Final ID: WP293
The Effect of Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors on Stroke Risk in Migraine
Abstract Body: Introduction: Migraine sufferers are at an increased risk of ischemic stroke which is one of the leading causes of disability worldwide. The impact of Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRI) on stroke risk remains inconclusive, and there has been no investigation yet into their effect on stroke risk among migraineurs.
Methods: Data was provided by Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Cohort (ARIC)’s ongoing, prospective, longitudinal community-based cohort study, where participants were given an interview ascertaining migraine history in 1993–1995, and were followed for all vascular events, including stroke. The medication list of migraine-experiencing participants was evaluated and if they were found to be taking an SSRI, were included in our exposure group while the remainder of the participants were included in the control group. We used survival analysis to evaluate the incidence of ischemic stroke in migraine-experiencing participants on SSRIs when compared to those who are not on SSRIs. Cox proportional hazards models were used to analyze the association among migraine sufferers on SSRIs, migraine sufferers not on SSRIs, and incidence of ischemic stroke.
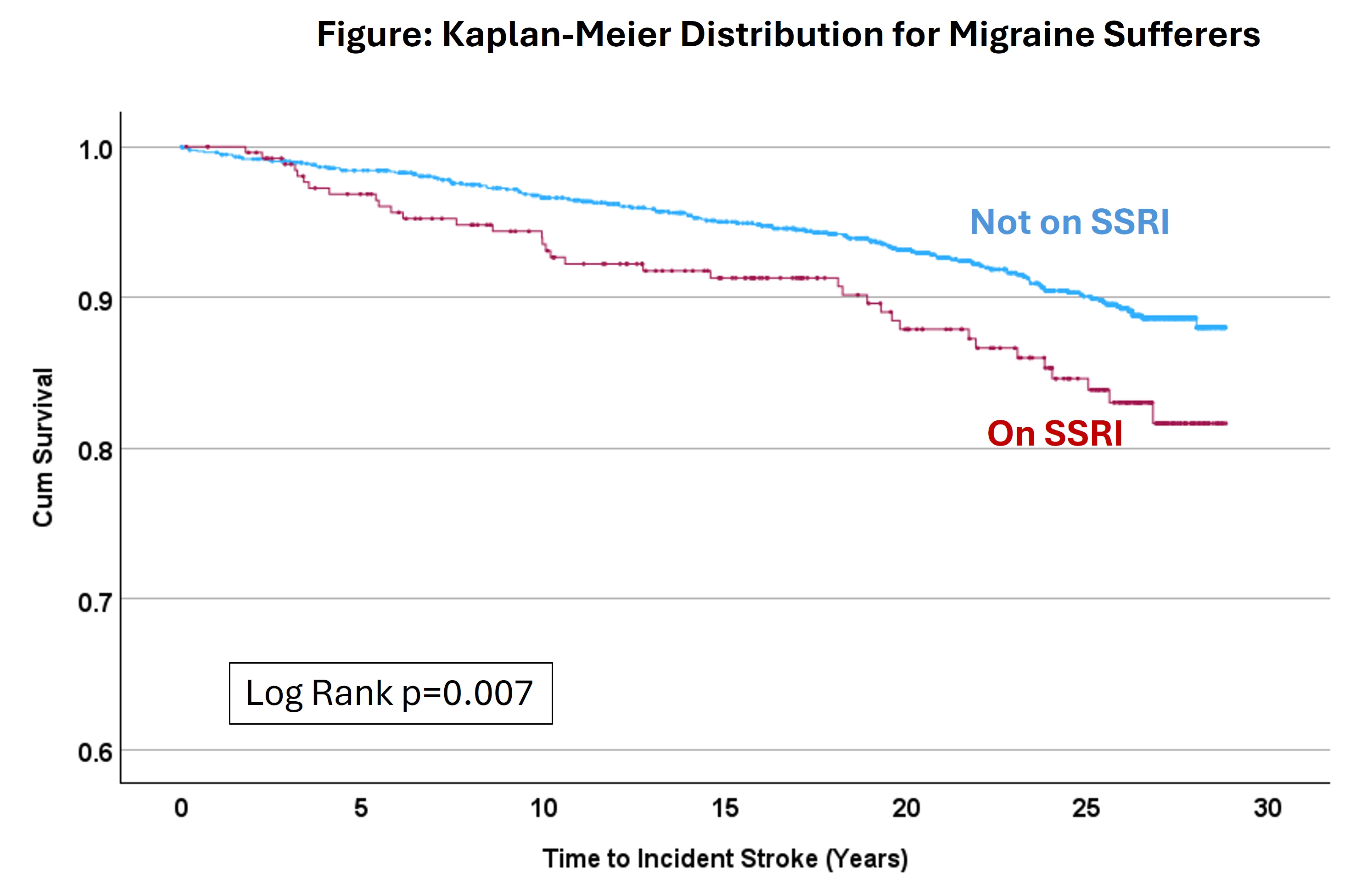
Results: Among the 1614 migraine-experiencing participants without prior history of stroke, 264 (16%) were on SSRIs while 1350 (84%) were not on SSRIs. Of the 264 on SSRIs, 35 (13%) of them had an incident stroke while 121 (9%) of the 1350 participants not on SSRIs, had an ischemic stroke. The mean age of the study participants was 58 years at the time of the start of the prospective follow up (visit 3) when migraine was assessed; 85% were white and 77% were women. It was found that migraine sufferers on SSRIs were more likely to have an incident stroke than those not on SSRIs (log rank p<0.001), as depicted in the Kaplan-Meier curve. Proportional hazards assumption was met. Cox regression produced a crude hazards ratio (HR) of 1.67 with a 95% confidence interval (CI) of 1.14-2.43. The HR remained significant after adjustment for age, gender and race, adjusted HR 1.72 with a 95% CI of 1.17-2.51. The HR was nonsignificant after adjustment for age, gender, race, hypertension, diabetes, hypercholesterolemia and smoking status, adjusted HR 1.33 with a 95% CI of 0.89-1.99.
Conclusion: We report a possible association between migraine sufferers on SSRIs and risk for incident stroke. This might be explained by the presence of vascular risk factors and helps understand this association.
Methods: Data was provided by Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Cohort (ARIC)’s ongoing, prospective, longitudinal community-based cohort study, where participants were given an interview ascertaining migraine history in 1993–1995, and were followed for all vascular events, including stroke. The medication list of migraine-experiencing participants was evaluated and if they were found to be taking an SSRI, were included in our exposure group while the remainder of the participants were included in the control group. We used survival analysis to evaluate the incidence of ischemic stroke in migraine-experiencing participants on SSRIs when compared to those who are not on SSRIs. Cox proportional hazards models were used to analyze the association among migraine sufferers on SSRIs, migraine sufferers not on SSRIs, and incidence of ischemic stroke.
Results: Among the 1614 migraine-experiencing participants without prior history of stroke, 264 (16%) were on SSRIs while 1350 (84%) were not on SSRIs. Of the 264 on SSRIs, 35 (13%) of them had an incident stroke while 121 (9%) of the 1350 participants not on SSRIs, had an ischemic stroke. The mean age of the study participants was 58 years at the time of the start of the prospective follow up (visit 3) when migraine was assessed; 85% were white and 77% were women. It was found that migraine sufferers on SSRIs were more likely to have an incident stroke than those not on SSRIs (log rank p<0.001), as depicted in the Kaplan-Meier curve. Proportional hazards assumption was met. Cox regression produced a crude hazards ratio (HR) of 1.67 with a 95% confidence interval (CI) of 1.14-2.43. The HR remained significant after adjustment for age, gender and race, adjusted HR 1.72 with a 95% CI of 1.17-2.51. The HR was nonsignificant after adjustment for age, gender, race, hypertension, diabetes, hypercholesterolemia and smoking status, adjusted HR 1.33 with a 95% CI of 0.89-1.99.
Conclusion: We report a possible association between migraine sufferers on SSRIs and risk for incident stroke. This might be explained by the presence of vascular risk factors and helps understand this association.
More abstracts on this topic:
1-year comparison of quadruple therapy sequencing strategies for heart failure with reduced ejection fraction using an individual-based state-transition microsimulation model
Turgeon Ricky, Van Minh Tri, Loewen Peter, Hawkins Nathaniel, Sadatsafavi Mohsen, Zhang Wei, Mackay Kelly
A mechanism whereby SGLT2 inhibitor dapagliflozin reverses cardiac diastolic dysfunction in a model of HFpEFLiu Man, Liu Hong, Kang Gyeoung-jin, Kim Eunji, Neumann Mitchell, Johnson Madeline, Murikinati Ruthvika, Dudley Samuel
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.
Rate this abstract
(Maximum characters: 500)