Final ID: TP301
Prevalence and In-Hospital Characteristics of Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke and CADASIL
Abstract Body: Background: Cerebral Autosomal Dominant Arteriopathy with Subcortical Infarcts and Leukoencephalopathy (CADASIL) is the most common hereditary stroke disorder due to pathogenic variants in the NOTCH3 gene on chromosome 19. Characteristics of CADASIL patients hospitalized with acute ischemic stroke (AIS) have not been widely reported.
Methods: We identified all adult hospitalizations in the National Inpatient Sample (NIS) from 2018-2020 with diagnosis codes for acute ischemic stroke (ICD-10 I63) and the newly available code as of October 2018 for CADASIL (I67.850) using weighted sampling. Descriptive statistics evaluated demographic and clinical characteristics among AIS patients with and without CADASIL.
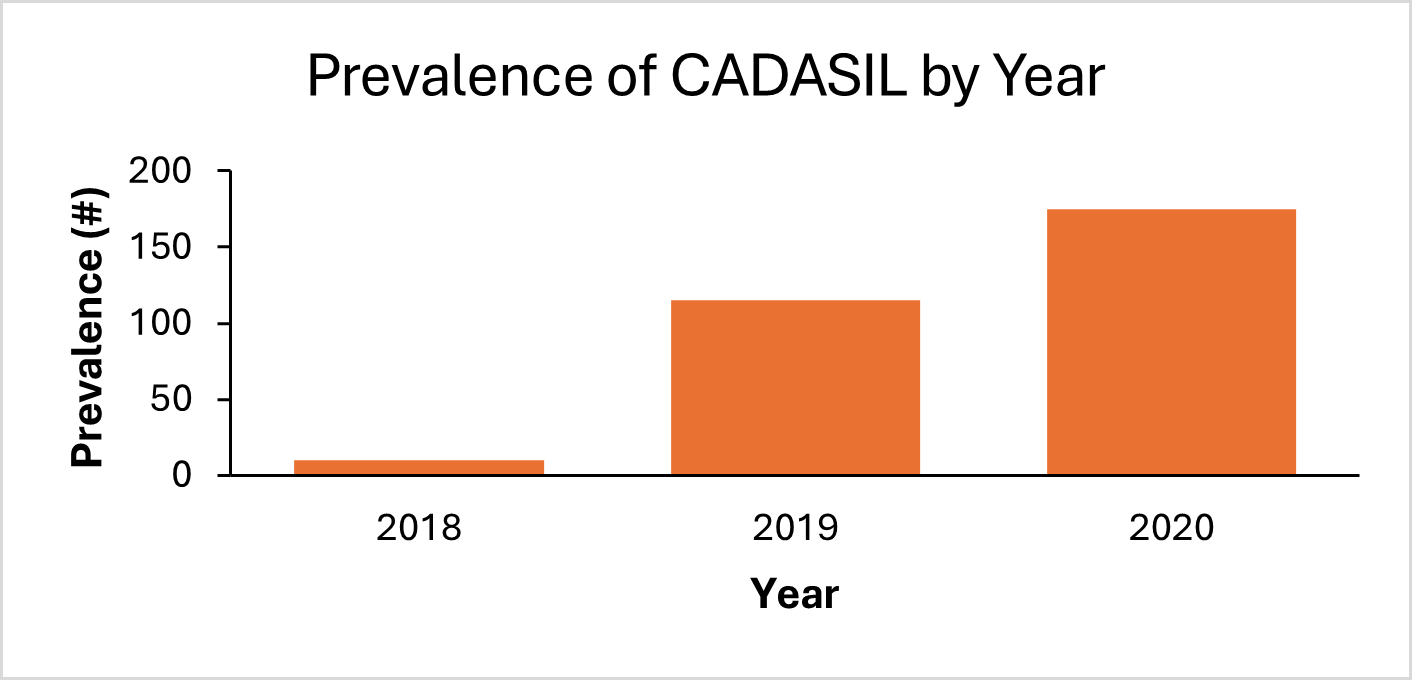
Results: Of a total 1,918,920 weighted AIS hospitalizations, there were 300 patients with CADASIL. The prevalence of CADASIL among AIS patients increased from 0.2% in 2018 to 2.8% in 2020. AIS patients with CADASIL were similar in sex and more likely to be younger (55.8 ± 25.2 vs 69.7 ± 31.4 years, p<0.001), White (70.0% vs 65.4%, p=0.03), and Asian/Pacific Islander (6.7% vs 3.1%, p<0.001) compared to those without CADASIL. CADASIL patients had lower rates of hypertension, diabetes, and coronary artery disease (55.0% vs 82.4%, p<0.001; 21.7% vs 38.9%, p<0.001; 3.3% vs 10.6%, p=0.004). There was no difference in the rate of dyslipidemia (43.3% vs 49.8%, p=0.31), obesity (15.0% vs 8.9%, p=0.19) and smoking (23.3% vs 18.5%, p=0.38) in patients with CADASIL vs those without. There was no difference in the rate of administration of IV thrombolysis (5.0% vs 8.3%, p=0.25), however CADASIL patients were less likely to undergo endovascular thrombectomy (EVT) (0.0% vs 4.1%, p<0.001). CADASIL patients had lower rates of in-hospital mortality and were more likely to be discharged home (0.0% vs 6.5%, 53.3% vs 33.3%, all p-values <0.001).
Conclusions: CADASIL was rare in our NIS population with a prevalence of 2.8% in 2020. Patients with CADASIL, in general, carried a lower burden of vascular risk factors. They received IV thrombolysis at an equal rate but EVT at a lower rate, likely due to the small vessel pathology of CADASIL. While less likely to experience in-hospital mortality, nearly two-thirds were not independent enough to be discharged home. Our findings highlight the need for targeted therapies addressing the pathophysiology of CADASIL to prevent AIS in these patients with an otherwise low burden of vascular risk factors.
Methods: We identified all adult hospitalizations in the National Inpatient Sample (NIS) from 2018-2020 with diagnosis codes for acute ischemic stroke (ICD-10 I63) and the newly available code as of October 2018 for CADASIL (I67.850) using weighted sampling. Descriptive statistics evaluated demographic and clinical characteristics among AIS patients with and without CADASIL.
Results: Of a total 1,918,920 weighted AIS hospitalizations, there were 300 patients with CADASIL. The prevalence of CADASIL among AIS patients increased from 0.2% in 2018 to 2.8% in 2020. AIS patients with CADASIL were similar in sex and more likely to be younger (55.8 ± 25.2 vs 69.7 ± 31.4 years, p<0.001), White (70.0% vs 65.4%, p=0.03), and Asian/Pacific Islander (6.7% vs 3.1%, p<0.001) compared to those without CADASIL. CADASIL patients had lower rates of hypertension, diabetes, and coronary artery disease (55.0% vs 82.4%, p<0.001; 21.7% vs 38.9%, p<0.001; 3.3% vs 10.6%, p=0.004). There was no difference in the rate of dyslipidemia (43.3% vs 49.8%, p=0.31), obesity (15.0% vs 8.9%, p=0.19) and smoking (23.3% vs 18.5%, p=0.38) in patients with CADASIL vs those without. There was no difference in the rate of administration of IV thrombolysis (5.0% vs 8.3%, p=0.25), however CADASIL patients were less likely to undergo endovascular thrombectomy (EVT) (0.0% vs 4.1%, p<0.001). CADASIL patients had lower rates of in-hospital mortality and were more likely to be discharged home (0.0% vs 6.5%, 53.3% vs 33.3%, all p-values <0.001).
Conclusions: CADASIL was rare in our NIS population with a prevalence of 2.8% in 2020. Patients with CADASIL, in general, carried a lower burden of vascular risk factors. They received IV thrombolysis at an equal rate but EVT at a lower rate, likely due to the small vessel pathology of CADASIL. While less likely to experience in-hospital mortality, nearly two-thirds were not independent enough to be discharged home. Our findings highlight the need for targeted therapies addressing the pathophysiology of CADASIL to prevent AIS in these patients with an otherwise low burden of vascular risk factors.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Scoping Review Exploring Cardiovascular Risk and Health Metrics and Cancer Prediction
Kim Ji-eun, Henriquez Santos Gretell, Kumar Sant, Livinski Alicia, Vo Jacqueline, Joo Jungnam, Shearer Joe, Hashemian Maryam, Roger Veronique
A Case of Hypertrophic Cardimyopathy: Digenic Variants of Uncertain Significance Mutations in MHY7 and RYR2 GenesDurukan Selina, Uzunoglu Ekin, Farahmandsadr Maryam, Soffer Daniel
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.
Rate this abstract
(Maximum characters: 500)