Final ID: DP1
Intravenous thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke patients with cerebral amyloid angiopathy
Methods: This was an explorative analysis of a nationwide database of hospitalizations in the United States. AIS patients with CAA were identified by ICD-10 codes and included in the study, and cases were divided into IVT and no-IVT groups. Propensity score matching was performed to balance treatment groups, and additional multivariable logistic regressions were used for doubly robust analyses. Primary outcome was routine discharge to home with self-care. Secondary outcomes include discharge to home, in-hospital mortality, intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH), and subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH).
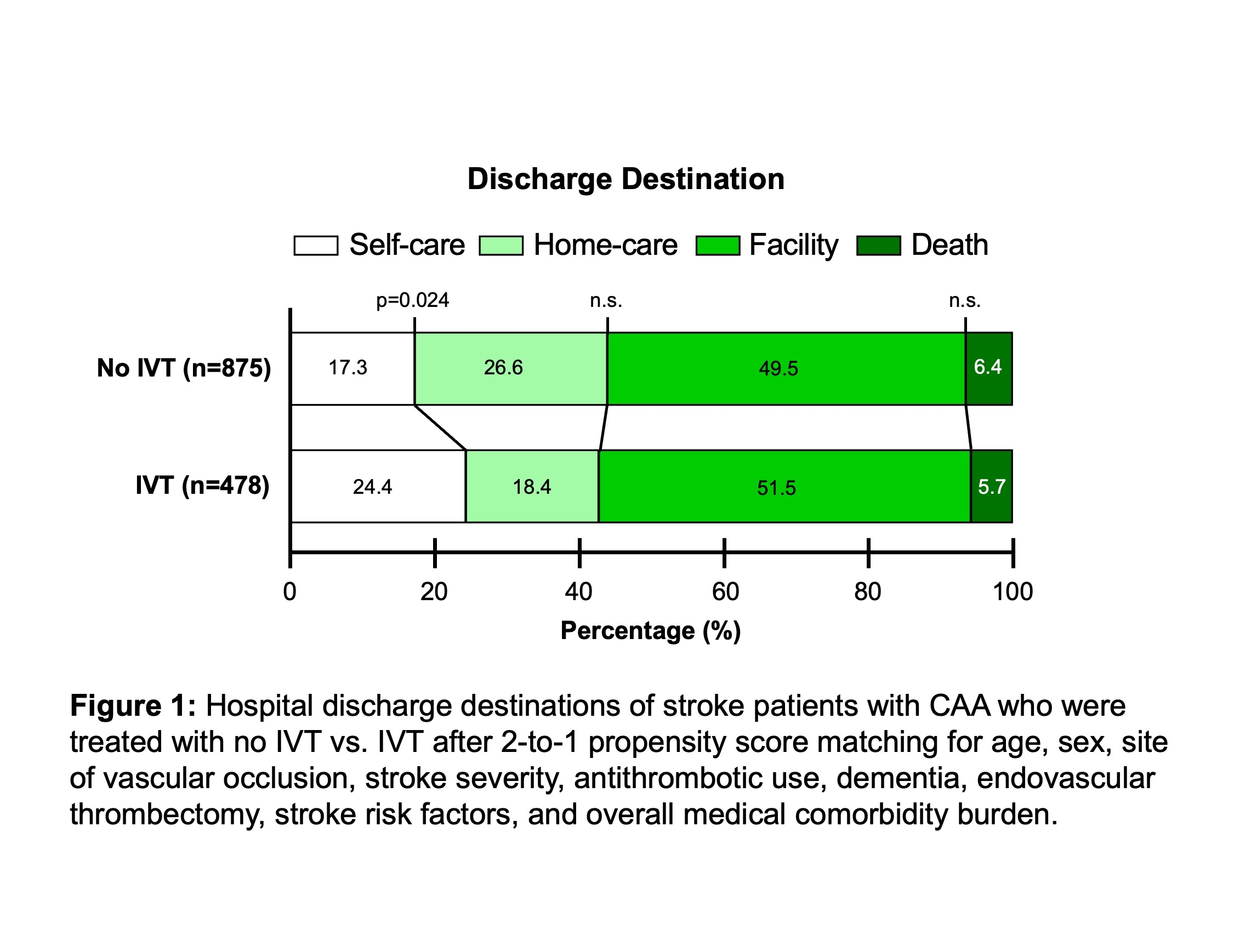
Results: 5,100 patients were identified; 498 (9.8%) received IVT. After propensity score matching and doubly robust analyses with additional multivariable logistic regression, IVT was associated with better discharge outcomes (Figure 1), with significantly higher odds of routine discharge (adjusted OR 1.77 [95%CI 1.12-2.80], p=0.015) despite higher odds of ICH (aOR 4.00 [95%CI 2.79 to 5.75], p<0.001), and SAH (aOR 2.42 [95%CI 1.41-4.16], p=0.001). IVT was not associated with significantly different odds of home discharge (aOR 0.99 [95%CI 0.69-1.41], p=0.94) or in-hospital mortality (aOR 0.91 [95%CI 0.45-1.84], p=0.80). Mediation analyses revealed that the higher rates of ICH associated with IVT treatment led to a statistically significant suppression of IVT’s association with higher odds of routine discharge (ACME of -0.03 [-0.01 to -0.06], p=0.004 and proportion suppressed of 49.3% [95%CI 8.0% to 360.6%], p=0.038).
Conclusion: IVT for AIS patients with CAA was associated with higher odds of short-term excellent outcomes despite higher odds of ICH and SAH, and it did not increase the odds of early mortality.
More abstracts on this topic:
Musheer Adeena, Faisal Noman, Haider Tehseen, Ahmed Ali, Arshad Usman, Ur Rehman Muneeb, Hassan Abbas Khan Muhammad, Said Sana, Iqbal Ahsan, Butt Abdur Rehman, Hassan Kazmi Zuha
A New Neurological Assessment Focused on Consciousness and Quantitative Motor Function in a Rat Model of Subarachnoid HemorrhageKanamaru Hideki, Zhu Shiyi, Han Mingyang, Huang Lei, Sherchan Prativa, Suzuki Hidenori, Tang Jiping, Zhang John
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.