Final ID: TMP68
Impact of Statin Initiation and Resumption on Mortality Following Intracranial Hemorrhage: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract Body: Background: The use of statins following intracranial hemorrhage (ICH) is disputed. Prior studies have found inconsistent effects of statins on the risk of subsequent ICH and other outcome measures. Moreover, many previous studies do not distinguish between post-ICH statin treatment in patients resuming previous statin therapy versus initiation in statin-naïve patients. This meta-analysis consolidates the evidence surrounding the use of therapies following ICH, with a focus on mortality in these two subgroups.
Methods: A comprehensive search of MEDLINE, EMBASE, and The Cochrane Library was conducted up to 2024 to identify studies on statin initiation or resumption versus no statin use in intracerebral/intraparenchymal hemorrhage patients, yielding 8 studies meeting inclusion/exclusion criteria. The protocol was registered with PROSPERO, and data were analyzed using a Pairwise Meta Analysis in R, applying common and random effects models with heterogeneity assessed via I2 statistics. Mortality outcomes were categorized into “short-term” (≤90 days) and “long-term” (>90 days to 1 year) mortality.
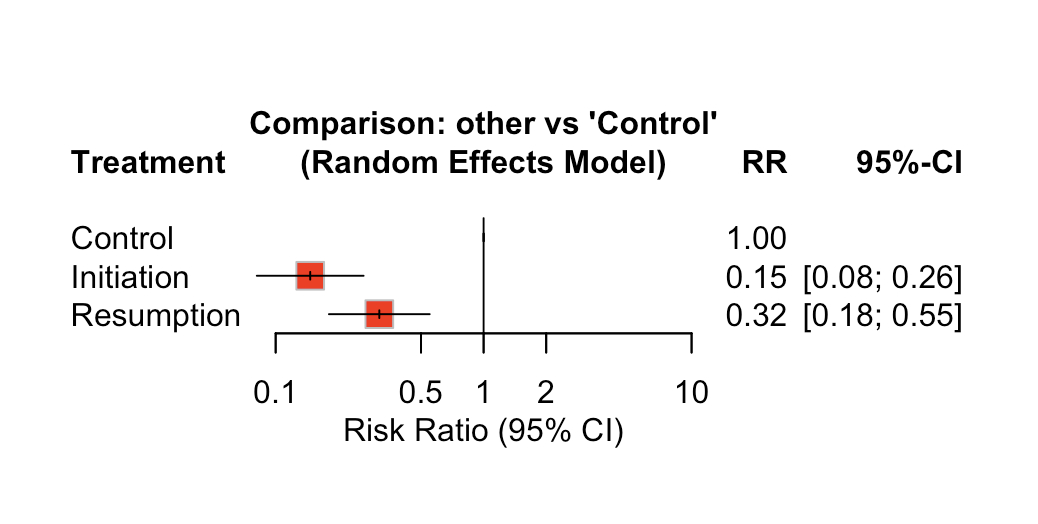
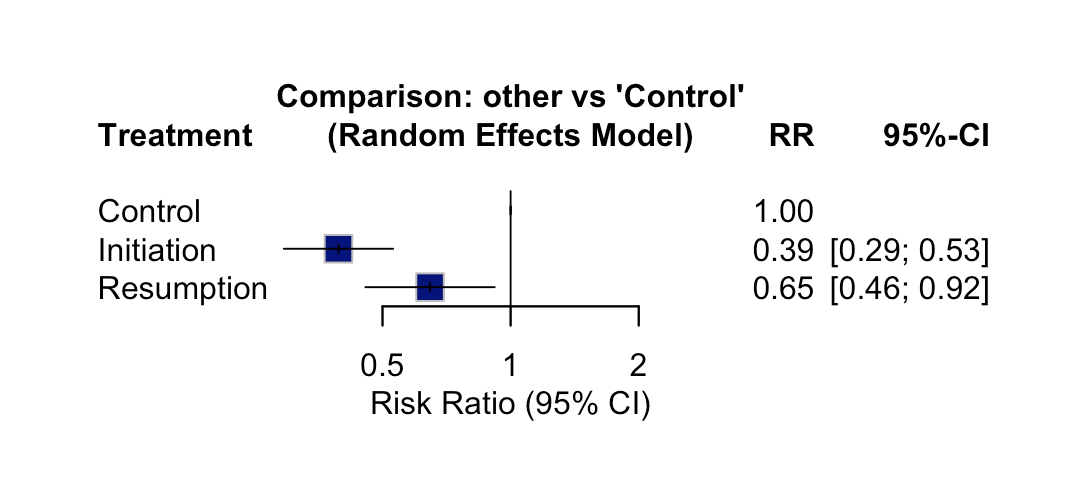
Results: Mortality events occurred in 2946 out of 9501 patients (31.0%) in the control group, 123 out of 2248 patients (5.5%) in the statin initiation group, and 787 out of 3944 patients (20.0%) in the statin resumption group. For the ≤90 days timeframe, the random effects model showed a significant reduction in mortality with statin initiation, with a relative risk (RR) of 0.15 (95% CI [0.081; 0.26], p < 0.0001), and with statin resumption, the RR was 0.32 (95% CI [0.18; 0.55], p < 0.0001). Heterogeneity was high, with an I2 of 84.3%. For the >90 days up to 1 year timeframe, statin initiation was associated with a reduction in mortality, with an RR of 0.39 (95% CI [0.29; 0.53], p < 0.0001). Statin resumption also showed a reduction in mortality, with an RR of 0.65 (95% CI [0.46; 0.92], p = 0.0145). Heterogeneity was moderate, with an I2 of 41.7%.
Conclusion: Statin therapy following ICH, whether through initiation or resumption, is associated with a significant reduction in mortality both within 90 days and beyond 90 days up to one year. Interestingly, statin initiation showed a stronger effect compared to resumption. These findings support the continuation or initiation of statins in the acute phases of ICH management regardless of previous statin use.
Methods: A comprehensive search of MEDLINE, EMBASE, and The Cochrane Library was conducted up to 2024 to identify studies on statin initiation or resumption versus no statin use in intracerebral/intraparenchymal hemorrhage patients, yielding 8 studies meeting inclusion/exclusion criteria. The protocol was registered with PROSPERO, and data were analyzed using a Pairwise Meta Analysis in R, applying common and random effects models with heterogeneity assessed via I2 statistics. Mortality outcomes were categorized into “short-term” (≤90 days) and “long-term” (>90 days to 1 year) mortality.
Results: Mortality events occurred in 2946 out of 9501 patients (31.0%) in the control group, 123 out of 2248 patients (5.5%) in the statin initiation group, and 787 out of 3944 patients (20.0%) in the statin resumption group. For the ≤90 days timeframe, the random effects model showed a significant reduction in mortality with statin initiation, with a relative risk (RR) of 0.15 (95% CI [0.081; 0.26], p < 0.0001), and with statin resumption, the RR was 0.32 (95% CI [0.18; 0.55], p < 0.0001). Heterogeneity was high, with an I2 of 84.3%. For the >90 days up to 1 year timeframe, statin initiation was associated with a reduction in mortality, with an RR of 0.39 (95% CI [0.29; 0.53], p < 0.0001). Statin resumption also showed a reduction in mortality, with an RR of 0.65 (95% CI [0.46; 0.92], p = 0.0145). Heterogeneity was moderate, with an I2 of 41.7%.
Conclusion: Statin therapy following ICH, whether through initiation or resumption, is associated with a significant reduction in mortality both within 90 days and beyond 90 days up to one year. Interestingly, statin initiation showed a stronger effect compared to resumption. These findings support the continuation or initiation of statins in the acute phases of ICH management regardless of previous statin use.
More abstracts on this topic:
Acute Exposure to High PM2.5 Levels Increases the Risk of Late All-Cause Mortality in Patients with STEMI
Fathieh Sina, Tran Hao, Faour Amir, Pahn Reece, Long Mitchell, Tam Gladys, Figtree Gemma, Negishi Kazuaki, French John
An Economic Evaluation of Non-HDL-Cholesterol and Apolipoprotein B as Treatment Targets for Lipid-Lowering Therapy in Primary PreventionLuebbe Samuel, Wilkins John, Moran Andrew, Sniderman Allan, Kohli-lynch Ciaran
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.
Rate this abstract
(Maximum characters: 500)