Final ID: MDP64
A Polygenic Score to Identify Risk of Incident Stroke and Benefit from Primary Prevention Statin Therapy
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background:
Primary prevention statin use has been shown to significantly reduce the incidence of stroke, however, clinical risk scores for statin eligibility do not predict stroke specifically. A polygenic risk score (PRS) for stroke is a tool that may help identify individuals at greatest risk of stroke and most likely to benefit from statin therapy.
Methods:
We performed a prospective cohort study using genotyped individuals from a large primary prevention RCT (JUPITER), which tested rosuvastatin 20 mg daily vs placebo. We applied the validated GIGASTROKE PRS categorized by quintiles: low (Q1), moderate (Q2-Q4) or high risk (Q5). The primary outcome was occurrence of all-cause stroke. PRS risk was modeled per 1-SD and hazard ratios calculated for the moderate and high-risk groups relative to low risk. Formal testing of treatment interaction for rosuvastatin and PRS was performed.
Results:
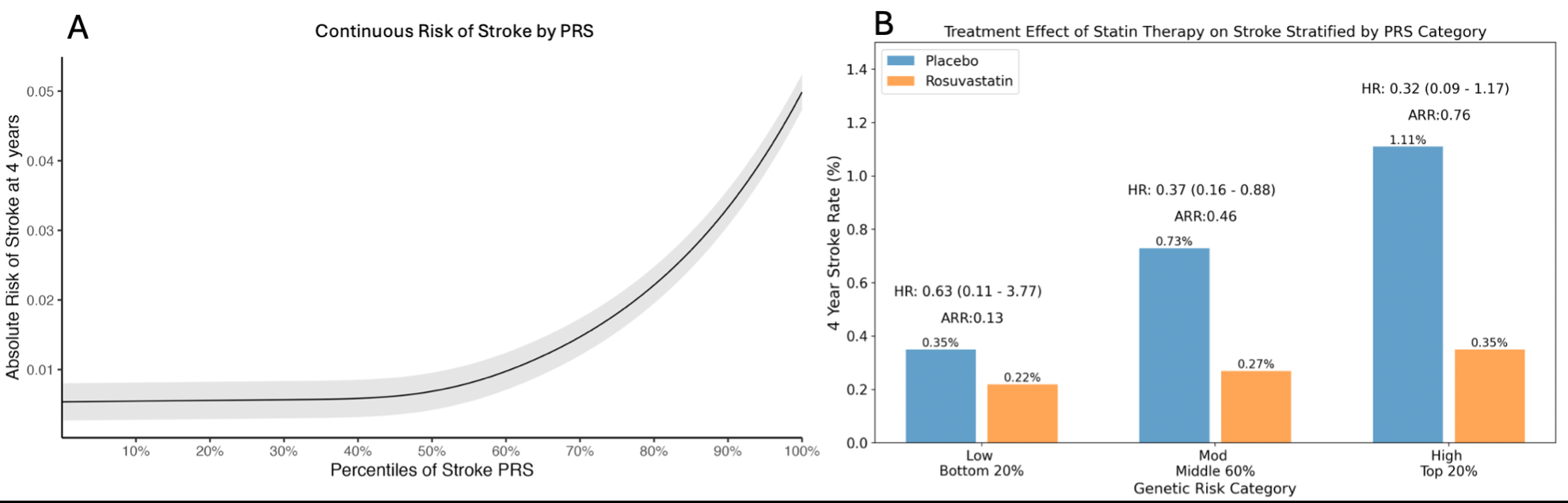
Of 8,749 patients with genetic data (32% male, mean age 66), the median LDL-C was 110 mg/dL and hsCRP was 4.05 mg/L. During 4 years of follow up, 44 patients suffered a stroke. The PRS was strongly associated with risk of incident stroke (Fig, A). Compared to those at low genetic risk, the absolute risk of stroke was more than 2-fold greater in the moderate group (HR: 2.10, 0.78-5.67) and nearly 4-fold greater in the high-risk group (HR: 3.72, 1.27-10.88, p-trend =0.011). In this genetic cohort, rosuvastatin reduced the risk of stroke by 61% (HR: 0.39, 0.20-0.76, p=0.006). The relative risk reductions with rosuvastatin were 37% (HR 0.63, 0.11-3.77), 63% (HR 0.37, 0.16-0.88), and 68% (HR 0.32, 0.09-1.17) in low, moderate, and high-risk groups, respectively. The absolute risk reductions with rosuvastatin were 0.13% (-0.38-0.63), 0.46% (0.08-0.84), and 0.76% (-0.03-1.56) (Fig, B). Rosuvastatin in the high-risk subgroup reduced the incidence of stroke to the level of the low-risk subgroup receiving placebo (0.35%).
Conclusion:
A PRS can identify primary prevention patients with a 2 to 4-fold increased risk of stroke, which appears to be largely offset with statin therapy. As the use of PRSs increase in clinical practice, it may be a useful tool to help guide statin initiation for primary stroke prevention.
Primary prevention statin use has been shown to significantly reduce the incidence of stroke, however, clinical risk scores for statin eligibility do not predict stroke specifically. A polygenic risk score (PRS) for stroke is a tool that may help identify individuals at greatest risk of stroke and most likely to benefit from statin therapy.
Methods:
We performed a prospective cohort study using genotyped individuals from a large primary prevention RCT (JUPITER), which tested rosuvastatin 20 mg daily vs placebo. We applied the validated GIGASTROKE PRS categorized by quintiles: low (Q1), moderate (Q2-Q4) or high risk (Q5). The primary outcome was occurrence of all-cause stroke. PRS risk was modeled per 1-SD and hazard ratios calculated for the moderate and high-risk groups relative to low risk. Formal testing of treatment interaction for rosuvastatin and PRS was performed.
Results:
Of 8,749 patients with genetic data (32% male, mean age 66), the median LDL-C was 110 mg/dL and hsCRP was 4.05 mg/L. During 4 years of follow up, 44 patients suffered a stroke. The PRS was strongly associated with risk of incident stroke (Fig, A). Compared to those at low genetic risk, the absolute risk of stroke was more than 2-fold greater in the moderate group (HR: 2.10, 0.78-5.67) and nearly 4-fold greater in the high-risk group (HR: 3.72, 1.27-10.88, p-trend =0.011). In this genetic cohort, rosuvastatin reduced the risk of stroke by 61% (HR: 0.39, 0.20-0.76, p=0.006). The relative risk reductions with rosuvastatin were 37% (HR 0.63, 0.11-3.77), 63% (HR 0.37, 0.16-0.88), and 68% (HR 0.32, 0.09-1.17) in low, moderate, and high-risk groups, respectively. The absolute risk reductions with rosuvastatin were 0.13% (-0.38-0.63), 0.46% (0.08-0.84), and 0.76% (-0.03-1.56) (Fig, B). Rosuvastatin in the high-risk subgroup reduced the incidence of stroke to the level of the low-risk subgroup receiving placebo (0.35%).
Conclusion:
A PRS can identify primary prevention patients with a 2 to 4-fold increased risk of stroke, which appears to be largely offset with statin therapy. As the use of PRSs increase in clinical practice, it may be a useful tool to help guide statin initiation for primary stroke prevention.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Genome-wide CRISPRi Screen Implicates Coronary Artery Disease GWAS Genes as Key Regulators of Adventitial Fibroblast Proliferation
Jackson William, Zhu Ashley, Gu Wenduo, Berezowitz Alexa, Iyer Meghana, Cheng Paul
A Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Polygenic Score Modifies Penetrance of Pathogenic Hypertrophic and Dilated Cardiomyopathy Variants in Opposite DirectionsAbramowitz Sarah, Hoffman-andrews Lily, Depaolo John, Judy Renae, Owens Anjali, Damrauer Scott, Levin Michael