Final ID: TH272
Adverse Maternal and Offspring Outcomes in Dahl Salt-Sensitive Rat Pregnancies: Impact of a Maternal Hypertensive High-Fat Diet
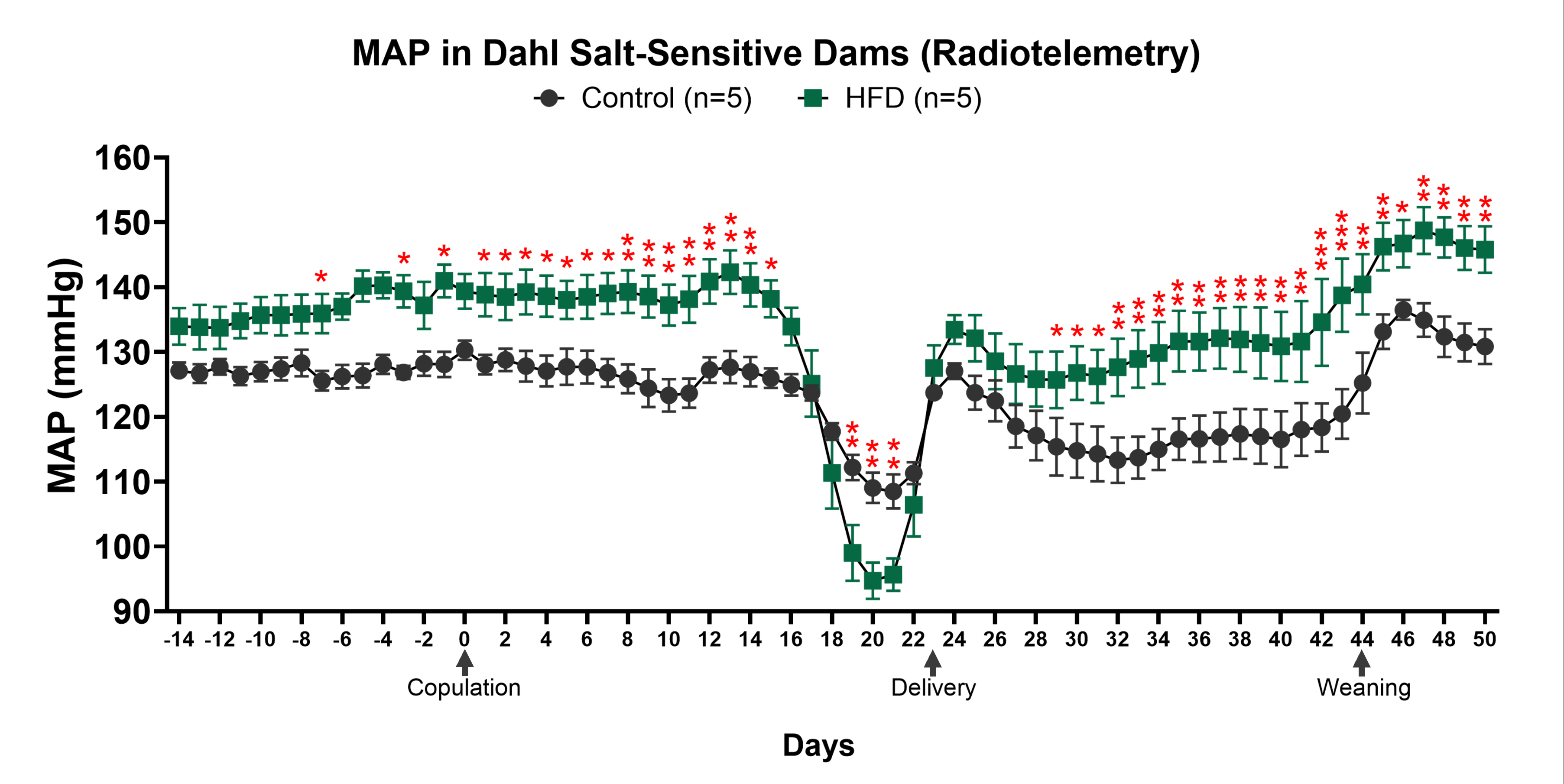
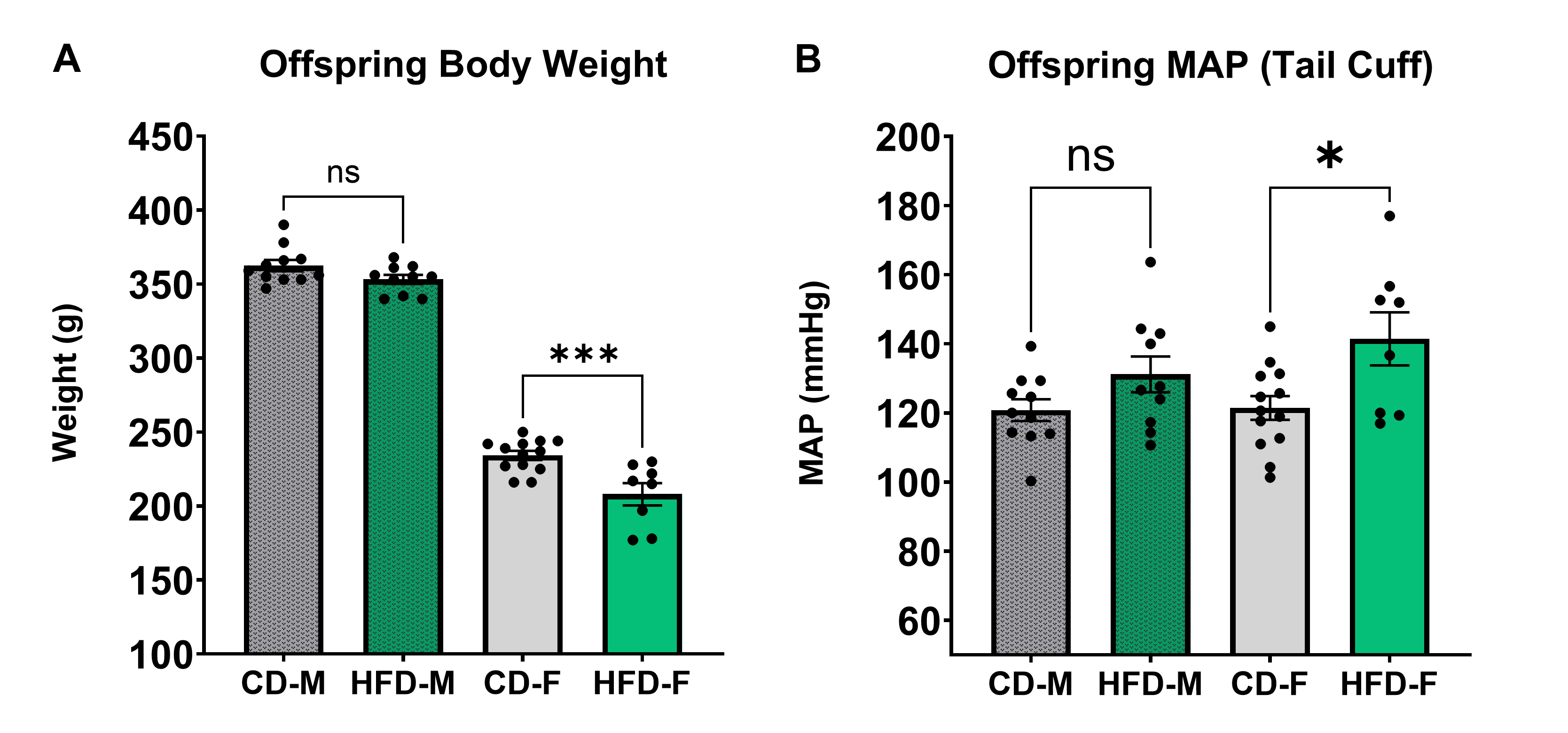
Abstract Body: Preeclampsia (PE), a hypertensive disorder of pregnancy, is a leading cause of adverse maternal and offspring outcomes globally. Excessive maternal adiposity significantly increases risk of PE, though underlying mechanisms remain poorly understood. The Dahl Salt-Sensitive (Dahl SS) rat is widely used as a spontaneous model of superimposed PE. Still, the impact of high-fat diet (HFD) in Dahl SS pregnancies remains understudied. We aimed to elucidate pregnancy outcomes in HFD-fed Dahl SS females and long-term offspring cardiometabolic programming. We hypothesized that HFD-fed Dahl SS dams would display exacerbated late-gestation blood pressure (BP) and fetal growth restriction compared to control diet (CD)-fed dams. Further, offspring from HFD Dahl SS dams were expected to experience sex-specific long-term hypertension, despite maintained on CD since weaning. Virgin Dahl SS females from Charles River Laboratories were fed CD (0.3% NaCl, 10% kcal fat) or HFD (0.3% NaCl, 60% kcal fat) starting at 3 weeks (wks) of age (Research Diets, Inc). At 13 wks of age, dams underwent continuous BP recording via radiotelemetry (PhysioTel™ HD-S10, DSI) and timed breeding, with day of copulation defined as gestational day (GD) 0 (n=5/group). Offspring were weaned at 3 wks of age, maintained on CD, and underwent sphyngmomanometry BP recording (CODA® High Throughput System, Kent Scientific) at 13, 20, and 27 wks (n=8-13/group). Statistical analyses included student’s t-tests, one-way ANOVAs, and mixed-effect model with post-hoc Tukey’s tests (GraphPad Prism 10.3.1). Pre-pregnancy and throughout most of gestation, 24h-average systolic, diastolic, and mean arterial pressure were ~7-15 mmHg higher in HFD vs CD dams (Fig. 1, p<0.05). Notably, both CD and HFD dams experienced late-gestation BP drop, with lower BP nadir in HFD dams at GD19-21 (p<0.05). Litter size and pup birth weights were not different (p>0.05). Female offspring from HFD dams were ~25g lighter and had ~20 mmHg higher BP at 13 wks of age compared to females born from CD dams (Fig. 2, p<0.05). No differences in body weight or BP were observed between CD and HFD offspring at other studied timepoints (p>0.05). In conclusion, HFD-fed Dahl SS dams experience higher BP pre-pregnancy and throughout most of gestation, but lower BP nadir prior to parturition. While short-term pregnancy complications were not observed, female offspring from HFD Dahl SS experienced abnormal cardiometabolic profile during early adulthood.
More abstracts on this topic:
A community-engaged approach to culturally tailoring a dietary intervention to improve cardiometabolic health among Black adults with obesity in Los Angeles County
Adeyemo Mopelola, Thorpe Roland
Beyond Preeclampsia: Hypertension and Proteinuria in PregnancyChen Victoria, William Jeffrey, Venkataraman Shilpa, Triot Alexa, Cluett Jennifer