Final ID: 011
Accuracy of Visually Estimated Mean Home Blood Pressure: Estimating Yield of Eyeballed BP Study
Abstract Body: Introduction
Home blood pressure (BP) monitoring is commonly used in clinical practice to assess out-of-office BP levels. However, providers often visually estimate (“eyeball”) the average BP from logs to make treatment decisions. This study tested the hypothesis that visual BP estimation is frequently inaccurate, potentially leading to suboptimal clinical management.
Methods
We surveyed 183 healthcare providers (including physicians, medical students, residents, and advanced practice providers) at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center. Participants reviewed three simulated BP logs and estimated the average systolic (SBP) and diastolic BP (DBP). They also reviewed two additional BP logs from a hypothetical patient with untreated stage 2 hypertension and assessed BP trajectory and treatment recommendations. Bland-Altman analysis assessed agreement between visually estimated and calculated mean BP. Fisher’s exact test compared incorrect clinical decisions based on BP underestimation versus accurate/overestimation.
Results
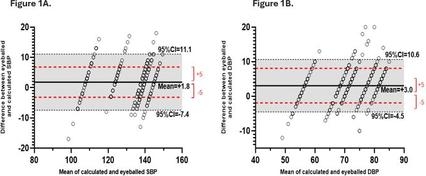
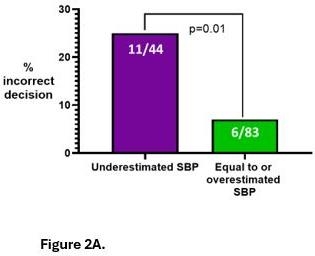
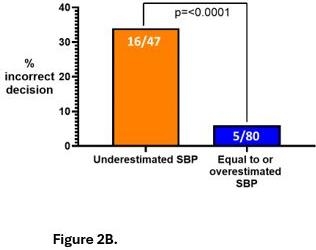
The mean participant age was 34 years (range 22–66), with 60% female and 22% physicians. Eyeball estimation overestimated SBP by 1.8 mmHg (95% CI: -7.4 to 11.1) and DBP by 3.0 mmHg (95% CI: -4.5 to 10.6) (Figure. 1A & 1B). A total of 25.3% of SBP and 21.1% of DBP estimates exceeded acceptable error thresholds (±5 mmHg for SBP and DBP[WV1] ). Half of the participants incorrectly judged that BP had not improved despite actual reduction in BP. Among those who underestimated SBP in the hypothetical case with stage 2 hypertension, 11 out of 44 (25%) failed to recommend antihypertensive initiation vs. 6 out of 83 (7%) who estimated accurately or overestimated (p=0.01) (Figure. 2A). Additionally, 34% of those who underestimated SBP did not intensify therapy in the same patient with persistent hypertension vs. 6% of others (p=0.0001) (Figure. 2B).
Conclusion
Accuracy of visual estimation of mean home BP is limited and often falls outside the acceptable error threshold. This inaccuracy contributes to misjudged BP trajectory and inappropriate treatment decisions. These findings suggest that subjective visual assessments of ambulatory BP data are unreliable and should not be used to guide clinical decision making/treatment plans in hypertension management.
Home blood pressure (BP) monitoring is commonly used in clinical practice to assess out-of-office BP levels. However, providers often visually estimate (“eyeball”) the average BP from logs to make treatment decisions. This study tested the hypothesis that visual BP estimation is frequently inaccurate, potentially leading to suboptimal clinical management.
Methods
We surveyed 183 healthcare providers (including physicians, medical students, residents, and advanced practice providers) at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center. Participants reviewed three simulated BP logs and estimated the average systolic (SBP) and diastolic BP (DBP). They also reviewed two additional BP logs from a hypothetical patient with untreated stage 2 hypertension and assessed BP trajectory and treatment recommendations. Bland-Altman analysis assessed agreement between visually estimated and calculated mean BP. Fisher’s exact test compared incorrect clinical decisions based on BP underestimation versus accurate/overestimation.
Results
The mean participant age was 34 years (range 22–66), with 60% female and 22% physicians. Eyeball estimation overestimated SBP by 1.8 mmHg (95% CI: -7.4 to 11.1) and DBP by 3.0 mmHg (95% CI: -4.5 to 10.6) (Figure. 1A & 1B). A total of 25.3% of SBP and 21.1% of DBP estimates exceeded acceptable error thresholds (±5 mmHg for SBP and DBP[WV1] ). Half of the participants incorrectly judged that BP had not improved despite actual reduction in BP. Among those who underestimated SBP in the hypothetical case with stage 2 hypertension, 11 out of 44 (25%) failed to recommend antihypertensive initiation vs. 6 out of 83 (7%) who estimated accurately or overestimated (p=0.01) (Figure. 2A). Additionally, 34% of those who underestimated SBP did not intensify therapy in the same patient with persistent hypertension vs. 6% of others (p=0.0001) (Figure. 2B).
Conclusion
Accuracy of visual estimation of mean home BP is limited and often falls outside the acceptable error threshold. This inaccuracy contributes to misjudged BP trajectory and inappropriate treatment decisions. These findings suggest that subjective visual assessments of ambulatory BP data are unreliable and should not be used to guide clinical decision making/treatment plans in hypertension management.
More abstracts on this topic:
A First-In-Human Phase 1 Study of the Safety, Tolerability, and Pharmacodynamics of REGN7544, a Novel Natriuretic Peptide Receptor 1–Blocking Monoclonal Antibody
Ahmed Mohsin, Morton Lori, Olenchock Benjamin, Herman Gary, Wynne Chris, Marin Ethan, Tuckwell Katie, Xu Meng, Cheng Xiping, Redington Emily, Koyani Bharatkumar, Mateo Katrina, Thakur Mazhar, Devalaraja-narashimha Kishor
A Framework for Developing Prehospital Intracerebral Hemorrhage Recognition Scales and TechnologiesTaleb Shayandokht, Hsu Jamie, Saver Jeffrey