Final ID: LBP23
ADAR1 inhibiting ZBP1-driven neuronal necroptosis to improve secondary injury after intracerebral hemorrhage
Abstract Body: Background: The volume of the hematoma after Intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) significantly influences the outcome. tumor necrosis factor (TNF) induces the activation of receptor-interacting protein 3 (RIPK3), which participates in the regulation of programmed cell death known as necroptosis. Following phosphorylation modification of RIP1, RIP3 is recruited via the RHIM domain, which also possesses the RHIM domain, triggering necroptosis and undergoing positive feedback regulation from the inflammatory response. Z-DNA binding protein 1 (ZBP1) is acknowledged as a nucleic acid sensor with the capability to bind to both Z-DNA and Z-RNA. It is notable for its capacity to initiate necroptosis by activating RIPK3. The relationship between endogenous dsRNA and ZBP1 remains elusive.
Methods: ICH was induced in vivo by collagenase VII injection. ADAR1 knock-down mice were constructed by Lentivirus (LVs) infection to explore the role of ADAR1 and its mechanism after ICH. By constructing ZBP1flox/flox / Thy1-Cre+/- mice to investigate the potential mechanism underlying ZBP1 and effect of ZBP1 inhibition on cognition after intracerebral hemorrhage in mice.
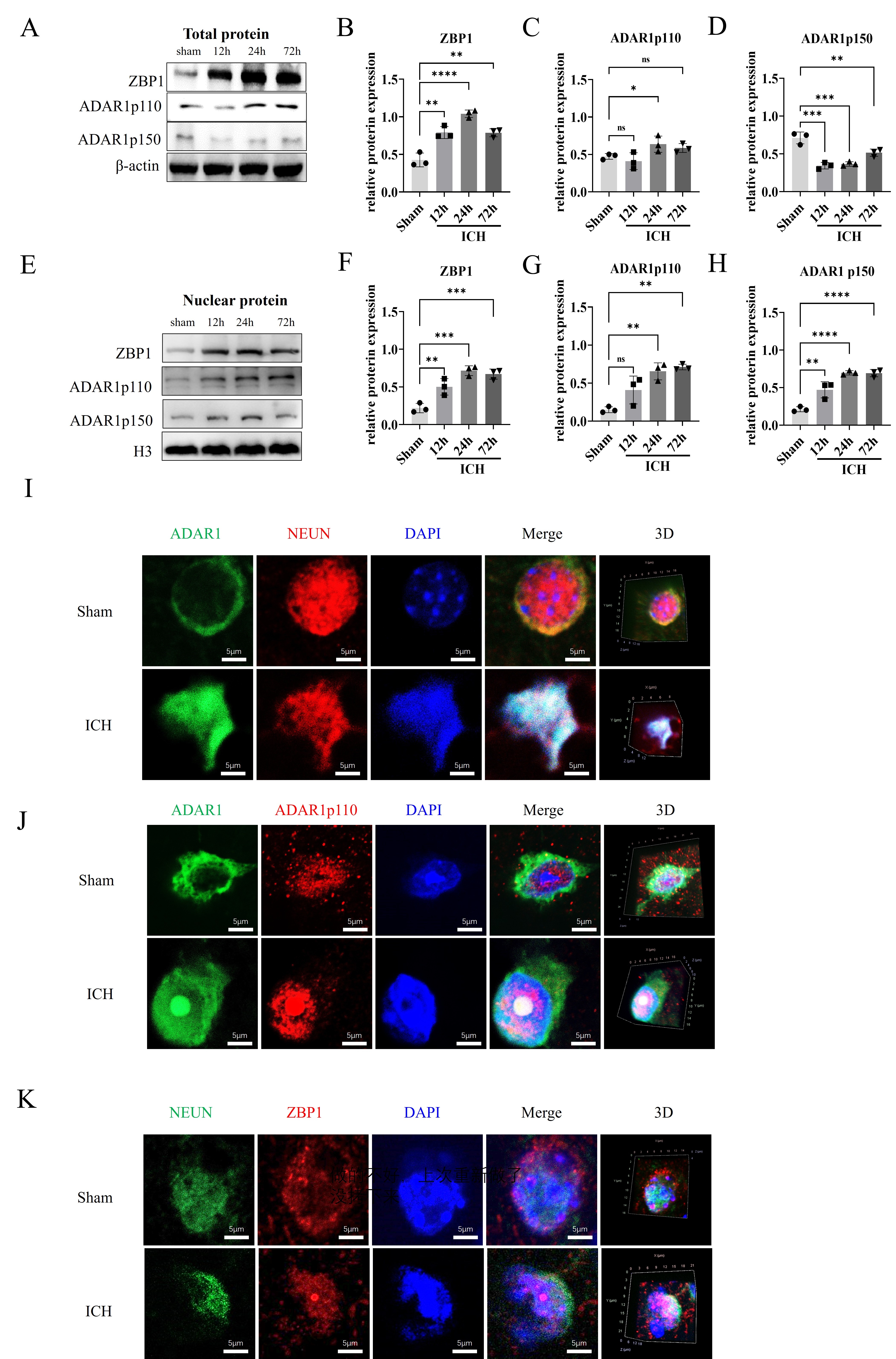
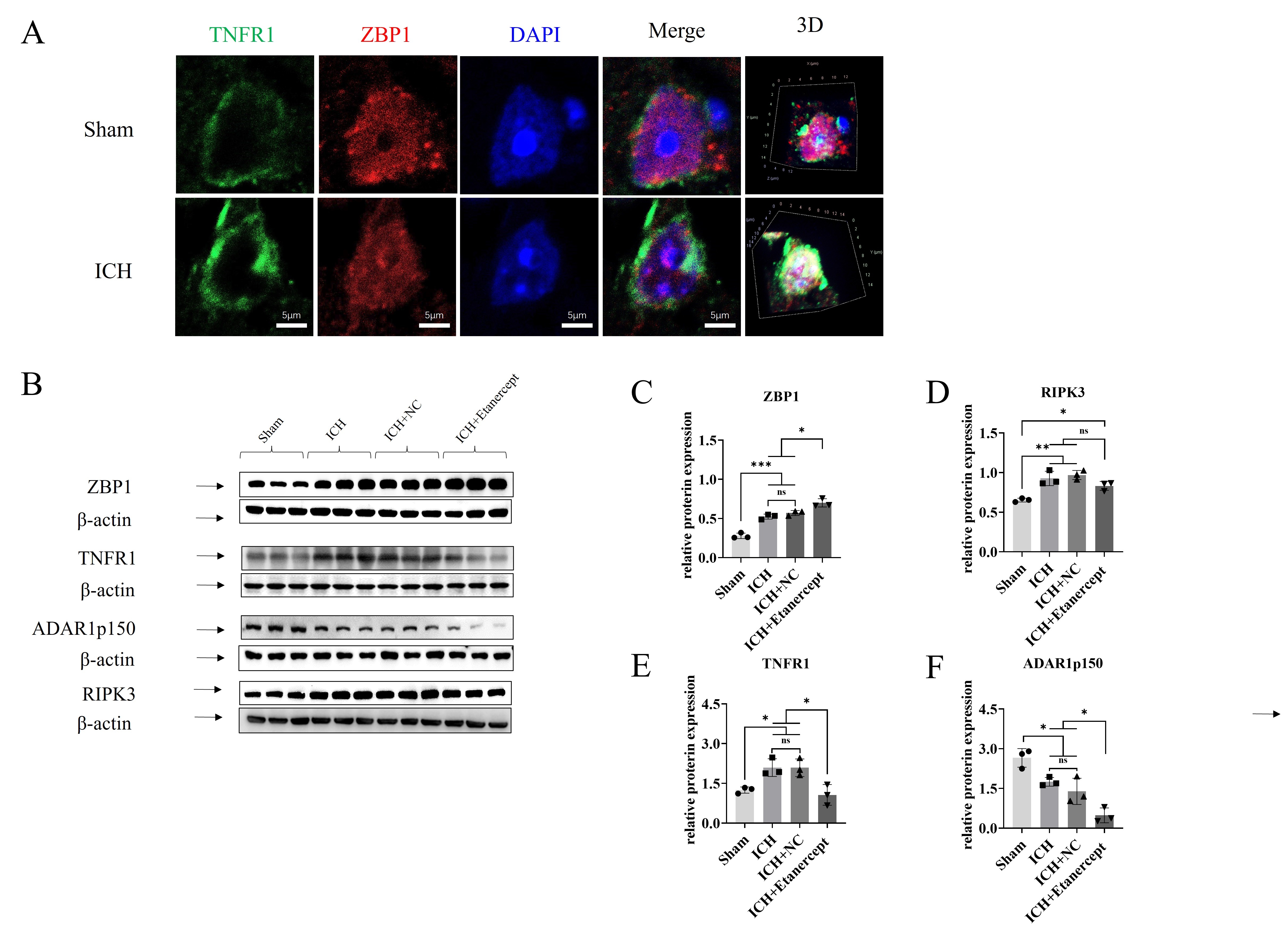
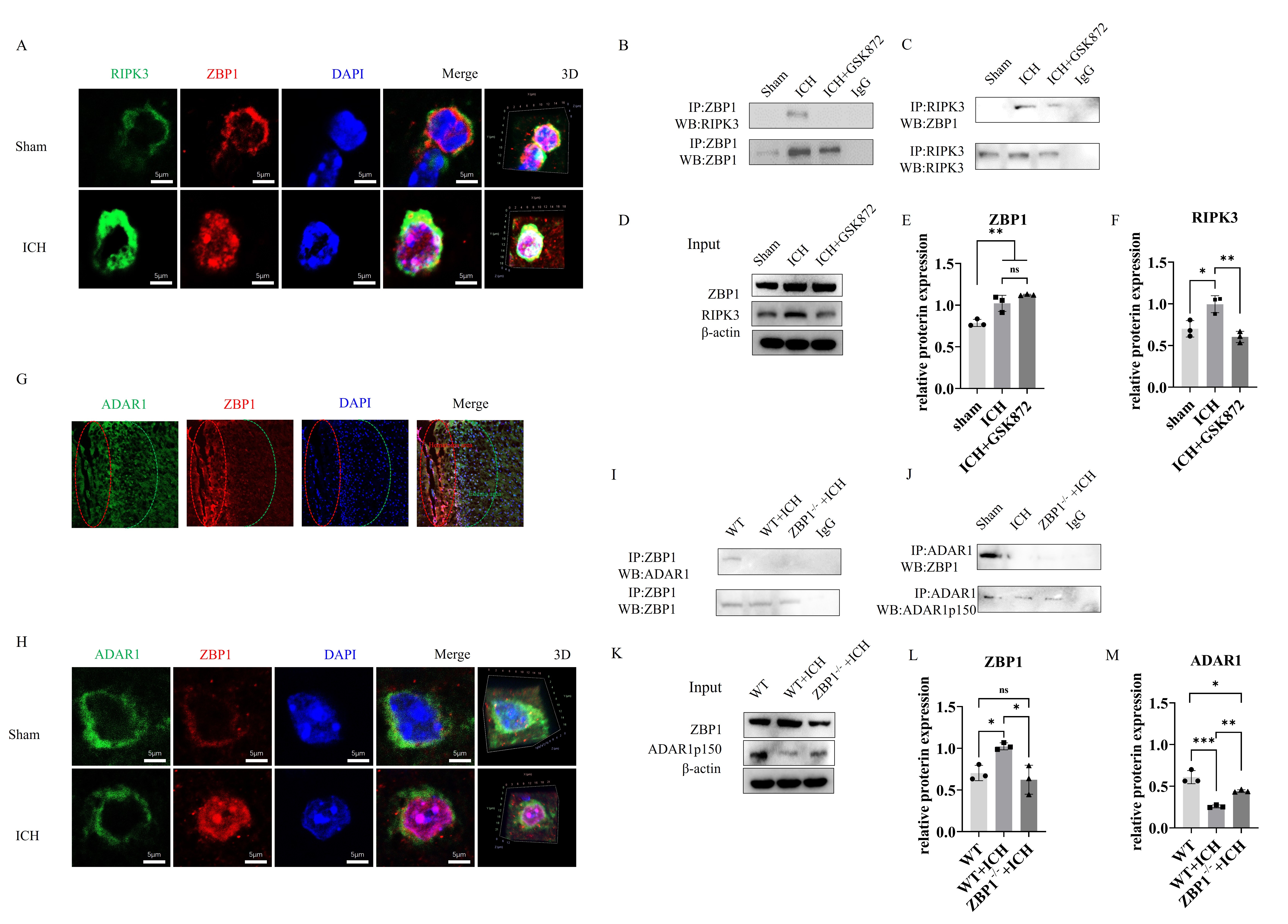
Results: ZBP1 increase with mice ICH injury duration. The ADAR1 p110 isoform shows an increasing trend, while p150 depletes over time. Both ADAR1 isoforms display increasing trends like ZBP1. Immunofluorescence indicates that ADAR1, typically cytoplasmic in the sham group, accumulates in neuron nuclei after ICH, and ADAR1 p110 is more abundant in nuclei after ICH injury, suggesting p150 cleavage into p110. Using the TNFR1 inhibitor shows that while TNFR1 inhibition reduces p150 levels, it does not affect RIPK3 expression. This suggests that RIPK3 activation occurs through ZBP1 in the absence of TNFR1 signaling. Both RIPK3 and ZBP1 translocate into the nucleus and colocalize after ICH injury. GSK872 disrupts the co-immunoprecipitation relationship between ZBP1 and RIPK3. Immunoprecipitation from ZBP1 knockout mice confirms the interaction between ZBP1 and ADAR1p150, which is weakened after ICH, particularly in the absence of ZBP1.
Conclusion: ADAR1p150 plays an important role in inhibiting necroptosis after ICH by suppressing the ZBP1/RIPK3 signaling pathway. Activation of ADAR1p150 may be a potential therapeutic strategy for the management of ICH.
Methods: ICH was induced in vivo by collagenase VII injection. ADAR1 knock-down mice were constructed by Lentivirus (LVs) infection to explore the role of ADAR1 and its mechanism after ICH. By constructing ZBP1flox/flox / Thy1-Cre+/- mice to investigate the potential mechanism underlying ZBP1 and effect of ZBP1 inhibition on cognition after intracerebral hemorrhage in mice.
Results: ZBP1 increase with mice ICH injury duration. The ADAR1 p110 isoform shows an increasing trend, while p150 depletes over time. Both ADAR1 isoforms display increasing trends like ZBP1. Immunofluorescence indicates that ADAR1, typically cytoplasmic in the sham group, accumulates in neuron nuclei after ICH, and ADAR1 p110 is more abundant in nuclei after ICH injury, suggesting p150 cleavage into p110. Using the TNFR1 inhibitor shows that while TNFR1 inhibition reduces p150 levels, it does not affect RIPK3 expression. This suggests that RIPK3 activation occurs through ZBP1 in the absence of TNFR1 signaling. Both RIPK3 and ZBP1 translocate into the nucleus and colocalize after ICH injury. GSK872 disrupts the co-immunoprecipitation relationship between ZBP1 and RIPK3. Immunoprecipitation from ZBP1 knockout mice confirms the interaction between ZBP1 and ADAR1p150, which is weakened after ICH, particularly in the absence of ZBP1.
Conclusion: ADAR1p150 plays an important role in inhibiting necroptosis after ICH by suppressing the ZBP1/RIPK3 signaling pathway. Activation of ADAR1p150 may be a potential therapeutic strategy for the management of ICH.
More abstracts on this topic:
Use of Photoacoustic Imaging to Discriminate Between Radiofrequency Ablation Lesions and Healthy Myocardium in a Large Animal Model
Fallon Blake, Vishwanath Krithik, Martino Antonio, Willson Richard, Valderrabano Miguel, Mathuria Nilesh, Bouchard Richard, Filgueira Carly
Beyond Repair: Resurrecting Neurons through Stem Cell TherapyHamdan Tesnim, Witt Iryna, Ascandar Nameer, Basaran Ali, Brewer Yukiko A., Chyshkevych Iryna
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.
Rate this abstract
(Maximum characters: 500)