Final ID: MDP512
Associations between High-density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Efflux and Brain Health
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Previous studies have linked plasma levels of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) with impaired cognitive function. However, few studies have investigated the associations between plasma HDL functionality and brain structure and function. Thus, our study aimed to elucidate the associations between plasma HDL measures and brain structure/function in a multiethnic cohort of middle-aged adults.
Accordingly, we conducted a cross-sectional study in 1,826 adults (mean age 51.0±9.7 years, 58% female, 47% Black adults) without preexisting cardiovascular disease or stroke who participated in the Dallas Heart Study to determine associations between HDL measures and brain structure/function. Whole brain white matter hyperintensities (WMH) and grey matter volume (GMV) was measured using a 3-T MRI scanner and normalized to total cranial volume (TCV), and the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) was used to measure cognition. HDL cholesterol efflux capacity (HDL-CEC) was assessed using fluorescence-labeled cholesterol efflux from J774 macrophages and was expressed in arbitrary units. HDL particle measures were assessed using NMR spectroscopy. Adjusted multivariable linear regression models were performed with standardized beta estimates reported.
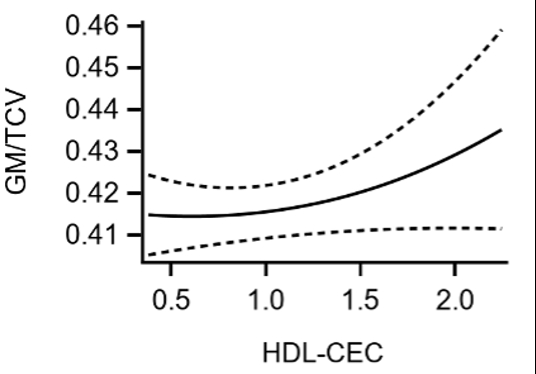
Higher HDL-CEC and small HDL particles (HDL-P) were positively associated with GMV/TCV after adjustment for relevant risk factors (β=0.078 [95% CI: 0.029, 0.126], Figure, and β=0.063 [95% CI: 0.014, 0.111], respectively, all p<0.05). Conversely, there were no associations between HDL measures and WMH or MoCA after adjustment (all p>0.05). Associations of HDL-CEC and small HDL-P with GMV were not modified by race/ethnicity or ApoE-ε4 status.
In conclusion, higher HDL function and small HDL-P were associated with higher GMV after adjustment for traditional risk factors and were not modified by race/ethnicity or ApoE-ε4 carrier status. As such, these findings suggest that better HDL functionality is linked with larger brain GM volume in middle-aged adults. Since GMV loss has been linked to the development of mild cognitive impairment (MCI) and conversion of MCI to Alzheimer's disease, our study may have implications for prevention of age-related decline in cognitive function.
Accordingly, we conducted a cross-sectional study in 1,826 adults (mean age 51.0±9.7 years, 58% female, 47% Black adults) without preexisting cardiovascular disease or stroke who participated in the Dallas Heart Study to determine associations between HDL measures and brain structure/function. Whole brain white matter hyperintensities (WMH) and grey matter volume (GMV) was measured using a 3-T MRI scanner and normalized to total cranial volume (TCV), and the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) was used to measure cognition. HDL cholesterol efflux capacity (HDL-CEC) was assessed using fluorescence-labeled cholesterol efflux from J774 macrophages and was expressed in arbitrary units. HDL particle measures were assessed using NMR spectroscopy. Adjusted multivariable linear regression models were performed with standardized beta estimates reported.
Higher HDL-CEC and small HDL particles (HDL-P) were positively associated with GMV/TCV after adjustment for relevant risk factors (β=0.078 [95% CI: 0.029, 0.126], Figure, and β=0.063 [95% CI: 0.014, 0.111], respectively, all p<0.05). Conversely, there were no associations between HDL measures and WMH or MoCA after adjustment (all p>0.05). Associations of HDL-CEC and small HDL-P with GMV were not modified by race/ethnicity or ApoE-ε4 status.
In conclusion, higher HDL function and small HDL-P were associated with higher GMV after adjustment for traditional risk factors and were not modified by race/ethnicity or ApoE-ε4 carrier status. As such, these findings suggest that better HDL functionality is linked with larger brain GM volume in middle-aged adults. Since GMV loss has been linked to the development of mild cognitive impairment (MCI) and conversion of MCI to Alzheimer's disease, our study may have implications for prevention of age-related decline in cognitive function.
More abstracts on this topic:
Association of Framingham 10-year Cardiovascular Disease Risk Scores with Incident Probable Dementia and Cognitive Impairment in the SPRINT trial
Samimisedeh Parham, Kazibwe Richard, Schaich Christopher, Hughes Timothy, Soliman Elsayed
Bempedoic Acid Lowers LDL-C and Reduces Risk of Major Cardiovascular Events in Hypercholesterolemia: Meta-Analysis of 13 Randomized Controlled TrialsDaid Simranpreet Singh, Sharma Anubhuti, Sharma Arundhati, Choudhary Khushal