Final ID: TP126
The association of patient outcomes with caregiver mental health and strain in a community-based study.
Objective: To determine if worse 90-day patient stroke outcomes result in greater caregiver strain and worse caregiver mental health in a multiethnic sample.
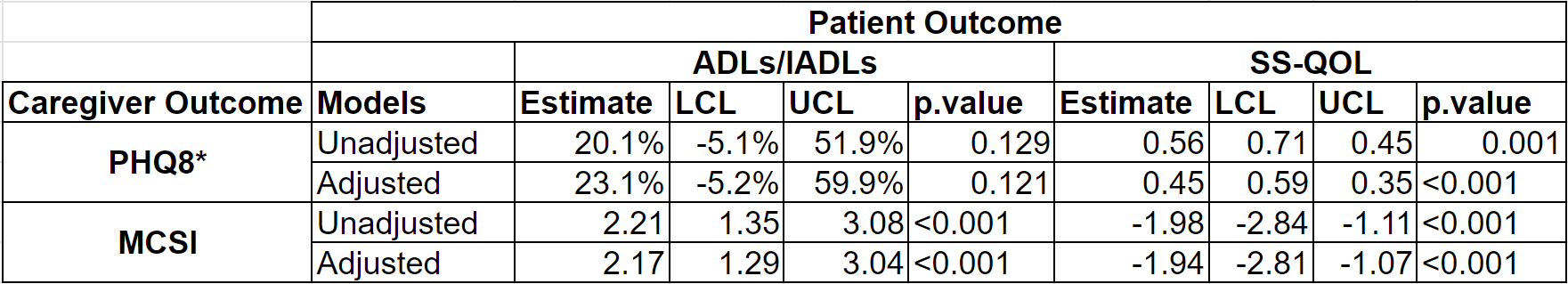
Methods: Using data from the Brain Attack Surveillance in Corpus Christi project, we prospectively determined 90-day ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke outcome from 2019-2023. Patient function based on ADLs/IADLs (higher scores worse) along with patient quality of life based on SS-QOL (higher scores better) were used to measure patient outcome. Stroke caregivers' depression was measured using the PHQ-8 (higher scores worse) and strain was measured by mCSI (higher scores worse). Generalized propensity scores (GPS) were calculated for the main exposures using caregiver and patient demographics, dyad characteristics, and clinical variables as predictors. Caregiver outcomes were modeled with linear regression, with caregiver depression and strain as main outcomes, unadjusted and adjusted for GPS.
Results: During this time period, 339 strokes were identified and their caregivers subsequently interviewed. The median age of interviewed caregivers was 55, with 46% being the sole informal caregiver. A majority of the caregivers interviewed were either the spouse of the stroke patient (42.2%) or the child of the stroke patient (38.1%). In adjusted analyses, functional status for stroke patients was not associated with caregiver depression (p=0.12), higher stroke patient quality of life was strongly associated with lower odds of any depression symptoms among caregivers (p<0.001), and worse patient functional status (continuous ADL/IADL) and lower patient quality of life were strongly associated with higher caregiver strain (p<0.001, p<0.001, respectively).
Conclusion: Worse stroke patient outcome has a negative association with caregiver mental health and caregiver strain. Interventions targeting caregivers of stroke patients are necessary to improve and protect caregiver mental health and strain.
More abstracts on this topic:
Jadhav Reshma, Shekar Arush, Westenhaver Zack, Skandhan Amith
Aortic Valve Calcium as a Predictor of Chronic Kidney Disease in a Multi-Ethnic Cohort: The MESA StudyAbdollahi Ashkan, Rotter Jerome, Post Wendy, Blumenthal Roger, Bluemke David, Lima Joao Ac, Whelton Seamus, Sani Maryam, Shabani Mahsima, Scarpa Bruna, Blaha Michael, Wu Colin, Ambale-venkatesh Bharath, Budoff Matthew, Strom Jordan
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.