Final ID: TP146
Disparities in risk factors between Black and White adults aged 18-64 years hospitalized for acute ischemic stroke, United States 2016-2020
Methods: The study population consisted of AIS hospitalizations among adults aged 18-64 years from the 2016-2020 Nationwide Inpatient Sample of the Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP, sample size: 691,645). AIS hospitalizations were identified based on a primary diagnosis of ICD 10 CM code I63, and risk factors (RFs) (hypertension, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, and tobacco use) were identified using secondary diagnoses codes. Prevalence ratios (PR) were calculated by dividing the prevalence among non-Hispanic Black adults (NHBA) by the prevalence among non-Hispanic White adults (NHWA).
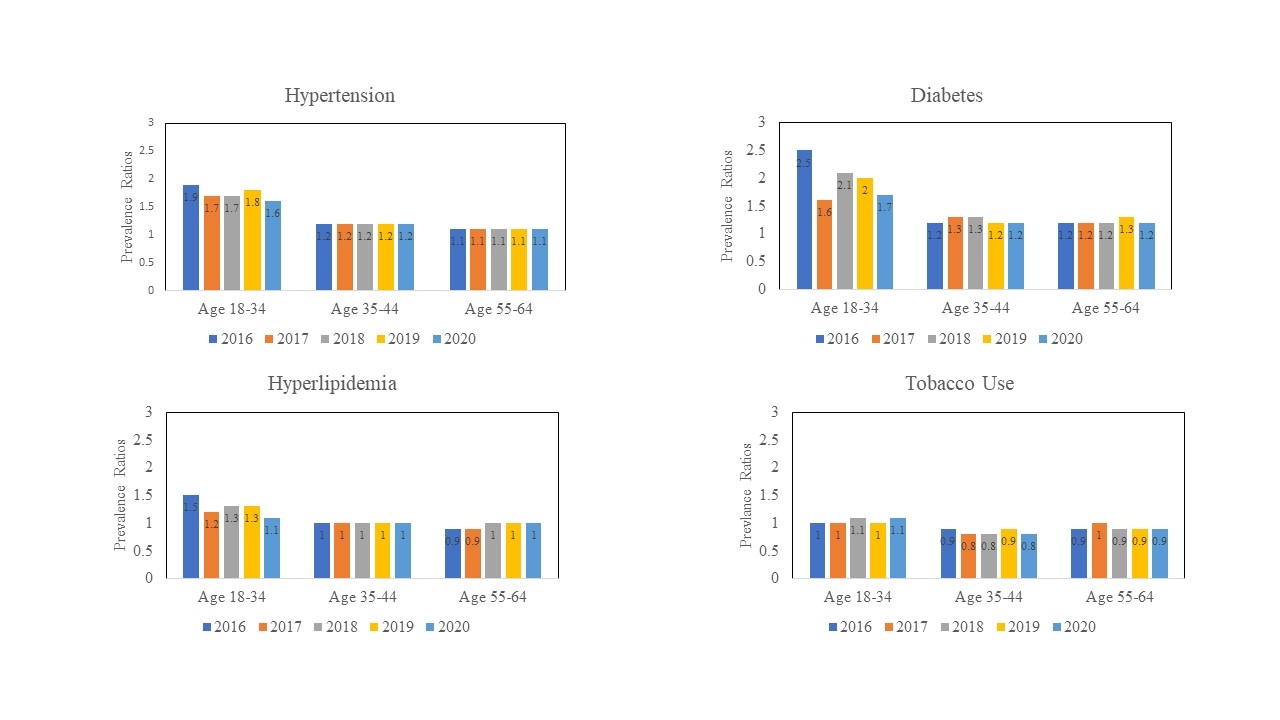
Results: The prevalence of hypertension and diabetes were higher among NHBA than NHWA hospitalized with AIS across all age groups. In 2020, the prevalence of hypertension was higher among NHBA compared to NHWA aged 18-34 years (55.3% vs. 33.8%, PR: 1.6), 35-54 years (86.7% vs. 74.4%, PR: 1.2), and 55-64 years (92.5% vs. 82.6%, PR: 1.1). Similarly, the prevalence of diabetes was higher among NHBA compared to NHWA aged 18-34 years (25.6% vs. 15.2%, PR: 1.7), 35-54 years (47.5% vs. 39.2%, PR: 1.2), and 55-64 years (53.8% vs. 44.2%, PR: 1.2). During 2016-2020, the age group specific PRs comparing the annual prevalence of hypertension and diabetes were similar across the years, and in each year, PRs among those aged 18-34 years were consistently higher compared to those aged 35-54 and 55-64 years. For hyperlipidemia, PRs comparing NHBA and NHWA were not significant except among those aged 18-34 years in 2016 (26.8% vs. 18.1%, PR: 1.5). Tobacco use was lower among NHBA compared to NHWA only among those aged 35-54 years (2020: 39.3% vs. 45.9%, PR: 0.8) and this PR was similar across years.
Conclusions: Persistent disparities in the prevalence of hypertension and diabetes between NHWA and NHBA existed during 2016 and 2020, and disparities were more pronounced among adults aged 18-34 years. The findings highlight the importance of addressing stroke risk factors among NHBA.
More abstracts on this topic:
Kothari Ruchita, Caplan Justin, Gonzalez L. Fernando, Jackson Christopher, Bettegowda Chetan, Huang Judy, Koehler Raymond, Tamargo Rafael, Xu Risheng, Dong Xinzhong, Abdulrahim Mostafa, Oh Hyun Jong, Capuzzi Daniel, Nair Sumil, Zhang Yaowu, Limjunyawong Nathachit, Saini Sarbjit, Kim Jennifer
A Novel Machine Learning-based Adverse Cardiovascular Events Risk Algorithm For Cancer Patients Treated With Tyrosine Kinase InhibitorsWahi Shawn, Cross James, Mora Ruben, Im Yunju, Kwan Jennifer
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.