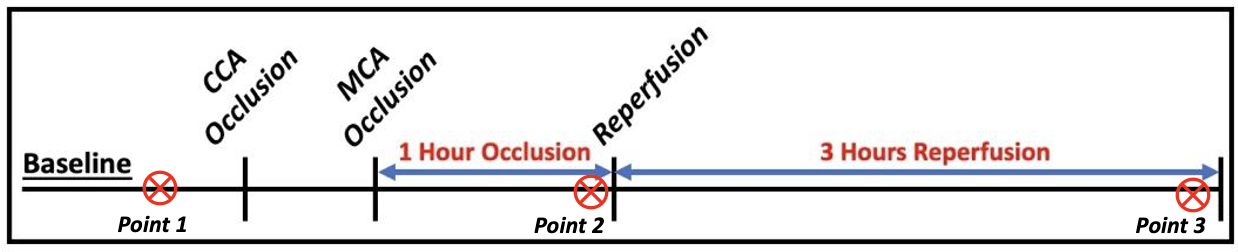
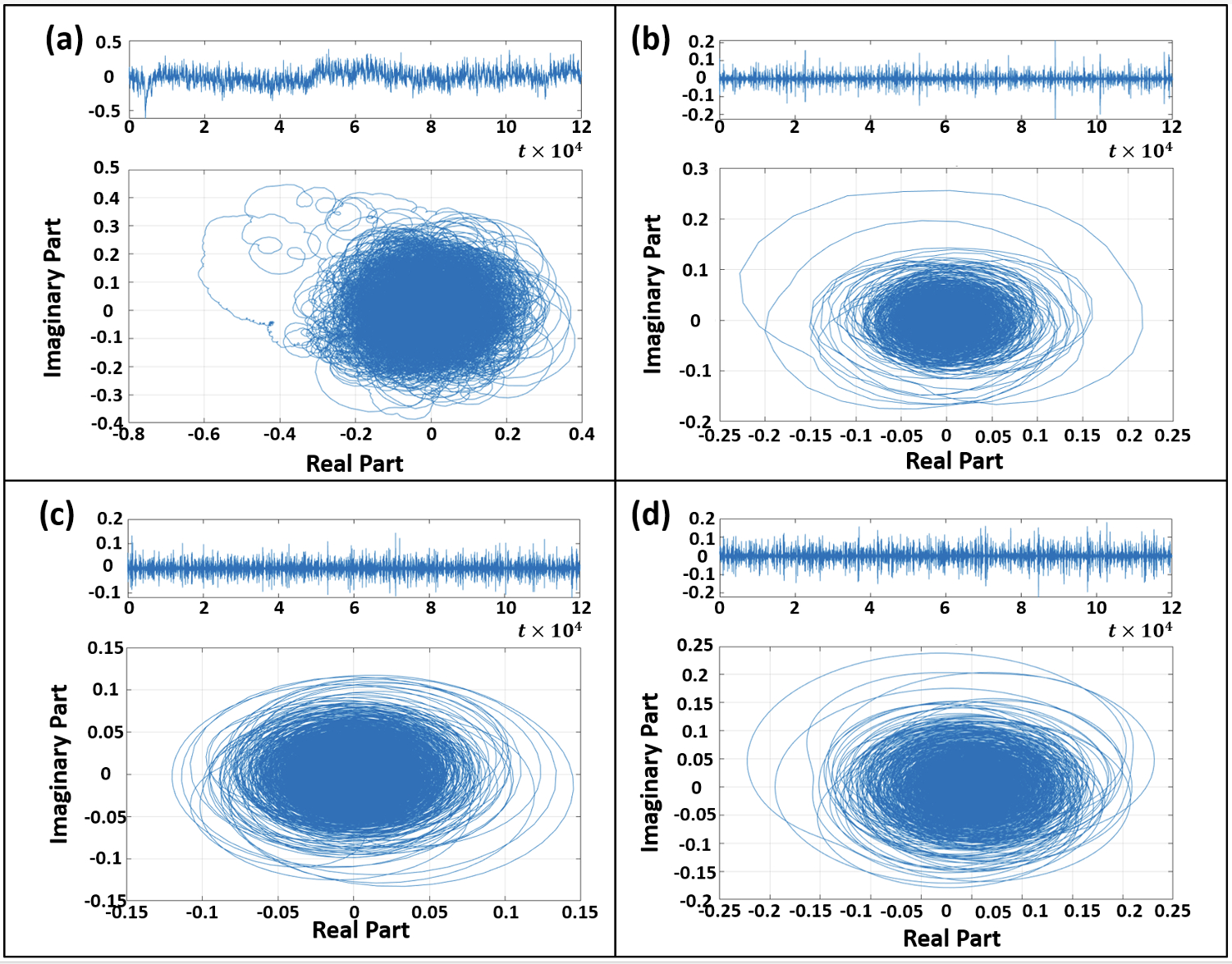
Methods: The standard intraluminal filament middle cerebral artery (MCA) occlusion model was used to induce ischemic stroke in 16 male Sprague Dawley rats (8-10 weeks old). A suture was advanced into the internal carotid artery to occlude the MCA for 1 hour, followed by 3 hours of reperfusion (Fig. 1). Cerebral infarction was confirmed post-surgery using TTC staining technique. EEG signals were continuously recorded throughout the procedure. We applied the Hilbert-Huang Transform (HHT) to analyze the EEG signals. HHT involves two main steps: 1) empirical mode decomposition (EMD), to decompose the EEG signal into a set of intrinsic mode functions (IMF); 2) the Hilbert Transform, which is applied to each IMF to obtain analytic signals. These analytic signals are represented in the complex plane, where they often exhibit circular or elliptical forms (Fig. 2). The area of these circles in the complex plane reflects unique information on variations in the signal properties. We computed the HHT area metric for the first 4 IMFs at three timepoints: baseline, 1 hour post-MCA occlusion (pre-reperfusion), and 3 hours post-reperfusion. 2-minute EEG recordings were used at each timepoint for the HHT analysis.
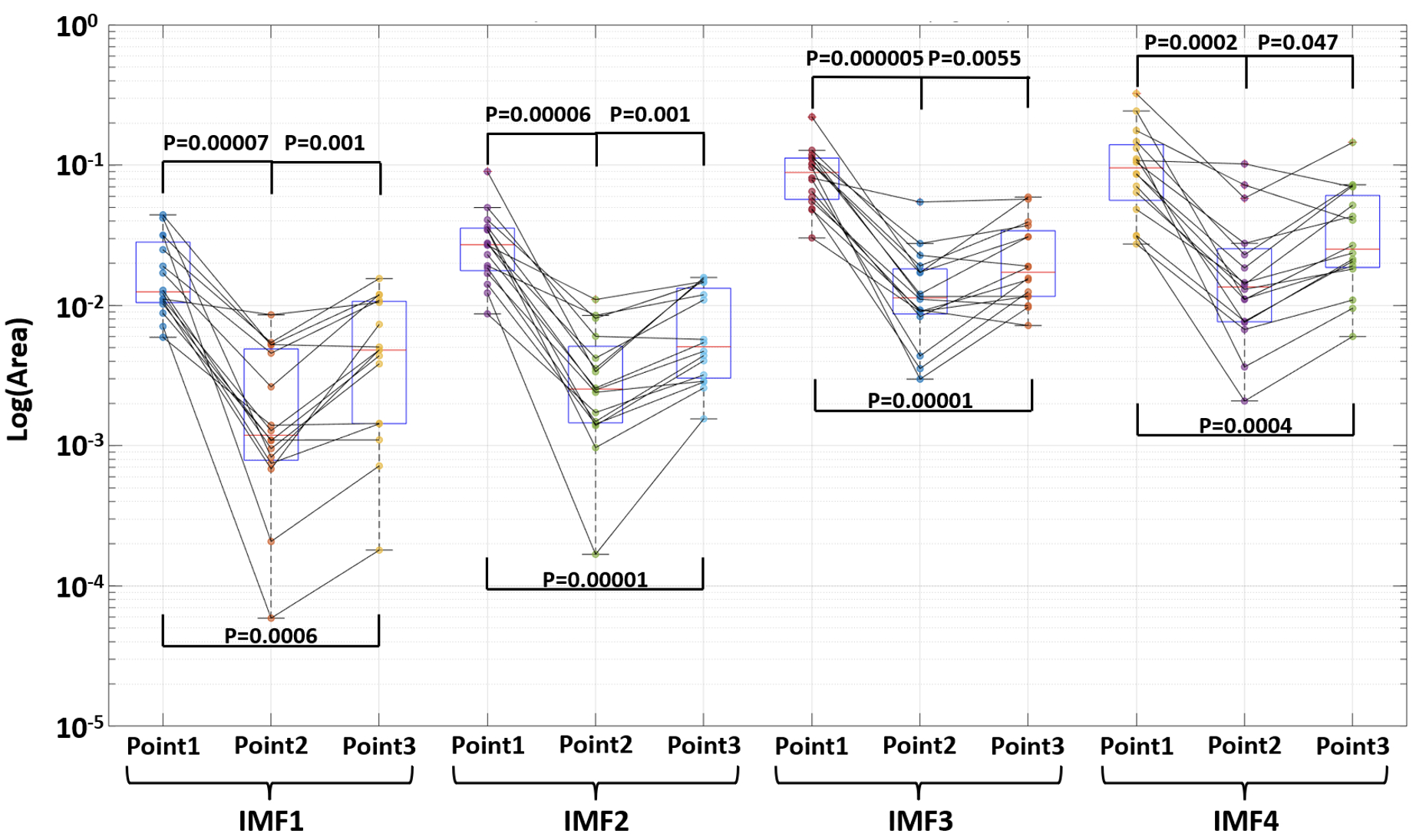
Results and Conclusions: Significant changes (P<0.05) were observed in the HHT area metric after the ischemic stroke occurrence (Fig. 3). For all IMFs, the HHT area metric reduced significantly from baseline to pre-MCA-reperfusion. However, it increased significantly from pre-MCA-reperfusion to 3 hours post-reperfusion. Comparing the baseline with post-reperfusion timepoint, significant reduction was still observed. Our results showed for the first time that the HHT can effectively analyze EEG signals to capture changes induced by ischemic stroke. Our new finding highlights the potential of HHT in providing insights into stroke-related changes in EEG, offering a valuable tool for detection or monitoring ischemic stroke.
More abstracts on this topic:
Reitan Christian, Watanabe Alexandre, Bash Lori, Galvain Thibaut, Arnet Urs, Jernberg Tomas
ADC-based Infarct Density – Validating a Novel Imaging Biomarker of Functional Outcome after Endovascular ThrombectomyFavilla Christopher, Bonkhoff Anna, Rost Natalia, Messe Steven, Regenhardt Robert, Denny Braden, Simonsen Claus, Shakibajahromi Banafsheh, Patel Aman, Leslie-mazwi Thabele, Dmytriw Adam, Schirmer Markus
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.