Final ID: 97
Association of Post-Stroke Cognitive Impairment with Impaired Glymphatic Function and Neurotoxin Waste Removal in Patients with Intracerebral Hemorrhage
To evaluate a potential relationship between post-stroke cognitive impairment (PSCI) and a radiographic measure of glymphatic function after intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH).
Introduction
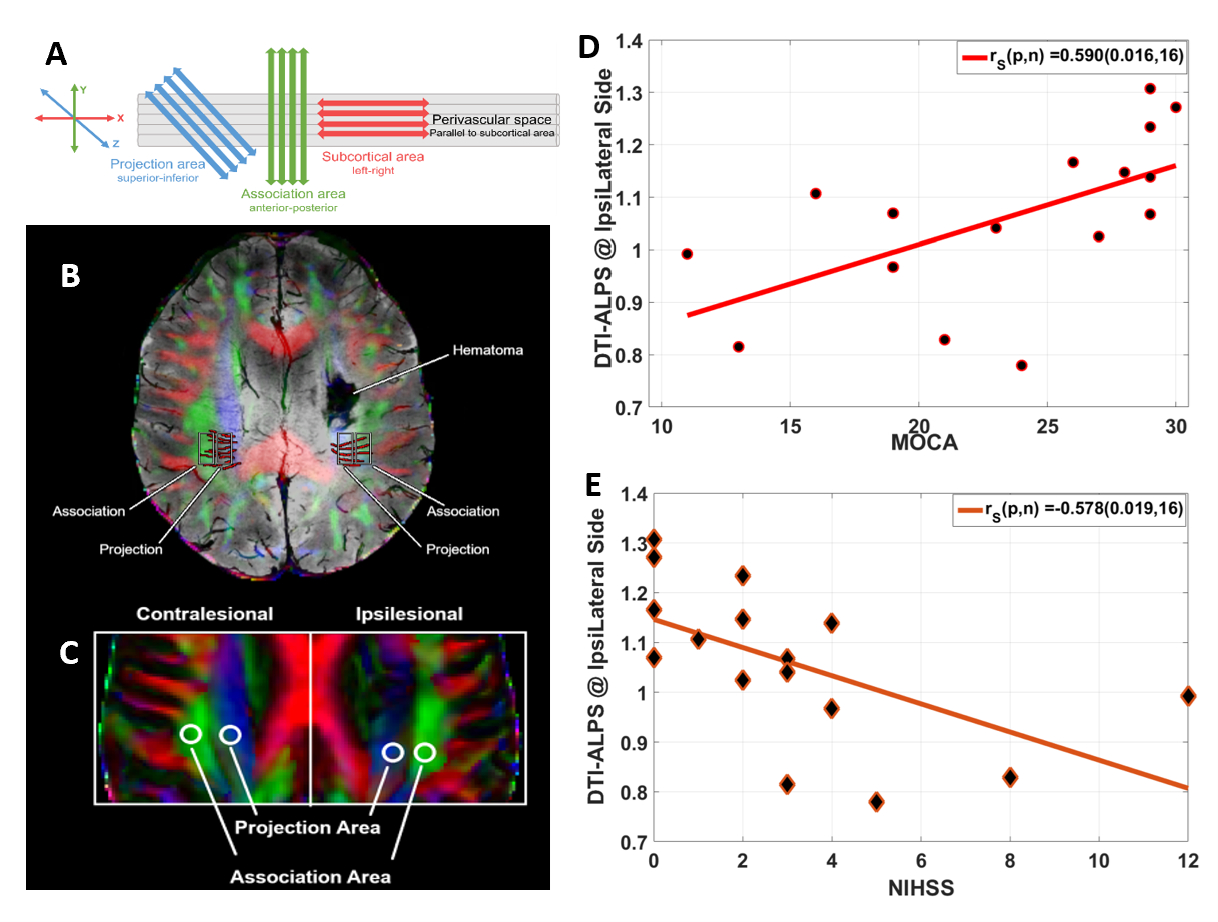
PSCI has been less studied in patients with ICH. Here we aim to evaluate the role of glymphatic function after ICH and its association with PSCI. Glymphatic cleanup occurs in the perivascular space (PVS) formed by astroglial end-feet loosely surrounding small arteries and veins. Here we applied non-invasive diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) to measure changes in brain diffusion due to dynamics changes of interstitial fluid (ISF) and CSF along the PVS. The application of DTI-along the perivascular space index (DTI-ALPSI) has been validated to evaluate glymphatic function. It computes the diffusivity ratio between projection and association fibers oriented orthogonally with the medullary veins at the level of the lateral ventricle body (Fig-1A).
Methods
We serially imaged 18 patients with deep ICH at 9.3±9.1 (V1) and 109±28 (V2) days of onset on a 3T MRI system. Cognitive assessment was obtained via MoCA scores. Fractional anisotropy (FA) and mean diffusivity (MD) maps were registered to the T1W and SWI images. Three regions of interest (ROI), remote from a lesion, in the association and projection fibers, orthogonal to the medullary veins at PVS were used to compute diffusivity (Fig-1C). Using the equation shown, the DTI-ALPSI was calculated. DTI-ALPSI = Mean (Dx proj, Dx assoc) / Mean (Dy proj, Dz assoc)
Using 3D-Flair images, hematoma (HV) and edema (EV) volumes were segmented. The ipsilesional DTI-ALPSI was correlated with MoCA, HV, and NIHSS. Contralesional DTI-ALPSI was used as a control. A non-linear regression model was used for statistical analysis.
Results
We enrolled 12M/6F with an average age of 49.3±13.3y. Compared to the control, the ipsilesional DTI-ALPSI was significantly decreased (p=0.036) at V2. Temporally the MoCA scores were significantly increased (19±8.5 to 23±6.0, p<0.001) whereas the NIHSS (8±6 to 3±3), HV (9.3±8.6 to 2.6±2.7 cm3), and EV (26.9±23.2 to 3.1±4.0 cm3) were significantly decreased (p<0.001). Ipsilesional DTI-ALPSI was positively associated with MoCA (r=0.59, p=0.02) (Fig-1D) and negatively associated with NIHSS (r=-0.58, p=0.02) (Fig-1E) and HV (r=-0.53, p=0.04) at V2.
Conclusion
Our data showed that DTI-ALPSI can be applied to evaluate the role of glymphatic dysfunction and its association with post-ICH cognitive impairment.
More abstracts on this topic:
Scott Kiersten, Kyriakopoulos Vasilia, Kim Gab Seok, Lee Juneyoung, Urayama Akihiko
ADC-based Infarct Density – Validating a Novel Imaging Biomarker of Functional Outcome after Endovascular ThrombectomyFavilla Christopher, Bonkhoff Anna, Rost Natalia, Messe Steven, Regenhardt Robert, Denny Braden, Simonsen Claus, Shakibajahromi Banafsheh, Patel Aman, Leslie-mazwi Thabele, Dmytriw Adam, Schirmer Markus
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.