Final ID: FR538
Evaluating the Effect of Hypertension on Aortic Stenosis and Cardiovascular Risk in a Real-World Population
Abstract Body: Introduction:
Patients with aortic stenosis (AS) have comorbid hypertension (HTN) and it increases the afterload in addition to fixed obstruction. However, vasodilator therapy increases the risk of end organ hypoperfusion in AS against fixed obstruction and there is seldom data on cardiovascular outcomes of AS in patients with HTN.
Hypothesis:
We compare cardiovascular outcomes of HTN in patients with AS.
Methods:
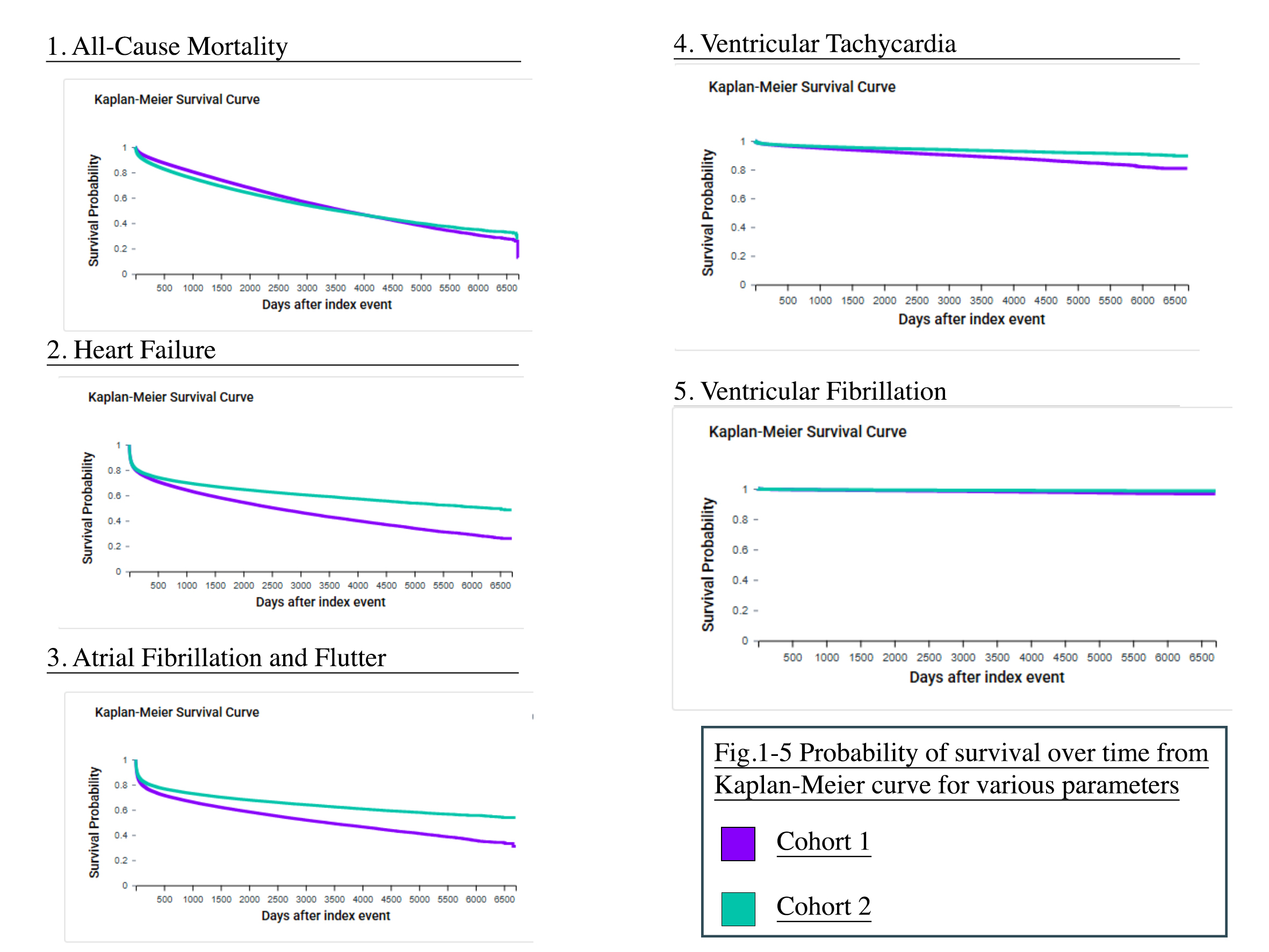
This retrospective cohort study, using TriNetX, analyzed patients aged ≥18 years from 1/1/2007 to 5/25/2025. After 1:1 propensity score matching, two cohorts were formed: Cohort 1 (AS + HTN; n = 318,965) and Cohort 2 (AS without HTN, n=318,965). The outcomes evaluated were mortality, HF, AF, VT, and VF. Risk differences, risk ratios (RR), and hazard ratios (HR) with corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CIs) and p-values were computed. Kaplan-Meier survival analyses and log-rank tests were performed to compare time-to-event outcomes.
Results:
Patients in group 1 demonstrated higher rates of adverse cardiovascular outcomes compared to group 2. The all-cause mortality risk was significantly higher in group 1 (24.7%) compared to group 2 (21.6%), with a RR of 1.146 (95% CI: 1.135–1.156; p < 0.0001) and HR of 0.852 (95% CI: 0.843–0.861; p < 0.0001). HF occurred in 34.6% of group 1 versus 23.7% of group 2 (RR: 1.463; 95% CI: 1.451–1.474; HR: 1.275; p < 0.0001). AF was also more prevalent in group 1 (31.7% vs. 20.8%; RR: 1.523; HR: 1.334; p < 0.0001). VT and VF were significantly more common in Group 1 (VT: 5.1% vs. 2.9%, RR: 1.738; VF: 0.88% vs. 0.50%, RR: 1.772; both p < 0.0001), with HR of 1.378 and 1.397 respectively.
Conclusion:
In this large, matched cohort study, the presence of HTN in patients with AS was associated with significantly higher risks of mortality and multiple adverse cardiovascular outcomes, including HF, AF, and ventricular arrhythmias. These findings highlight the importance of vigilant cardiovascular monitoring and hypertension management in AS patients with concurrent HTN.
Patients with aortic stenosis (AS) have comorbid hypertension (HTN) and it increases the afterload in addition to fixed obstruction. However, vasodilator therapy increases the risk of end organ hypoperfusion in AS against fixed obstruction and there is seldom data on cardiovascular outcomes of AS in patients with HTN.
Hypothesis:
We compare cardiovascular outcomes of HTN in patients with AS.
Methods:
This retrospective cohort study, using TriNetX, analyzed patients aged ≥18 years from 1/1/2007 to 5/25/2025. After 1:1 propensity score matching, two cohorts were formed: Cohort 1 (AS + HTN; n = 318,965) and Cohort 2 (AS without HTN, n=318,965). The outcomes evaluated were mortality, HF, AF, VT, and VF. Risk differences, risk ratios (RR), and hazard ratios (HR) with corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CIs) and p-values were computed. Kaplan-Meier survival analyses and log-rank tests were performed to compare time-to-event outcomes.
Results:
Patients in group 1 demonstrated higher rates of adverse cardiovascular outcomes compared to group 2. The all-cause mortality risk was significantly higher in group 1 (24.7%) compared to group 2 (21.6%), with a RR of 1.146 (95% CI: 1.135–1.156; p < 0.0001) and HR of 0.852 (95% CI: 0.843–0.861; p < 0.0001). HF occurred in 34.6% of group 1 versus 23.7% of group 2 (RR: 1.463; 95% CI: 1.451–1.474; HR: 1.275; p < 0.0001). AF was also more prevalent in group 1 (31.7% vs. 20.8%; RR: 1.523; HR: 1.334; p < 0.0001). VT and VF were significantly more common in Group 1 (VT: 5.1% vs. 2.9%, RR: 1.738; VF: 0.88% vs. 0.50%, RR: 1.772; both p < 0.0001), with HR of 1.378 and 1.397 respectively.
Conclusion:
In this large, matched cohort study, the presence of HTN in patients with AS was associated with significantly higher risks of mortality and multiple adverse cardiovascular outcomes, including HF, AF, and ventricular arrhythmias. These findings highlight the importance of vigilant cardiovascular monitoring and hypertension management in AS patients with concurrent HTN.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Meta-Analysis Comparing Same-Day Discharge to Later-Day Discharge in Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement
Jain Hritvik, Passey Siddhant, Jain Jyoti, Goyal Aman, Wasir Amanpreet, Ahmed Mushood, Patel Nandan, Yadav Ashish, Shah Janhvi, Mehta Aryan
Anti-inflammatory regimen associated with reduced incidence of early homograft stenosis following the Ross procedureKhan Kathleen, Degraaff Dominique, Gray Mary Anne, Korukonda Samhita, Flodin Rachel, Degraaff Bret, Dhanekula Arjune, Deroo Scott, Burke Christopher