Final ID: TP7
Comparison of inflammatory clot markers in higher and lower shear stress environments: is there really that big of a difference?
Abstract Body: Introduction
Venous thromboembolism (VTE) manifesting as deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolus (PE) and arterial thromboembolism (ATE) manifesting as acute ischemic stroke (AIS) result in ~1 million US deaths annually. Increased levels of circulating inflammatory markers, particularly von Willebrand factor (VWF), may indicate poor outcomes in ATE, but previous studies limit this response to high shear stress milieu. We compared VTE and AIS thrombi inflammatory markers at time of intervention.
Methods
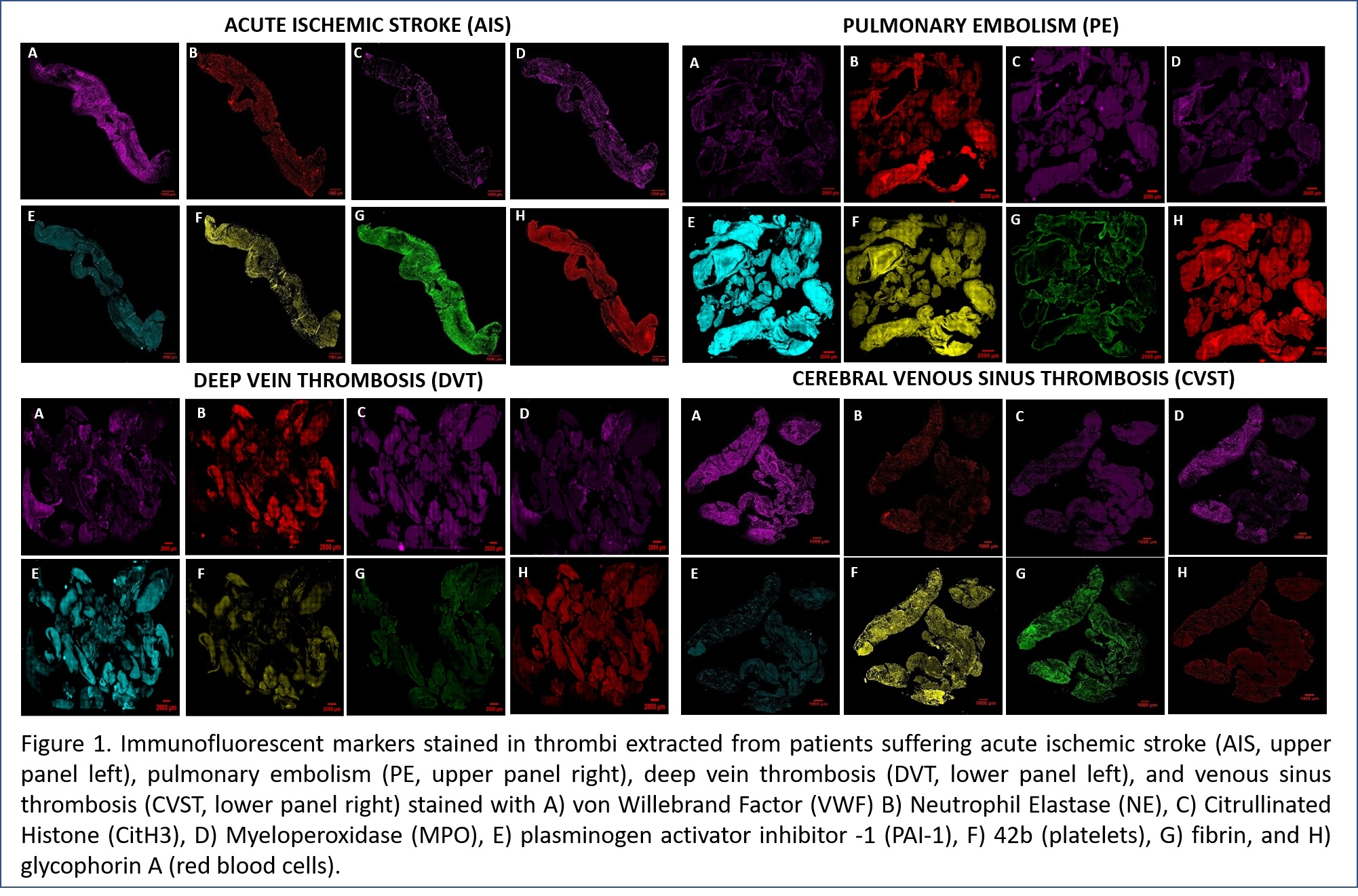
Clots were harvested from 20 PE, 9 DVT, and 74 AIS patients and immunofluorescent staining completed in duplicate with VWF, plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 (PAI-1), glycophorin A (RBCs), CD42b (platelets), fibrinogen, and neutrophil endothelial trap constituents (NETs). NETs were defined as citrullinated histones (CitH3), neutrophil elastase (NE) and myeloperoxidase (MPO). Clot sections were analyzed with Image J.
Results
VWF levels were lower in AIS clots (21.02 +/- 12.02%) compared to DVT (24.87 +/- 12.98%, p=0.0212) and higher in PE (12.21 +/- 5.96%, p=0.0001). PAI-1 levels were higher in AIS clots (42.80 +/- 16.28%) compared to DVT (27.43 +/- 15.61%, p=0.0001) and lower in PE (51.23 +/- 10.89%, p=0.0016). Although RBCs were not significantly different in AIS (35.34 +/- 15.32%) compared to DVT, they were more prevalent in PE (52.93 +/- 8.31%, p=0.0001). Surprisingly, although platelets were lower in DVT thrombi (15.30 +/- 12.33%, p=0.0105) compared to AIS (23.06 +/- 13.71%), they were increased in PE (32.70 +/- 8.46%, p=0.0001. Lastly, although there was no difference in DVT thrombi compared to AIS clots, fibrinogen (21.307 +/- 8.75%) was lower in PE clots (14.85 +/- 7.56%, p=0.0001), as was CitH3 (8.42 +/- 10.42% vs 7.03 +/- 4.18%, p=0.0001, and NE (31.10 +/- 18.31% vs 37.18 +/- 14.31% in PE, p=0.0025). MPO was unremarkable.
Conclusion
Inflammatory marker levels in AIS vs VTE have a complexity beyond shear stress and offer insights into targeting thrombolytics.
Venous thromboembolism (VTE) manifesting as deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolus (PE) and arterial thromboembolism (ATE) manifesting as acute ischemic stroke (AIS) result in ~1 million US deaths annually. Increased levels of circulating inflammatory markers, particularly von Willebrand factor (VWF), may indicate poor outcomes in ATE, but previous studies limit this response to high shear stress milieu. We compared VTE and AIS thrombi inflammatory markers at time of intervention.
Methods
Clots were harvested from 20 PE, 9 DVT, and 74 AIS patients and immunofluorescent staining completed in duplicate with VWF, plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 (PAI-1), glycophorin A (RBCs), CD42b (platelets), fibrinogen, and neutrophil endothelial trap constituents (NETs). NETs were defined as citrullinated histones (CitH3), neutrophil elastase (NE) and myeloperoxidase (MPO). Clot sections were analyzed with Image J.
Results
VWF levels were lower in AIS clots (21.02 +/- 12.02%) compared to DVT (24.87 +/- 12.98%, p=0.0212) and higher in PE (12.21 +/- 5.96%, p=0.0001). PAI-1 levels were higher in AIS clots (42.80 +/- 16.28%) compared to DVT (27.43 +/- 15.61%, p=0.0001) and lower in PE (51.23 +/- 10.89%, p=0.0016). Although RBCs were not significantly different in AIS (35.34 +/- 15.32%) compared to DVT, they were more prevalent in PE (52.93 +/- 8.31%, p=0.0001). Surprisingly, although platelets were lower in DVT thrombi (15.30 +/- 12.33%, p=0.0105) compared to AIS (23.06 +/- 13.71%), they were increased in PE (32.70 +/- 8.46%, p=0.0001. Lastly, although there was no difference in DVT thrombi compared to AIS clots, fibrinogen (21.307 +/- 8.75%) was lower in PE clots (14.85 +/- 7.56%, p=0.0001), as was CitH3 (8.42 +/- 10.42% vs 7.03 +/- 4.18%, p=0.0001, and NE (31.10 +/- 18.31% vs 37.18 +/- 14.31% in PE, p=0.0025). MPO was unremarkable.
Conclusion
Inflammatory marker levels in AIS vs VTE have a complexity beyond shear stress and offer insights into targeting thrombolytics.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Fat Chance: Paradoxical Embolic Stroke from Lipomatous Hypertrophy of the Interatrial Septum
Kalathoor Abraham
Comparative Trends and Characteristics in the Use of Catheter-Directed Therapies for Acute Pulmonary EmbolismKim Joseph, Horbal Steven, Mewaldt Christian, Ramachandran Abhinay, Yeh Robert, Secemsky Eric, Carroll Brett
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.
Rate this abstract
(Maximum characters: 500)