Final ID: Mo3075
Aortic Root Pressure for Detecting Aortic Stenosis using Machine Learning
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Aortic stenosis (AS) is a progressive, deteriorative valvular condition that is associated with significant morbidity and mortality. The best method to diagnose the severity of AS is controversial as all of the current modalities have multiple potential sources of error. As severity of AS increases, the time from aortic valve opening to peak systolic pressure increases. We hypothesized that machine learning applied to pressure measured in the aortic root via a fluid filled catheter at the time of cardiac catheterization would accurately diagnose aortic stenosis.
Aims: Use a long-short term memory (LSTM) neural network to identify AS using aortic root pressure.
Methods: We assessed aortic root pressure recordings in 102 consecutive patients undergoing transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) at our institution between 2014 and 2017. A LSTM was trained, validated, and tested using pre- and post- TAVR aortic root pressure 1 Hz digital recordings of 3.5 seconds duration. Recordings were selected to be artifact-free and in sinus rhythm. A 10-fold cross-validation structure was used (170 training, 17 validation, 17 testing tracings). The model was assessed using area under the receiver operating curve (AUROC) and F1 score.
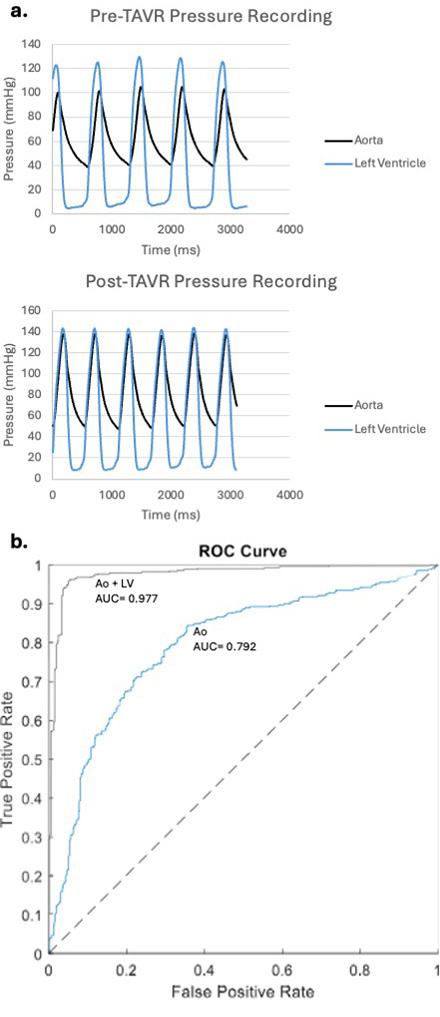
Results: The LSTM was able to distinguish between pre-TAVR (severe AS) and post-TAVR (no AS) tracings with sensitivity of 0.764, specificity of 0.703, AUROC of 0.792, and F1 score of 0.741. In comparison, when pressure tracings of the left ventricle were added to the model, the LSTM performance improved to sensitivity of 0.956, specificity of 0.950, AUROC of 0.977, and F1 score of 0.954.
Conclusion: This proof-of-concept study demonstrated that aortic pressure alone can be used to detect severe AS. A larger analysis is needed to validate these findings across gradients of severity. This study has implications for using automatic AS severity assessments during cardiac catheterization to accurately diagnose AS.
Aims: Use a long-short term memory (LSTM) neural network to identify AS using aortic root pressure.
Methods: We assessed aortic root pressure recordings in 102 consecutive patients undergoing transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) at our institution between 2014 and 2017. A LSTM was trained, validated, and tested using pre- and post- TAVR aortic root pressure 1 Hz digital recordings of 3.5 seconds duration. Recordings were selected to be artifact-free and in sinus rhythm. A 10-fold cross-validation structure was used (170 training, 17 validation, 17 testing tracings). The model was assessed using area under the receiver operating curve (AUROC) and F1 score.
Results: The LSTM was able to distinguish between pre-TAVR (severe AS) and post-TAVR (no AS) tracings with sensitivity of 0.764, specificity of 0.703, AUROC of 0.792, and F1 score of 0.741. In comparison, when pressure tracings of the left ventricle were added to the model, the LSTM performance improved to sensitivity of 0.956, specificity of 0.950, AUROC of 0.977, and F1 score of 0.954.
Conclusion: This proof-of-concept study demonstrated that aortic pressure alone can be used to detect severe AS. A larger analysis is needed to validate these findings across gradients of severity. This study has implications for using automatic AS severity assessments during cardiac catheterization to accurately diagnose AS.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Deep Learning Digital Biomarker for Mitral Valve Prolapse using Echocardiogram Videos
Al-alusi Mostafa, Khurshid Shaan, Sanborn Danita, Picard Michael, Ho Jennifer, Maddah Mahnaz, Ellinor Patrick, Lau Emily, Small Aeron, Reeder Christopher, Shnitzer Dery Tal, Andrews Carl, Kany Shinwan, Ramo Joel, Haimovich Julian
Association Between Pre-Existing Chronic Total Occlusion and Post-TAVR Pacemaker Implantation: A Retrospective Propensity Matched AnalysisHaseeb Shahan, Ansari Umair, Munir Shafia, Lee Sang, Chan Marvyn, Goldbarg Seth