Final ID: TAC228
Trends in Salt Substitute Use Among US Adults, 2003–2020
Adults aged ≥18 years were categorized into 4 subgroups based on presence of HTN (BP ≥130/80 mmHg) and antihypertensive medication use: 1) treated/controlled HTN, 2) treated/uncontrolled HTN, 3) untreated HTN, and 4) normotensive. Salt types were classified as ordinary salt (e.g., iodized salt, sea salt, etc.), SS (e.g., K-enriched or other SS), and no salt use. Additional analysis was performed in SS-eligible subjects with estimated glomerular filtration rate ≥ 60 ml/min/1.73m2 and not taking concomitant medications that reduce K excretion or K supplement. We also evaluated frequency of eating out to assess its influence on SS use. All analyses incorporated NHANES sampling weights and complex survey design.
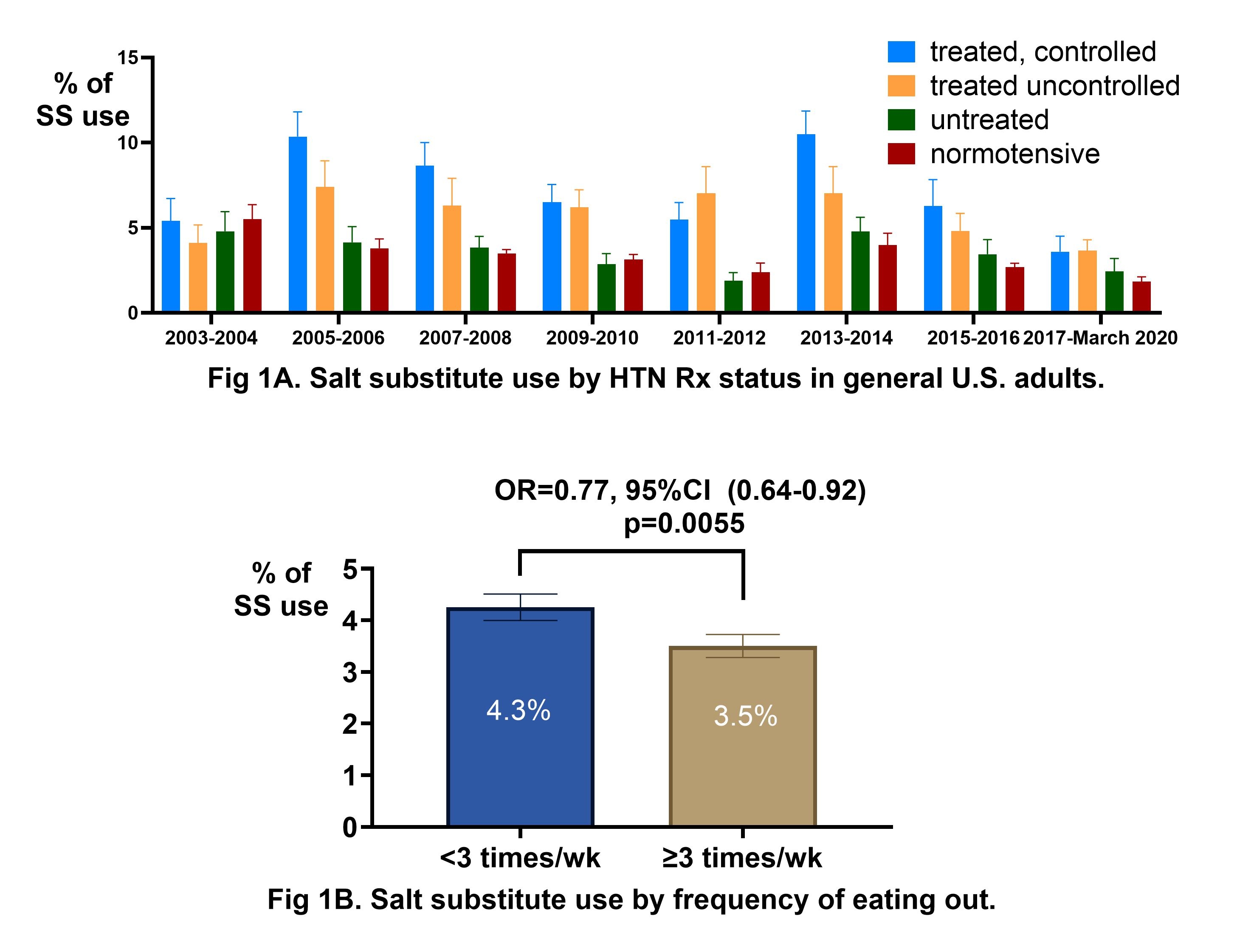
SS use among all U.S. adults remained low, peaking at 5.4% in 2013–2014 and falling to 2.5% by 2017–March 2020. Among eligible adults, use ranged from 2.3% to 5.1%. Usage was highest in individuals with treated and controlled hypertension (3.6–10.5%), followed by those with treated but uncontrolled hypertension (3.7–7.4%), while use remained consistently <5.6% among untreated and normotensive individuals (Figure 1A). Adults eating out ≥3 times/week had 23% lower odds of using SS compared to those who ate out less frequently (OR: 0.77, 95% CI: 0.64–0.92, p=0.0055; Figure 1B).
In a nationally representative sample of U.S. adults, SS use remained uncommon over two decades, including among those with HTN. Even among individuals with treated/ uncontrolled or untreated HTN, fewer than 8% reported using SS, while the majority continued to use ordinary salt. Low SS use may be related to higher frequency of eating out where individuals have limited control over the salt type. Greater efforts are needed to promote SS as part of dietary strategies to support HTN control, particularly among individuals with persistent or poorly controlled HTN.
More abstracts on this topic:
Abdollahi Ashkan, Rotter Jerome, Post Wendy, Blumenthal Roger, Bluemke David, Lima Joao Ac, Whelton Seamus, Sani Maryam, Shabani Mahsima, Scarpa Bruna, Blaha Michael, Wu Colin, Ambale-venkatesh Bharath, Budoff Matthew, Strom Jordan
Anticoagulation versus antiplatelet for secondary prevention in embolic stroke of undetermined source: The Cardiac Abnormalities in Stroke Prevention and Risk of Recurrence StudySiegler James, Aboul-nour Hassan, De Havenon Adam, Culbertson Collin, Melkumova Emiliya, Jillella Dinesh, Dumitrascu Oana, Doolittle Charles, Yahnke Ian, Sathya Anvitha, Brown Samantha, Penckofer Mary, Kang Jieun, Bowman Anna, Brorson James, Shahrivari Mahan, Elangovan Cheran, Sloane Kelly, Alvi Muhammad, Krishnaiah Balaji, Kam Wayneho, Farooqui Mudassir, Badillo Goicoechea Elena, Nahab Fadi, Rojas-soto Diana, Sharma Richa, Thottempudi Neeharika, Nedelcu Simona, Smith Matthew, Herpich Franziska, Glover Patrick, Chahien Dalia, Sehgal Siddharth, Eklund Kelsey, Liebeskind David, Linares Guillermo, Daniel Jean-philippe, Al Kasab Sami, Singh Eesha, D'souza Marissa, Gaudio Elizabeth, Aziz Yasmin, Yaghi Shadi, Salehi Omran Setareh, Stretz Christoph, Thon Jesse, Lineback Christina, Khasiyev Farid, Kerrigan Deborah, Ali Hamid