Final ID: WP116
Lesion Volume and Location Correlate with Picture Description using the New NIH Stroke Scale Stimuli
Abstract Body: Introduction: In January 2024, the picture stimuli used to elicit language on the NIH Stroke Scale were updated. Descriptions elicited using the now-retired Cookie Theft picture are informative regarding the size and location of stroke. An important dimension of validation for the new stimuli is to demonstrate that the language patients produce when describing the new Precarious Painter picture that is now part of the NIH Stroke Scale is similarly informative.
Methods: Participants included 62 patients with acute ischemic stroke (24 left and 38 right) compared with 10 control participants with transient ischemic attack. Descriptions of the Precarious Painter image were analyzed for content and structure. Bilateral regions of interest were selected based on their role in language processing, and lesion volume and location were measured on diffusion-weighted imaging. Analyses of variance were used to contrast discourse performance across groups, and correlations between discourse characteristics and proportion of region lesioned were calculated.
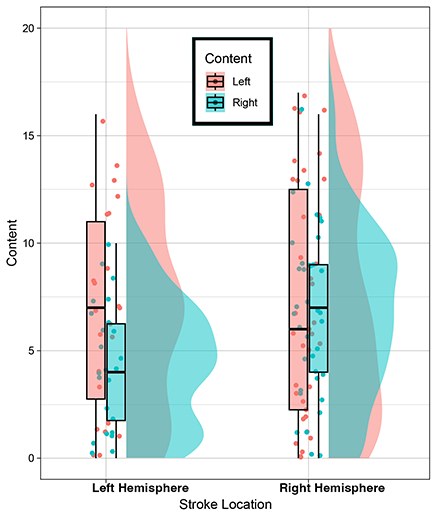
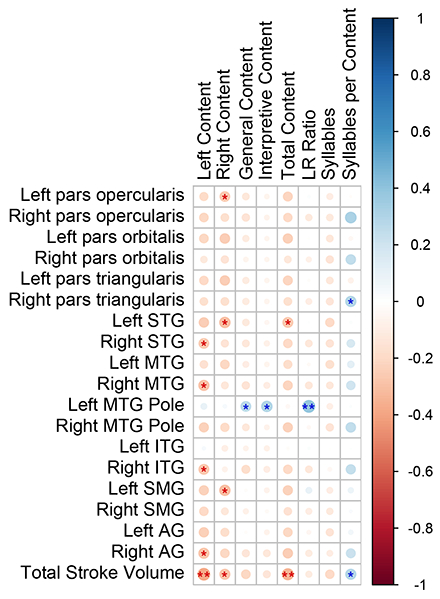
Results: Patients with left hemisphere strokes included less content from the right side of the picture, F(2) = 4.5, p = 0.02, η2P= 0.12, than those in the other groups. Patients with right hemisphere stroke produced similar samples to controls across all dimensions examined, though there was evidence of a trend in including less content from the left side of the image, similarly consistent with contralesional spatial neglect (Figure 1). Correlations between discourse variables and lesion locations were grossly consistent with those previously reported (Figure 2) and provided evidence of a relationship between lesions to the left middle temporal pole and a greater use of holistic description.
Conclusion: Features of picture description that may be appraised without specialized training in communication, such as how many things a patient includes, their location, and the inclusion of inferences or summarizing statements in the description, provide insight into stroke location and severity. The samples elicited using the new Precarious Painter stimulus perform similarly to those elicited using the retired Cookie Theft stimulus.
Methods: Participants included 62 patients with acute ischemic stroke (24 left and 38 right) compared with 10 control participants with transient ischemic attack. Descriptions of the Precarious Painter image were analyzed for content and structure. Bilateral regions of interest were selected based on their role in language processing, and lesion volume and location were measured on diffusion-weighted imaging. Analyses of variance were used to contrast discourse performance across groups, and correlations between discourse characteristics and proportion of region lesioned were calculated.
Results: Patients with left hemisphere strokes included less content from the right side of the picture, F(2) = 4.5, p = 0.02, η2P= 0.12, than those in the other groups. Patients with right hemisphere stroke produced similar samples to controls across all dimensions examined, though there was evidence of a trend in including less content from the left side of the image, similarly consistent with contralesional spatial neglect (Figure 1). Correlations between discourse variables and lesion locations were grossly consistent with those previously reported (Figure 2) and provided evidence of a relationship between lesions to the left middle temporal pole and a greater use of holistic description.
Conclusion: Features of picture description that may be appraised without specialized training in communication, such as how many things a patient includes, their location, and the inclusion of inferences or summarizing statements in the description, provide insight into stroke location and severity. The samples elicited using the new Precarious Painter stimulus perform similarly to those elicited using the retired Cookie Theft stimulus.
More abstracts on this topic:
Advanced Diffusion and Functional MRI Measures Are Associated with Microstructural Morphology and Cognitive Function in Subacute Ischemic Cerebellar Stroke
Urday Sebastian, Clements Rebecca, Kurani Ajay, Montero Miguel, Grafman Jordan H., Harvey Richard, Ingo Carson
Large Core Trials – Game Changing for Stroke Care or falling on deaf ears?Nguyen Dan, Ezzeldin Mohamad, Ezzeldin Rime, Mealer Leighann, Mir Osman
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.
Rate this abstract
(Maximum characters: 500)