Final ID: WP58
Retinal Optical Coherence Tomography Abnormalities Associated with CADASIL: A Case-Control Study from the UK Biobank
Abstract Body: Introduction: Cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy (CADASIL) is an inherited cerebral small vessel disease, yet there is currently no biomarker for early detection. This study aims to identify retinal biomarkers of NOTCH3 carriers using optical coherence tomography (OCT) from the UK Biobank.
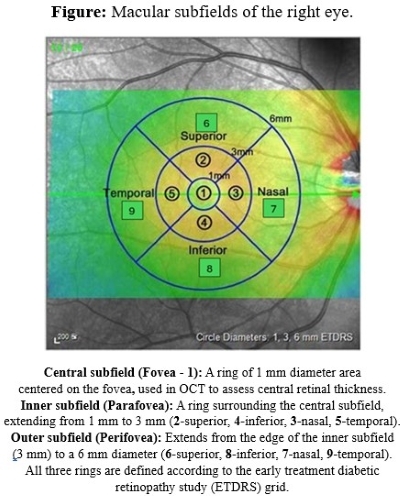
Methods: We conducted a cross-sectional, matched case-control study of individuals with or without CADASIL from the UK Biobank between 2006 and 2010. All participants had retinal OCT scan and cognitive assessment. Cases were identified based on pathogenic NOTCH3 mutations and 1:1 matched with healthy controls based on age, sex, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and smoking status. Baseline characteristics and cognitive test scores were compared using chi-square or Mann-Whitney-U test appropriately. Macular thickness (central, inner, and outer subfields) (Figure) and retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL) thickness were compared using Wilcoxon signed-rank test.
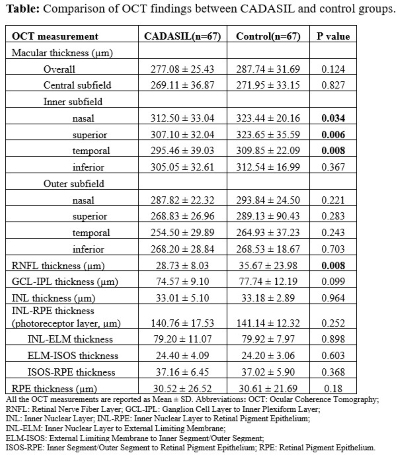
Results: Our analysis included 134 participants (67 CADASIL cases, 67 controls) with a mean age of 54±8 years. There were no differences in visual acuity between the two groups. CADASIL performed worse in prospective memory (0.043), verbal and numerical reasoning (p=0.178), visual memory (p=0.227), and processing speed (p=0.101) than matched controls. Participants with CADASIL had significantly thinner macular inner subfield at the superior (p=0.006), temporal (p=0.008), and nasal (p=0.034) quadrants, and significantly thinner RNFL (p=0.008) compared to controls (Table).
Conclusion: Individuals with CADASIL have reduced thickness in the inner macular subfield and RFNL relative to matched controls. These retinal group differences were not associated with differences in visual acuity and may reflect early pericyte dysfunction and microvascular ischemia. Longitudinal studies are needed to assess the temporal relationship between these retinal changes and disease progression.
Methods: We conducted a cross-sectional, matched case-control study of individuals with or without CADASIL from the UK Biobank between 2006 and 2010. All participants had retinal OCT scan and cognitive assessment. Cases were identified based on pathogenic NOTCH3 mutations and 1:1 matched with healthy controls based on age, sex, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and smoking status. Baseline characteristics and cognitive test scores were compared using chi-square or Mann-Whitney-U test appropriately. Macular thickness (central, inner, and outer subfields) (Figure) and retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL) thickness were compared using Wilcoxon signed-rank test.
Results: Our analysis included 134 participants (67 CADASIL cases, 67 controls) with a mean age of 54±8 years. There were no differences in visual acuity between the two groups. CADASIL performed worse in prospective memory (0.043), verbal and numerical reasoning (p=0.178), visual memory (p=0.227), and processing speed (p=0.101) than matched controls. Participants with CADASIL had significantly thinner macular inner subfield at the superior (p=0.006), temporal (p=0.008), and nasal (p=0.034) quadrants, and significantly thinner RNFL (p=0.008) compared to controls (Table).
Conclusion: Individuals with CADASIL have reduced thickness in the inner macular subfield and RFNL relative to matched controls. These retinal group differences were not associated with differences in visual acuity and may reflect early pericyte dysfunction and microvascular ischemia. Longitudinal studies are needed to assess the temporal relationship between these retinal changes and disease progression.
More abstracts on this topic:
Age-Associated CD8+ T Cells Accumulate in the Aging Brain
A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Double-Blinded Clinical Trial
Ali Md Akkas, Vardaman, Donald, Bolding Chase, Tidwell Harrison, Tyrrell Daniel
Atorvastatin Treatment and Rebleeding in Cerebral Cavernous Malformations:A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Double-Blinded Clinical Trial
Awad Issam
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.
Rate this abstract
(Maximum characters: 500)