Final ID: WP292
Efficacy of Lipid-Lowering Therapies in Reducing Stroke Risk in Intracranial Atherosclerosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Objective: To perform a systematic review and meta-analysis assessing the efficacy of lipid-lowering therapies in improving stroke outcomes among patients with ICAS.
Methods: A systematic search of PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, Cochrane, and other databases was conducted from inception to November 2023. Eligible studies compared lipid-lowering therapies (Statins and PCSK9i) to standard care or placebo in patients with ICAS. The primary outcome was the incidence of stroke. Pooled relative risks (RR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI) were calculated using a random-effects model, and forest plots were constructed. Chi-square and I 2 statistics were used to assess heterogeneity.
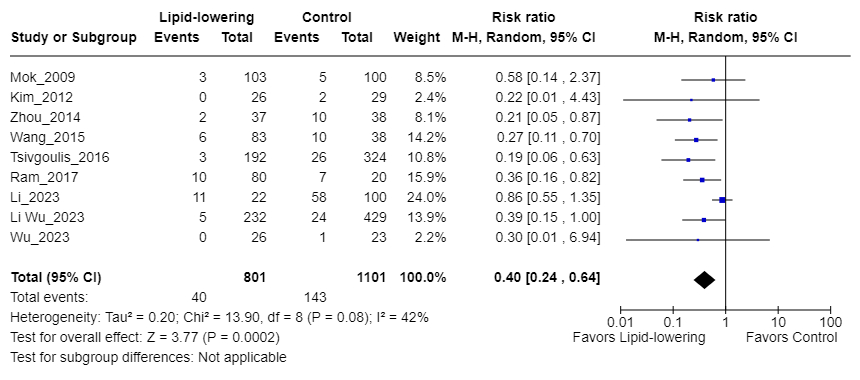
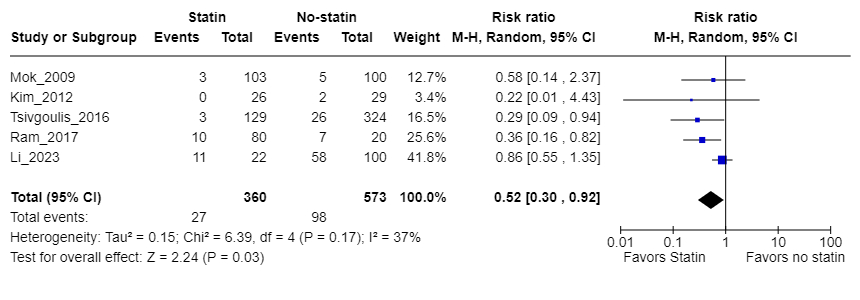
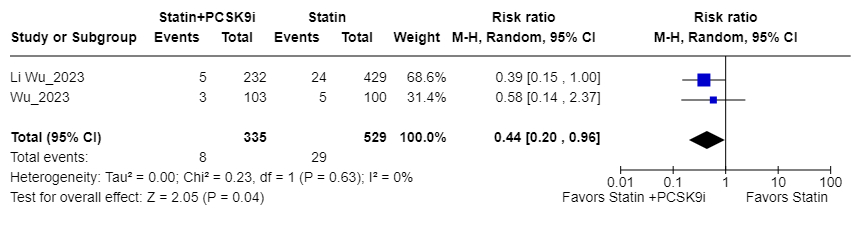
Results: Seven observational studies and two randomized controlled trials involving 1,902 ICAS patients were included. Of these, 801 received lipid-lowering therapy, and 1,101 received standard care or placebo. The weighted mean follow-up was 17.6 months (IQR 9.75-25.5). The weighted mean age was 63.7 years (range 55-68) for the lipid-lowering group and 64.0 years (range 50-66) for controls. Females comprised 42% of both groups. Hypertension was present in 74% of the intervention group and 71% of controls. A history of stroke was reported in 32% of the intervention group and 29% of controls. The weighted mean baseline LDL level was 105 mg/dL in the intervention group and 107 mg/dL in controls. The weighted mean change in LDL pre- and post-treatment in the intervention group was -47.18 mg/dL, compared to -12.39 mg/dL in controls. The incidence of ischemic stroke was 5.0% (40/801) in the lipid-lowering group versus 13.0% (143/1,101) in controls (RR 0.40; 95% CI 0.24-0.64; P<0.001, Figure 1a). Subgroup analysis of studies comparing statin versus no statin treatment showed an RR of 0.40 (95% CI 0.30-0.92; P<0.05, Figure 1b). Another subgroup analysis comparing PCSK9 inhibitors and statins versus statins only found an RR of 0.44; 95% CI 0.20-0.96; P<0.05, Figure 1c).
Conclusions: Lipid-lowering therapies significantly reduce the risk of ischemic stroke in patients with intracranial atherosclerosis. The addition of PCSK9 inhibitors to statins appears to provide added stroke risk reduction.
More abstracts on this topic:
Wong Ka-ho, De Havenon Adam, Sulken Amy, Knebusch Clara, Reed Rachel, Faraco Carlos, Martin Renee, Amin-hanjani Sepideh, Chatterjee Arindam, Liebeskind David
Longitudinal Assessment of Vessel Wall Radiomics and Luminal Blood Flow During Evaluation of Intracranial Atherosclerotic PlaquesVeeturi Sricharan, Pinter Nandor, Mecca Nicholas, Morrish Benjamin, Levy Elad, Siddiqui Adnan, Tutino Vincent
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.