Final ID: 075
Blood pressure polygenic score predicts long-term blood pressure control and treatment-resistant hypertension
Objectives We examined the associations of BP polygenic score (PGS) with long-term BP control and treatment-resistant hypertension among patients with hypertension.
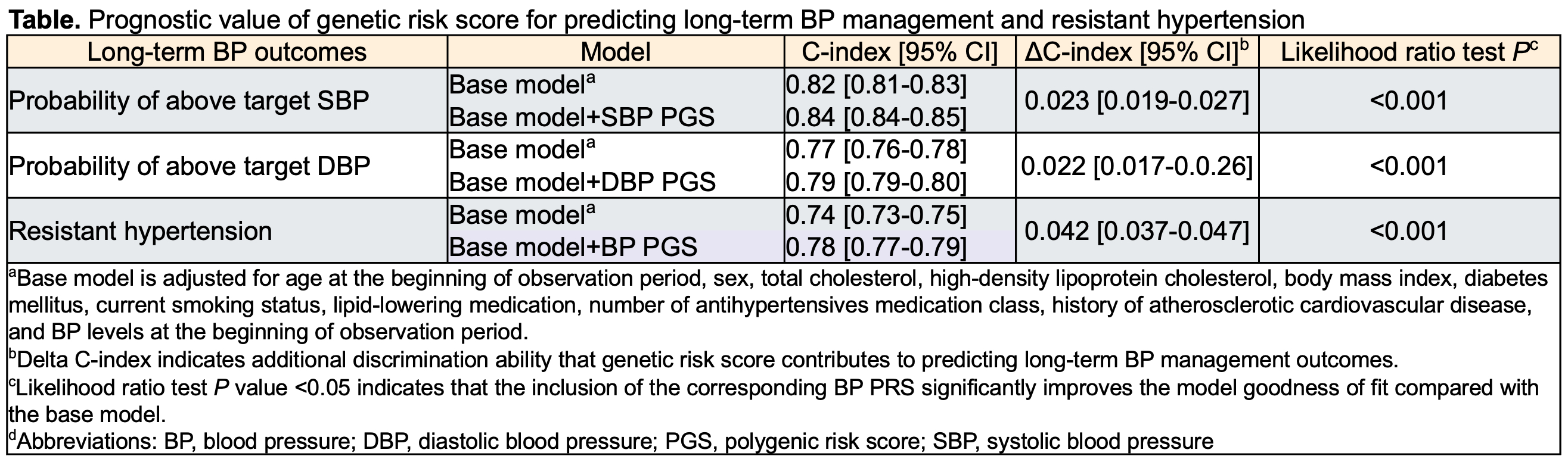
Methods Using Mass General Brigham Biobank nested within the U.S. healthcare system, we identified 22,466 individuals aged 18-64 years with established hypertension between January 2018 and May 2019. Multiancestral BP PGS was fine-tuned using the external UK Biobank cohort. Longitudinal BP control was defined as cumulative duration above target systolic BP (SBP) ≥130 mmHg or diastolic BP (DBP) ≥80 mmHg in percentage over a 5-year follow-up. Treatment-resistant hypertension was defined as SBP ≥140 or DBP ≥90 mmHg despite the concurrent use of 3 antihypertensive classes, use of ≥4 antihypertensive classes at any BP level, or physician adjudication. Using multivariable regression, we assessed the associations of BP PRS with 5-year BP control and lifetime resistant hypertension incidence adjusting for traditional cardiometabolic risk factors and comorbidities. Incremental prognostic utility of BP PRS was assessed based on improvement in discrimination C-index or the likelihood ratio test.
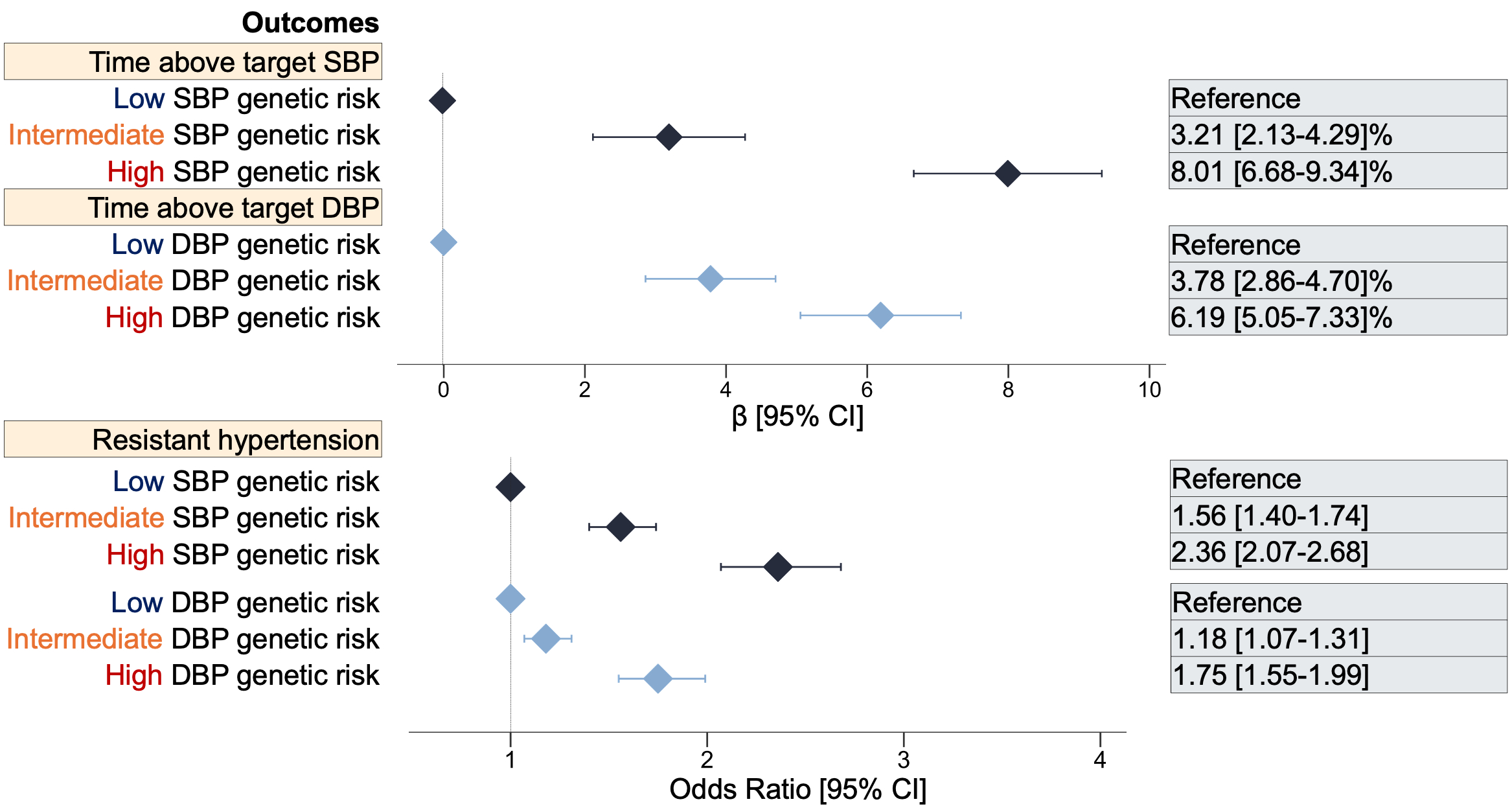
Results The mean SBP/DBP (standard deviation) at index date was 132(18) / 75(11) mmHg, and 4126 (18.4%) developed resistant hypertension over a lifetime. In reference to the low (<20th percentile) PGS group, the high (≥80th percentile) genetic risk group was associated with 8.01 [6.68-9.34]% longer duration lived with above-target SBP and 6.19 [5.05-7.33]% longer with high DBP. In parallel, the high SBP genetic risk group had a 2.36 [2.07-2.68]-folds higher odds of developing treatment-resistant hypertension. Adding BP PGSs to traditional risk factors improved discrimination C-index [95% CI] for predicting resistant hypertension from 0.74 [0.73-0.75] to 0.78 [0.77-0.79] (P <0.001). BP PGS consistently predicted longitudinal BP management in the validation population-based UK Biobank cohort in adherence to the UK clinical guideline.
Conclusions BP PGS predicts long-term BP control and treatment-resistant hypertension. Harnessing BP PGS may inform anticipated trends in long-term BP control to better enable optimal hypertension management.
- Cho, So Mi ( Massachusetts General Hospital , Boston , Massachusetts , United States )
- Honigberg, Michael ( Massachusetts General Hospital , Boston , Massachusetts , United States )
- Fahed, Akl ( Massachusetts General Hospital , Boston , Massachusetts , United States )
- Patel, Aniruddh ( Massachusetts General Hospital , Boston , Massachusetts , United States )
- Hornsby, Whitney ( Massachusetts General Hospital , Boston , Massachusetts , United States )
- Natarajan, Pradeep ( Massachusetts General Hospital , Boston , Massachusetts , United States )
- Ruan, Yunfeng ( Massachusetts General Hospital , Boston , Massachusetts , United States )
- Lee, Hyeok-hee ( Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center , Boston , Massachusetts , United States )
- Koyama, Satoshi ( Massachusetts General Hospital , Boston , Massachusetts , United States )
- Juraschek, Stephen ( Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center , Boston , Massachusetts , United States )
- Allen, Norrina ( NORTHWESTERN UNIVERSITY , Chicago , Illinois , United States )
- Yang, Eugene ( University of Washington , Seattle , Washington , United States )
- Mcevoy, John ( University of Galway , Galway , Ireland )
- Secemsky, Eric ( Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center , Boston , Massachusetts , United States )
Meeting Info:
Session Info:
Concurrent A: Genetics, Proteomics, and Metabolomics
Saturday, 09/06/2025 , 01:30PM - 03:00PM
Oral Abstract Session
More abstracts on this topic:
Mamprejew Nicole, Abusulb Ammar, Cubeddu Robert, Kassar Emily, Labovitz Arthur, Orringer Carl, Alvi Mohammed Ali, Albaghdadi Mazen
A Heart-pounding Case of Cardiomyopathy in PregnancyTran Linh, Everitt Ian, Vaught Arthur, Barth Andreas, Minhas Anum
More abstracts from these authors:
Cho So Mi, Yang Eugene, Shimbo Daichi, Natarajan Pradeep, Urbut Sarah, Ruan Yunfeng, Bhatnagar Aarushi, Ganesh Shriienidhie, Hornsby Whitney, Bhattacharya Romit, Honigberg Michael, Juraschek Stephen
Premature Menopause and Polygenic Risk on Incident Coronary Artery Disease among Postmenopausal WomenGanesh Shriienidhie, Hornsby Whitney, Paruchuri Kaavya, Ruan Yunfeng, Patel Aniruddh, Honigberg Michael, Natarajan Pradeep