Final ID: 071
Comparative Antihypertensive Effects of Emerging Cardiorenal Therapies in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Network Meta-Analysis of SGLT2 Inhibitors, MRAs, and GLP-1 Receptor Agonists
Abstract Body: Background:
Blood pressure (BP) control is essential to slowing chronic kidney disease (CKD) progression and reducing cardiovascular risk. While sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors (SGLT2i), mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (MRAs), and GLP-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) provide cardiorenal benefits, their relative antihypertensive efficacy in CKD remains unclear.
Methods:
We conducted a network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials and high-quality observational studies (2015–2025) involving adults with CKD (eGFR <90 mL/min/1.73 m2) that reported BP outcomes with SGLT2i, MRAs (including finerenone), or GLP-1 RAs. The primary outcome was mean change in systolic BP (SBP); secondary outcomes included diastolic BP (DBP) change and hypotension incidence. Subgroup analyses compared early (majority with eGFR ≥45) versus advanced CKD (majority with eGFR <45). Random-effects models were used unless heterogeneity (I2) was negligible. Evidence certainty was graded via GRADE. Funnel plots assessed publication bias, for SGLT2i.
Results:
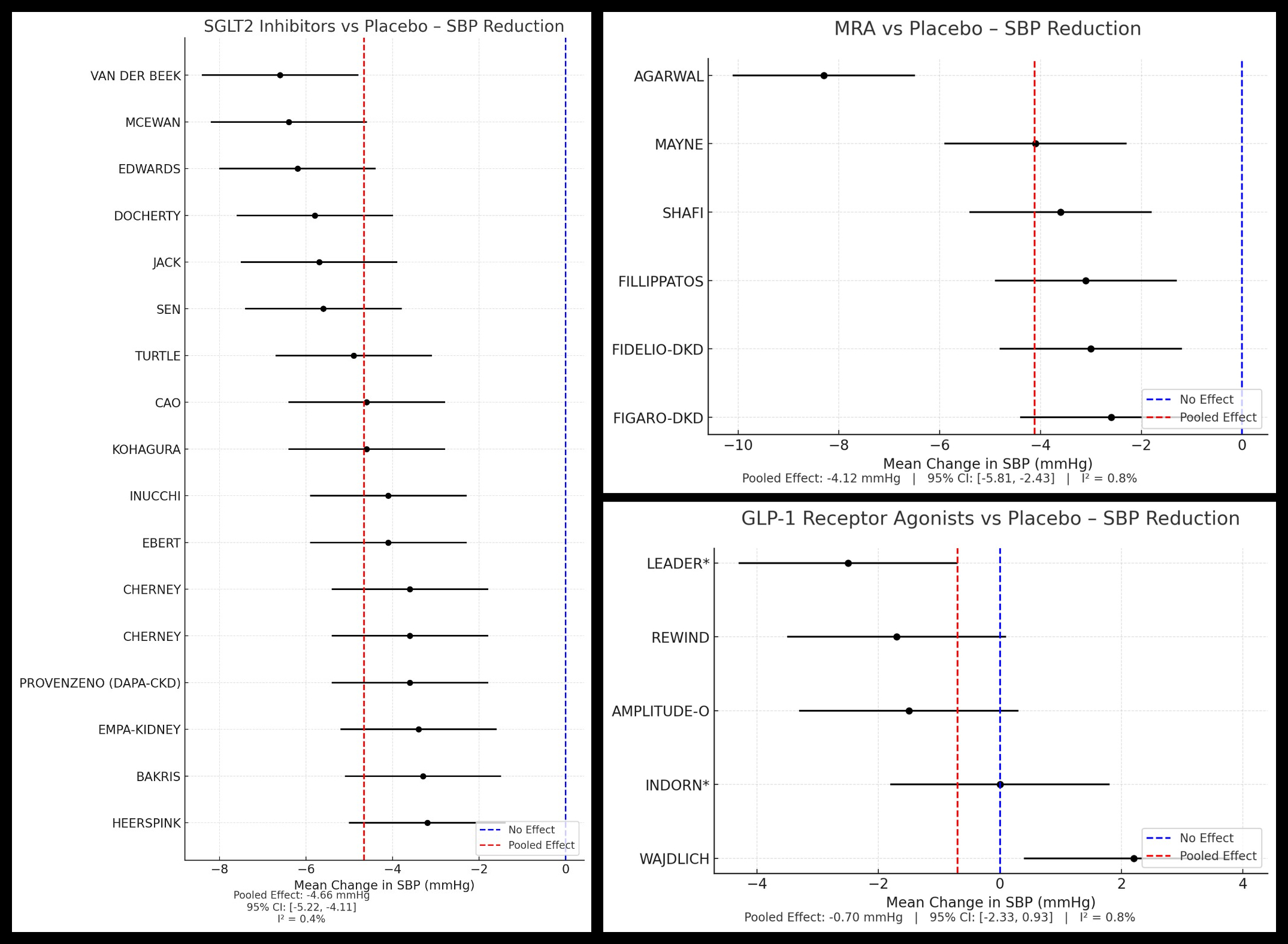
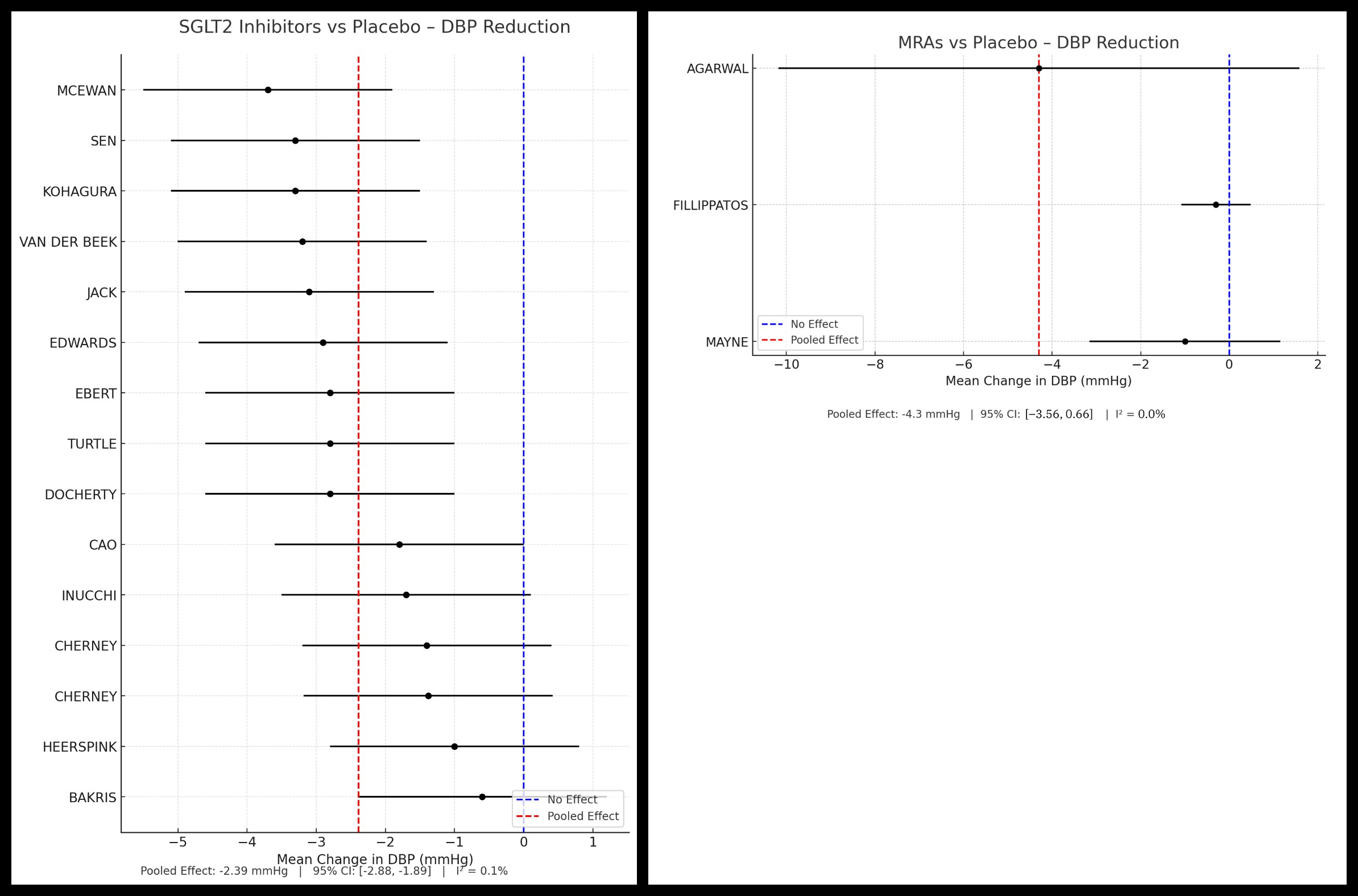
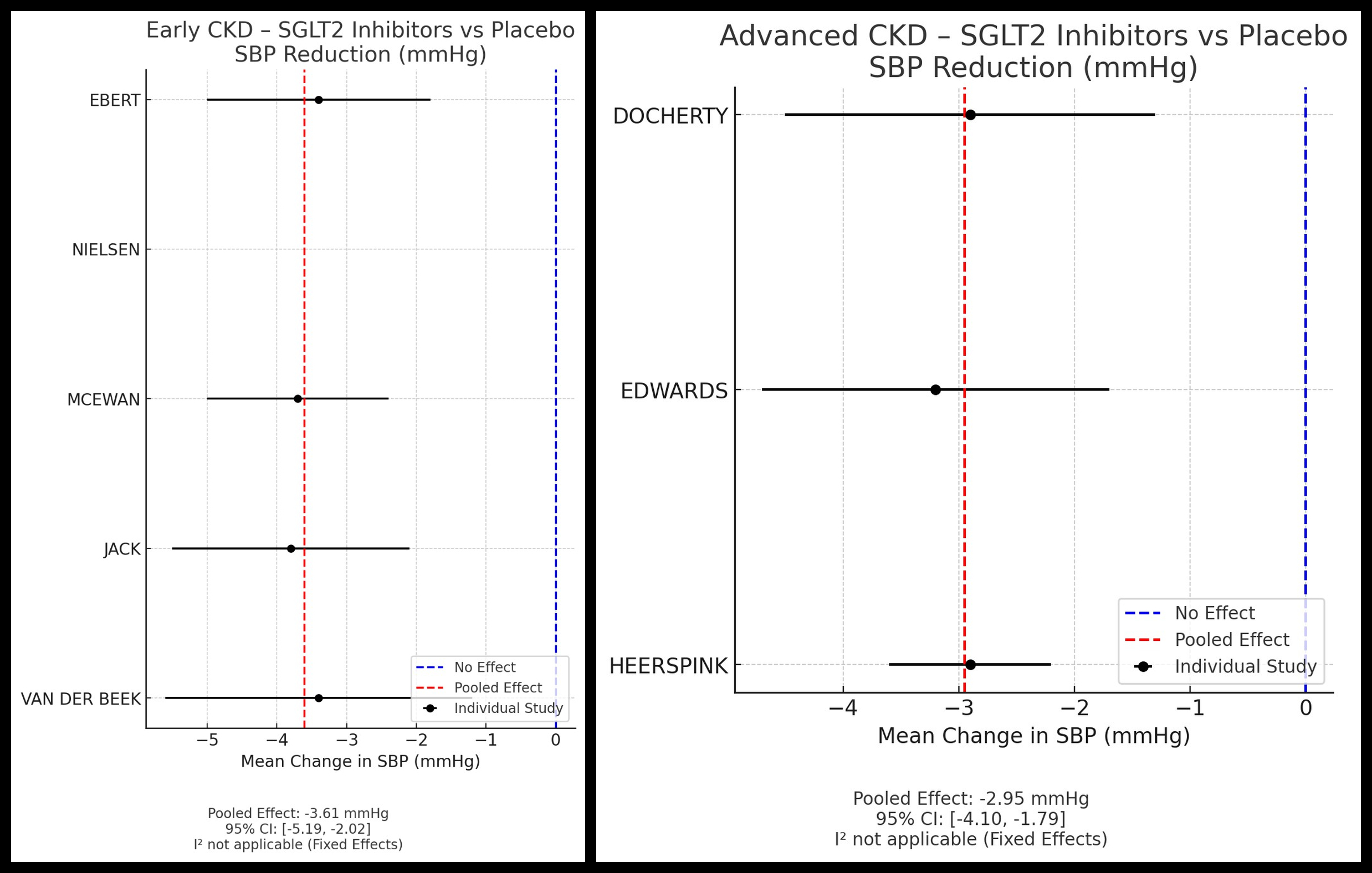
Seventeen studies were included. SGLT2 inhibitors produced the greatest SBP reduction (–4.66 mmHg; 95% CI: –5.22 to –4.11; I2 = 0.4%), followed by MRAs (–4.12 mmHg; 95% CI: –5.81 to –2.43; I2 = 0.8%). GLP-1 RAs had a non-significant SBP reduction (–0.70 mmHg; 95% CI: –2.33 to 0.93; I2 = 0.8%). Diastolic BP reductions followed a similar trend: SGLT2i (–2.39 mmHg; 95% CI: –2.88 to –1.89, I2 = 0.1%), MRAs (–4.3 mmHg; 95% CI: –3.56 to 0.66, I2 = 0.0%). DBP trend could not be performed for GLP-1 RAs. Subgroup analysis confirmed significant SBP reductions with SGLT2i in both early (–3.61 mmHg; 95% CI: –5.19 to –2.02) and advanced CKD (–2.95 mmHg; 95% CI: –4.10 to –1.79). Hypotension was least frequent with SGLT2i (4.4%) versus MRAs (14.6%); GLP-1 RA trials inconsistently reported hypotension. Visual inspection of funnel plots for SGLT2i suggested minimal publication bias.
Conclusions:
SGLT2i provided the most consistent and clinically meaningful BP reductions in CKD, with high-certainty evidence and the lowest hypotension risk. Their effect may reflect broader populations, volume-mediated mechanisms, and longer follow-up. MRAs also reduced BP but had more hypotension, possibly limiting dosing. GLP-1 RAs offered minimal BP benefit, with low certainty and variable reporting. SGLT2i appear preferable for BP control in CKD, though limited direct comparisons call for further study.
Blood pressure (BP) control is essential to slowing chronic kidney disease (CKD) progression and reducing cardiovascular risk. While sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors (SGLT2i), mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (MRAs), and GLP-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) provide cardiorenal benefits, their relative antihypertensive efficacy in CKD remains unclear.
Methods:
We conducted a network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials and high-quality observational studies (2015–2025) involving adults with CKD (eGFR <90 mL/min/1.73 m2) that reported BP outcomes with SGLT2i, MRAs (including finerenone), or GLP-1 RAs. The primary outcome was mean change in systolic BP (SBP); secondary outcomes included diastolic BP (DBP) change and hypotension incidence. Subgroup analyses compared early (majority with eGFR ≥45) versus advanced CKD (majority with eGFR <45). Random-effects models were used unless heterogeneity (I2) was negligible. Evidence certainty was graded via GRADE. Funnel plots assessed publication bias, for SGLT2i.
Results:
Seventeen studies were included. SGLT2 inhibitors produced the greatest SBP reduction (–4.66 mmHg; 95% CI: –5.22 to –4.11; I2 = 0.4%), followed by MRAs (–4.12 mmHg; 95% CI: –5.81 to –2.43; I2 = 0.8%). GLP-1 RAs had a non-significant SBP reduction (–0.70 mmHg; 95% CI: –2.33 to 0.93; I2 = 0.8%). Diastolic BP reductions followed a similar trend: SGLT2i (–2.39 mmHg; 95% CI: –2.88 to –1.89, I2 = 0.1%), MRAs (–4.3 mmHg; 95% CI: –3.56 to 0.66, I2 = 0.0%). DBP trend could not be performed for GLP-1 RAs. Subgroup analysis confirmed significant SBP reductions with SGLT2i in both early (–3.61 mmHg; 95% CI: –5.19 to –2.02) and advanced CKD (–2.95 mmHg; 95% CI: –4.10 to –1.79). Hypotension was least frequent with SGLT2i (4.4%) versus MRAs (14.6%); GLP-1 RA trials inconsistently reported hypotension. Visual inspection of funnel plots for SGLT2i suggested minimal publication bias.
Conclusions:
SGLT2i provided the most consistent and clinically meaningful BP reductions in CKD, with high-certainty evidence and the lowest hypotension risk. Their effect may reflect broader populations, volume-mediated mechanisms, and longer follow-up. MRAs also reduced BP but had more hypotension, possibly limiting dosing. GLP-1 RAs offered minimal BP benefit, with low certainty and variable reporting. SGLT2i appear preferable for BP control in CKD, though limited direct comparisons call for further study.
More abstracts on this topic:
Acute Effects of Isometric Handgrip Exercise on Cardiac Baroreflex Sensitivity in Chronic Kidney Disease
Sabino-carvalho Jeann, Park Jeanie
A Framework for Developing Prehospital Intracerebral Hemorrhage Recognition Scales and TechnologiesTaleb Shayandokht, Hsu Jamie, Saver Jeffrey