Final ID: WP173
The Influence of Social Isolation on SSQOL in a Community-Based Study
Abstract Body: Introduction:
Quality of Life (QOL) is a critical patient-centered indicator for evaluating recovery in individuals who have experienced life-altering illnesses such as stroke. Social isolation and family structure may affect a stroke survivor’s QOL and could be influenced by depression, potentially intensifying its impact on an individual’s recovery from stroke. We studied how social isolation impacts Stroke-Specific QOL (SSQOL) in a community-based study.
Hypothesis: Stroke survivors who are more socially isolated will have worse SSQOL.
Methods:
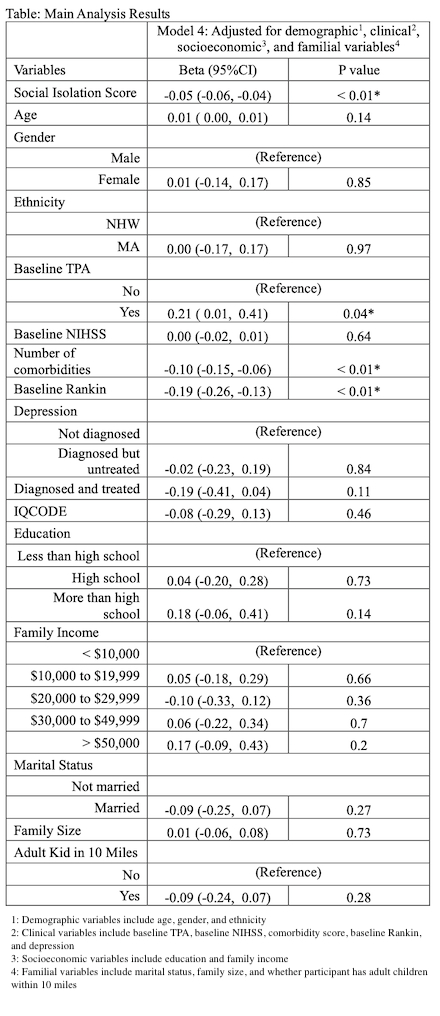
Participants in the Brain Attack Surveillance in Corpus Christi (BASIC) project in Nueces County, Texas, were interviewed 90 days after stroke between October 2019 and June 2023 to determine QOL using the SSQOL scale (higher scores better), social isolation using the Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System (PROMIS) scale (higher scores more isolation), family structure using marital status, family size, and whether an adult child lived within 10 miles and covariates. Patients with ICH or ischemic stroke who survived 90 days were the target population. We analyzed the relationship between social isolation scores and SSQOL by applying four weighted linear regression models. Model 1 included social isolation score and demographic variables. Model 2 added clinical variables to Model 1 and Model 3 further included socioeconomic variables with Model 2. The fully adjusted Model 4 added familial variables to Model 3.
Results:
A final study population of 706 stroke survivors completed the 90 day follow-up interview and were included after removing extreme values (beyond the 1st and 99th percentiles). Mean age of the participants was 65 and 47% identified as women. Mexican Americans comprised 64% of the sample. Social isolation was negatively associated with SSQOL in all models with little change in the strength of association after adjustment for demographics, clinical variables, socioeconomic and family structure. The Table shows the fully adjusted Model 4; social isolation was negatively associated with SSQOL (Beta -0.05 (95% CI -0.06, -.04); p<0.01).
Conclusions:
Social isolation is associated with lower SSQOL among stroke survivors. Recovering from a stroke is a long and challenging process. This study highlights the significance of psychosocial factors, like social isolation, as key elements in that recovery.
Quality of Life (QOL) is a critical patient-centered indicator for evaluating recovery in individuals who have experienced life-altering illnesses such as stroke. Social isolation and family structure may affect a stroke survivor’s QOL and could be influenced by depression, potentially intensifying its impact on an individual’s recovery from stroke. We studied how social isolation impacts Stroke-Specific QOL (SSQOL) in a community-based study.
Hypothesis: Stroke survivors who are more socially isolated will have worse SSQOL.
Methods:
Participants in the Brain Attack Surveillance in Corpus Christi (BASIC) project in Nueces County, Texas, were interviewed 90 days after stroke between October 2019 and June 2023 to determine QOL using the SSQOL scale (higher scores better), social isolation using the Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System (PROMIS) scale (higher scores more isolation), family structure using marital status, family size, and whether an adult child lived within 10 miles and covariates. Patients with ICH or ischemic stroke who survived 90 days were the target population. We analyzed the relationship between social isolation scores and SSQOL by applying four weighted linear regression models. Model 1 included social isolation score and demographic variables. Model 2 added clinical variables to Model 1 and Model 3 further included socioeconomic variables with Model 2. The fully adjusted Model 4 added familial variables to Model 3.
Results:
A final study population of 706 stroke survivors completed the 90 day follow-up interview and were included after removing extreme values (beyond the 1st and 99th percentiles). Mean age of the participants was 65 and 47% identified as women. Mexican Americans comprised 64% of the sample. Social isolation was negatively associated with SSQOL in all models with little change in the strength of association after adjustment for demographics, clinical variables, socioeconomic and family structure. The Table shows the fully adjusted Model 4; social isolation was negatively associated with SSQOL (Beta -0.05 (95% CI -0.06, -.04); p<0.01).
Conclusions:
Social isolation is associated with lower SSQOL among stroke survivors. Recovering from a stroke is a long and challenging process. This study highlights the significance of psychosocial factors, like social isolation, as key elements in that recovery.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Novel Approach of Monitoring Stroke Recovery: Contactless Sensor for Gait Speed and Fugl-Meyer Action Duration Estimation
Gu Zhuangzhuang, Titus Ryan, Regmi Hem, Tavasoli Reza, Sur Sanjib, Sen Souvik
Bleeding Risks for Acute Ischemic Stroke Patients on Serotonergic Antidepressants and Anticoagulation/Dual Anti-Platelet TherapySimmonds Kent, Chavez Audrie, Ifejika Nneka
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.
Rate this abstract
(Maximum characters: 500)