Final ID: WP250
Post-thrombectomy subarachnoid hemorrhage: incidence, predictors, clinical relevance, and effect modulators
Abstract Body: Background: Subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) following endovascular thrombectomy (EVT) is a poorly understood phenomenon, and whether it is associated with clinical detriment is unclear.
Methods: This was an explorative analysis of a national database of real-world hospitalizations in the United States. Patients who underwent EVT were included. Patients were divided into SAH and non-SAH groups, and hospitalization outcomes were compared using multivariable logistic regression models. Regression models were also used to identify significant predictors for post-EVT SAH, and significant modulators of SAH’s association with hospitalization outcomes were also assessed.
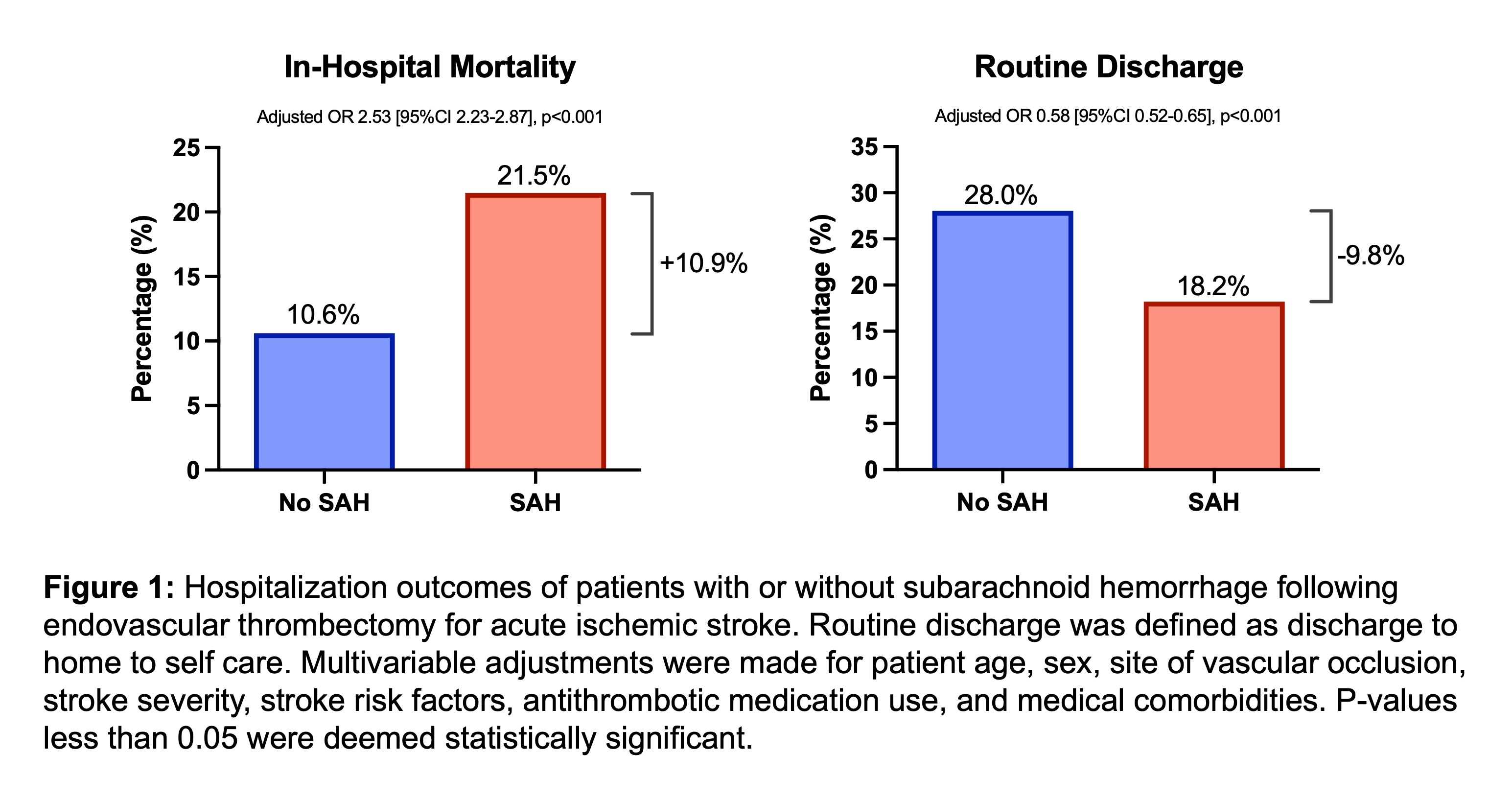
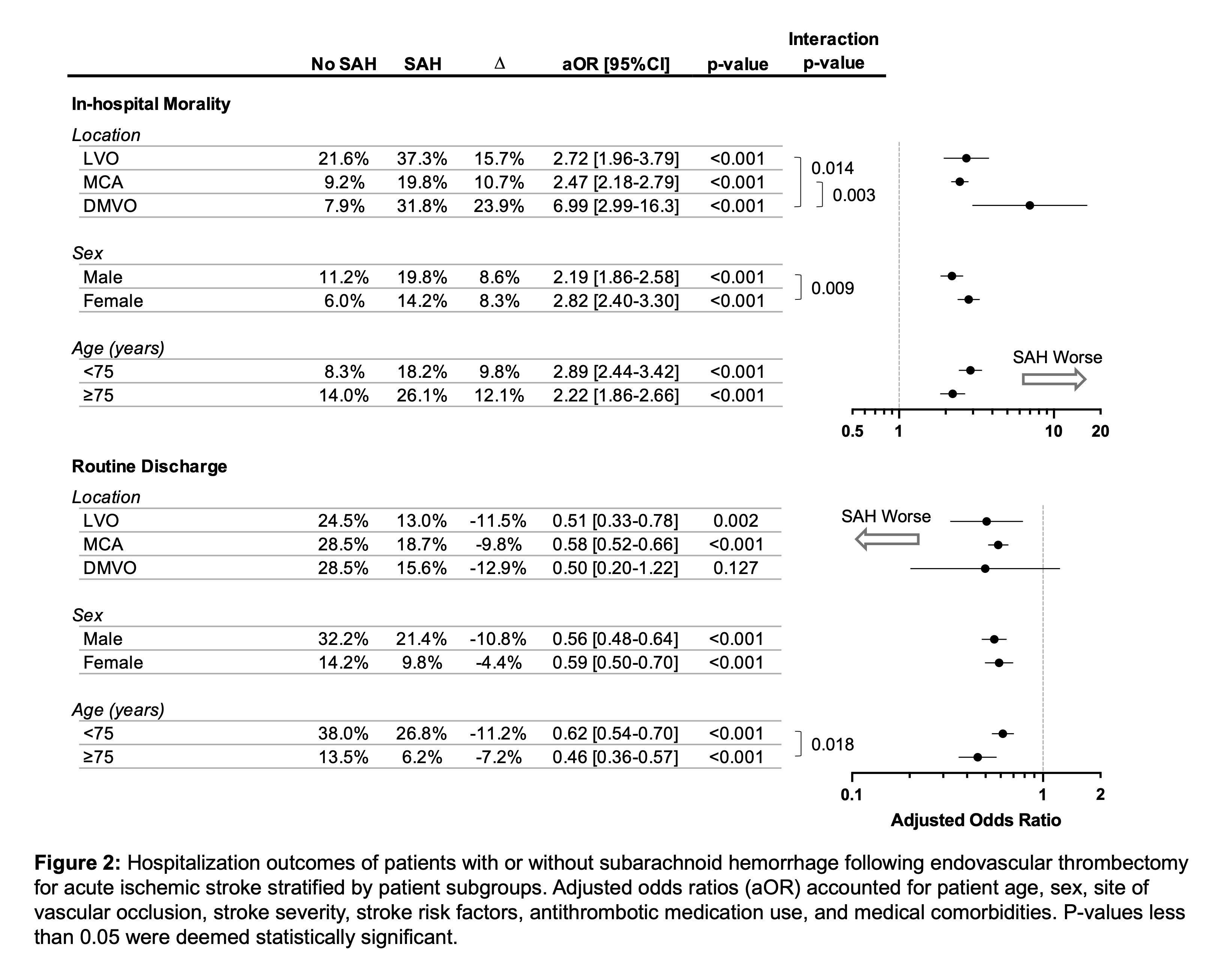
Results: 99,219 EVT patients were identified; 6,174 (6.2%) had SAH. Overall, SAH was independently associated with increased odds of in-hospital mortality (21.5% vs. 10.6%, adjusted OR 2.53 [95%CI 2.23-2.87], p<0.001; Figure 1) and lower odds of routine discharge to home with self-care (18.2% vs. 28.0%, aOR 0.58 [95%CI 0.52-0.65], p<0.001; Figure 1). Distal/medium vessel occlusion (DMVO), coagulopathy, angioplasty or stenting, concurrent intraparenchymal hemorrhage (IPH), and female sex were associated with higher odds of SAH. DMVO was associated particularly heightened risk of death (31.8% vs. 7.9%, aOR 6.99 [95%CI 2.99 to 16.3], p<0.001; Figure 2), which was an effect size significantly larger than other sites of vascular occlusion (interaction p>0.05; Figure 2)
Conclusion: SAH is an uncommon but likely clinically detrimental post-EVT complication. DMVO, coagulopathy, angioplasty or stenting, concurrent IPH, and female sex were independently associated with higher odds of post-EVT SAH. SAH associated with DMVO-EVT may be particularly harmful.
Methods: This was an explorative analysis of a national database of real-world hospitalizations in the United States. Patients who underwent EVT were included. Patients were divided into SAH and non-SAH groups, and hospitalization outcomes were compared using multivariable logistic regression models. Regression models were also used to identify significant predictors for post-EVT SAH, and significant modulators of SAH’s association with hospitalization outcomes were also assessed.
Results: 99,219 EVT patients were identified; 6,174 (6.2%) had SAH. Overall, SAH was independently associated with increased odds of in-hospital mortality (21.5% vs. 10.6%, adjusted OR 2.53 [95%CI 2.23-2.87], p<0.001; Figure 1) and lower odds of routine discharge to home with self-care (18.2% vs. 28.0%, aOR 0.58 [95%CI 0.52-0.65], p<0.001; Figure 1). Distal/medium vessel occlusion (DMVO), coagulopathy, angioplasty or stenting, concurrent intraparenchymal hemorrhage (IPH), and female sex were associated with higher odds of SAH. DMVO was associated particularly heightened risk of death (31.8% vs. 7.9%, aOR 6.99 [95%CI 2.99 to 16.3], p<0.001; Figure 2), which was an effect size significantly larger than other sites of vascular occlusion (interaction p>0.05; Figure 2)
Conclusion: SAH is an uncommon but likely clinically detrimental post-EVT complication. DMVO, coagulopathy, angioplasty or stenting, concurrent IPH, and female sex were independently associated with higher odds of post-EVT SAH. SAH associated with DMVO-EVT may be particularly harmful.
More abstracts on this topic:
Clonal hematopoiesis of indeterminate potential promotes the development of intracranial aneurysm rupture
Uchikawa Hiroki, Maeda Takuma, Cisneros Oscar, Nisson Peyton, Fraser Claire, Bowen Sara, Ai Jinglu, Lawton Michael, Hashimoto Tomoki
A Retrospective Analysis of the Association of Rehab Time on Discharge Disposition and Length of Stay in Hospitalized Patients with Ischemic Stroke or Intracerebral HemorrhageEperjesi Sarah, Yutrzenka Kayla, Marginean Horia, Crawford Erin, Lesko Alexandra, Clark Diane
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.
Rate this abstract
(Maximum characters: 500)