Final ID: FR472
Comparison of Deaths Preventable Through Improved Hypertension Control vs. Increased Utilization of Other Preventive Services
Abstract Body: Background: The global burden of non-communicable diseases (NCD) is rapidly increasing, and about 3 in 5 deaths worldwide are caused by NCDs. The goal of this analysis was to estimate the number of deaths that could be prevented by increasing the utilization of NCD preventive services.
Methods: We included 22 countries with the highest burden of NCD deaths globally, and estimated the potential reduction in cardiovascular and cancer-specific mortality from increasing utilization of 7 evidence-based preventive services that could be delivered through routine clinical care: hypertension control, hyperlipidemia control, diabetes control, smoking cessation, and screening for colon cancer, breast cancer, and cervical cancer. Preventive service eligibility and control targets were defined according to major guidelines (e.g., blood pressure targets <140/90 mmHg, colon cancer screening in adults aged 45-75 years). Data inputs for each country included age- and sex-specific demographics and preventive service utilization rates ascertained from the Global Burden of Disease network, the NCD Risk Factor Collaboration, the WHO STEPwise approach to NCD risk factor surveillance (STEPS), and the WHO cancer screening databases. Population size, mortality rates, service eligibility and utilization data, and associated relative risks were used to calculate annual deaths averted from increased service utilization, with means and 95% uncertainty intervals derived from means and percentiles (2.5th and 97.5th) of n=1,000 Monte Carlo simulations.
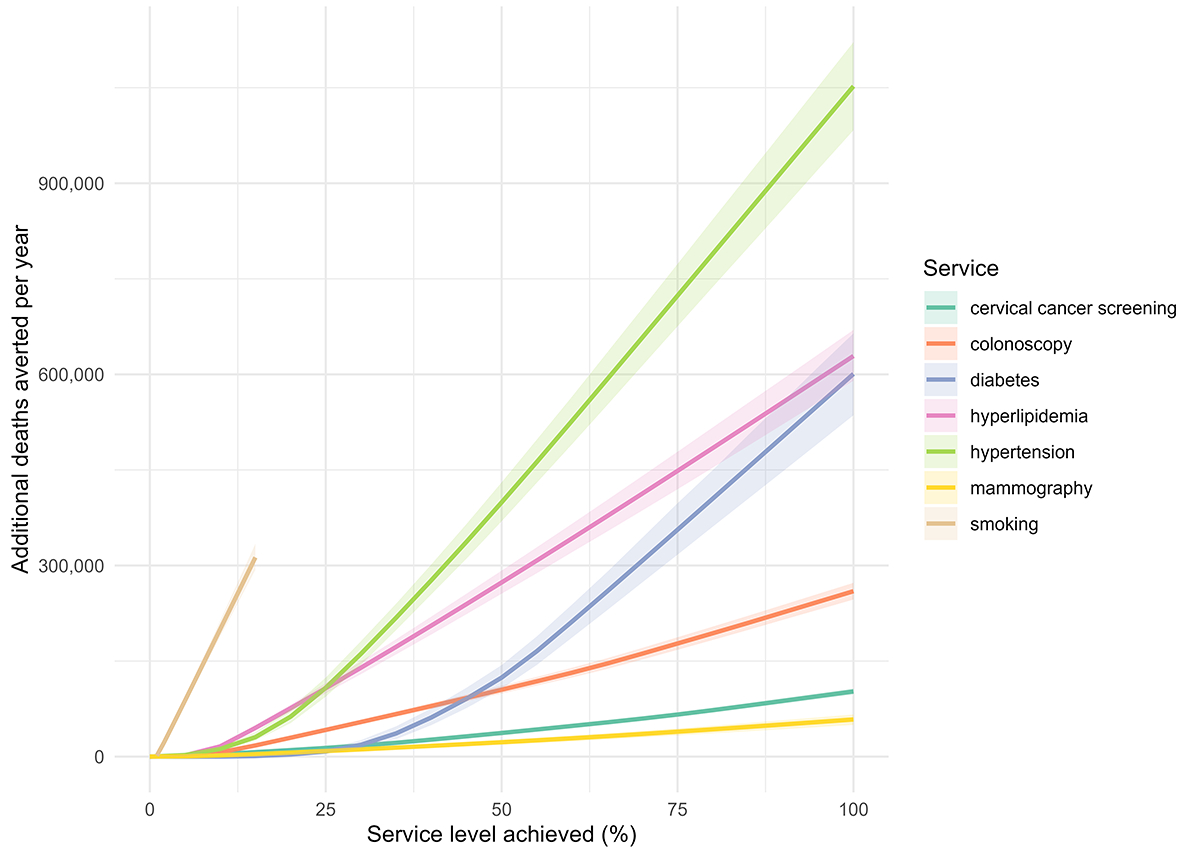
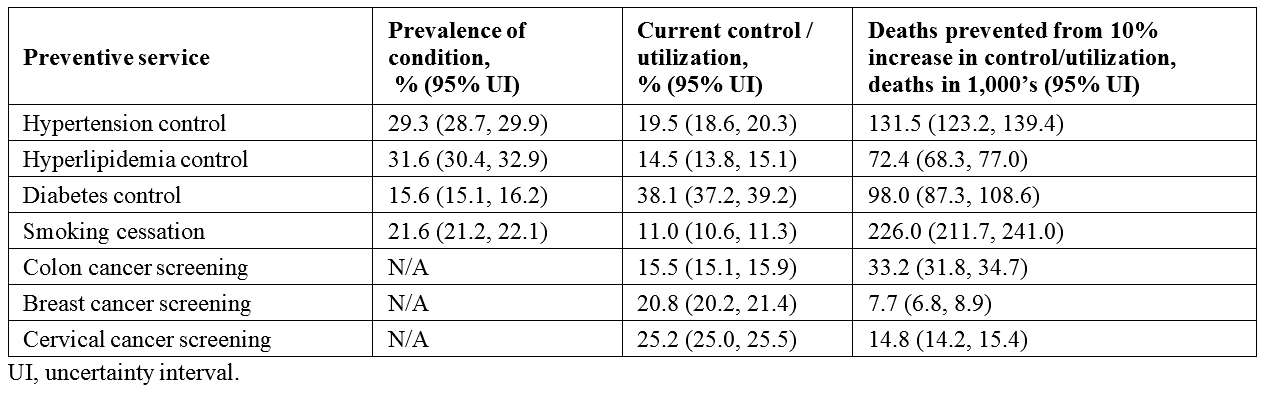
Results: Across all included countries, rates of NCD control and preventive service utilization were low, with large opportunities for reducing premature mortality (Figure 1). Among preventive services, increasing hypertension control and smoking cessation could have the greatest impact on mortality by achieving high control rates. A 10% absolute increase in hypertension control (from the current ~20% to ~30%) could prevent ~132,000 deaths annually (Table 2). Increasing smoking cessation rates from the current ~11% to ~21% could prevent ~230,000 deaths annually. Deaths preventable from increased cancer screening were lower.
Conclusions: This analysis of 22 countries with high NCD burden identified substantial opportunities to reduce deaths from NCD through increasing preventive service utilization. These findings support hypertension and smoking cessation as top priority targets across major NCDs to prevent premature mortality globally.
Methods: We included 22 countries with the highest burden of NCD deaths globally, and estimated the potential reduction in cardiovascular and cancer-specific mortality from increasing utilization of 7 evidence-based preventive services that could be delivered through routine clinical care: hypertension control, hyperlipidemia control, diabetes control, smoking cessation, and screening for colon cancer, breast cancer, and cervical cancer. Preventive service eligibility and control targets were defined according to major guidelines (e.g., blood pressure targets <140/90 mmHg, colon cancer screening in adults aged 45-75 years). Data inputs for each country included age- and sex-specific demographics and preventive service utilization rates ascertained from the Global Burden of Disease network, the NCD Risk Factor Collaboration, the WHO STEPwise approach to NCD risk factor surveillance (STEPS), and the WHO cancer screening databases. Population size, mortality rates, service eligibility and utilization data, and associated relative risks were used to calculate annual deaths averted from increased service utilization, with means and 95% uncertainty intervals derived from means and percentiles (2.5th and 97.5th) of n=1,000 Monte Carlo simulations.
Results: Across all included countries, rates of NCD control and preventive service utilization were low, with large opportunities for reducing premature mortality (Figure 1). Among preventive services, increasing hypertension control and smoking cessation could have the greatest impact on mortality by achieving high control rates. A 10% absolute increase in hypertension control (from the current ~20% to ~30%) could prevent ~132,000 deaths annually (Table 2). Increasing smoking cessation rates from the current ~11% to ~21% could prevent ~230,000 deaths annually. Deaths preventable from increased cancer screening were lower.
Conclusions: This analysis of 22 countries with high NCD burden identified substantial opportunities to reduce deaths from NCD through increasing preventive service utilization. These findings support hypertension and smoking cessation as top priority targets across major NCDs to prevent premature mortality globally.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Metabolomic Study of Cardiac Dysfunction in Hyperglycemia
Yoshida Yilin, Qi Qibin, Cheng Susan, Kaplan Robert, Rodriguez Carlos, Shah Amil, Yu Bing, Nguyen Ngoc Quynh, Moon Eun Hye, Casey Rebholz, Skali Hicham, Arthur Victoria, Echouffo Justin, Ballantyne Christie, Selvin Elizabeth
Aspirin for Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Events in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus: An Updated Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis & Trial Sequential Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials post-ASCEND TrialPuthia Valappil Omer Mohammed, John M Rose, Mallikarjun Samanth, D Souza Leroy, Rongala Sai Anurag, Chakraborty Diya, Balarishnan Rojith, Kutty Shelby