Final ID: P-107
Training for home blood pressure monitoring among women with a diagnosis or risk factors for hypertensive disorders of pregnancy
Abstract Body: Introduction
Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy (HDP) are leading causes of morbidity and mortality among pregnant women. Despite the potential benefits of home blood pressure monitoring (HBPM) for early diagnosis and monitoring of patients with HDP, its utilization is limited by inconsistent training by healthcare providers. This study sought to examine the use of and training for HBPM in those at risk for HDP.
Methods
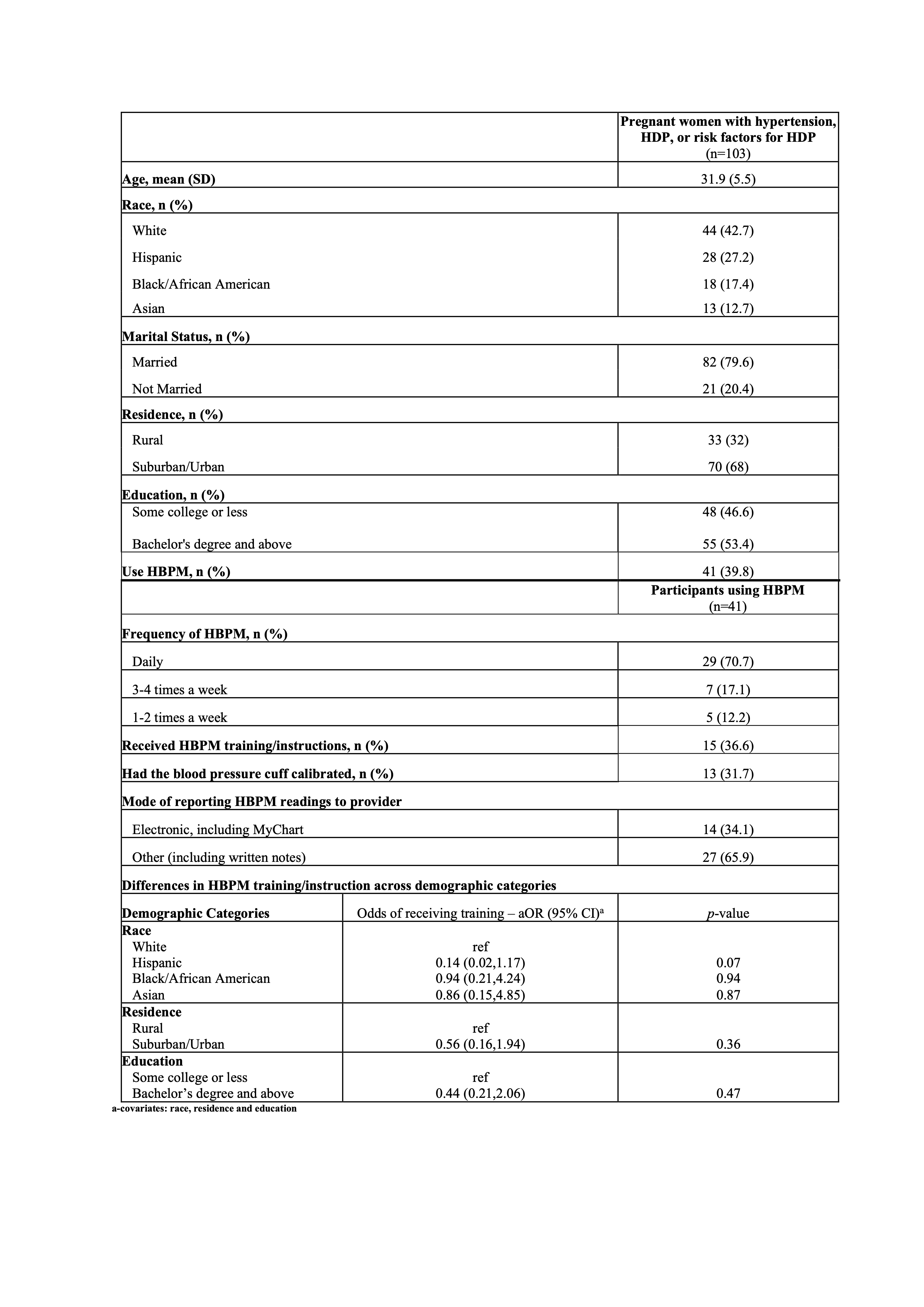
Pregnant women, aged 20-50 (N = 103), diagnosed with either hypertension, HDP, or risk factors for HDP, were recruited from a large academic medical center to complete a survey on HBPM practices from June 2020 to January 2024. Thisincluded questions about HBPM, frequency of HBPM, and prior HBPM training provision by providers. Statistical analysis was performed using STATA/BE 18.0.
Results
Of the 103 participants, 41 (39.8%) did HBPM and the most common frequency was daily (70.7%). Of those who did HBPM, 36.6% had received training from their healthcare providers and 31.7% had their BP monitors calibrated in the clinic. There was a trend towards Hispanic women being less likely to receive training compared to white women (p =0.07). There were no significant differences in training across categories of education and location of residence.
Conclusion
In this sample where nearly 40% of pregnant women used HBPM, we observed that only 1 in 3 received training for HBPM with little difference observed across demographic categories. Given the time constraints in clinic visits hindering appropriate training for HBPM, exploring alternative methods of HBPM training such as leveraging mobile health applications may be beneficial to ensure that pregnant women receive necessary training to effectively conduct HBPM.
Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy (HDP) are leading causes of morbidity and mortality among pregnant women. Despite the potential benefits of home blood pressure monitoring (HBPM) for early diagnosis and monitoring of patients with HDP, its utilization is limited by inconsistent training by healthcare providers. This study sought to examine the use of and training for HBPM in those at risk for HDP.
Methods
Pregnant women, aged 20-50 (N = 103), diagnosed with either hypertension, HDP, or risk factors for HDP, were recruited from a large academic medical center to complete a survey on HBPM practices from June 2020 to January 2024. Thisincluded questions about HBPM, frequency of HBPM, and prior HBPM training provision by providers. Statistical analysis was performed using STATA/BE 18.0.
Results
Of the 103 participants, 41 (39.8%) did HBPM and the most common frequency was daily (70.7%). Of those who did HBPM, 36.6% had received training from their healthcare providers and 31.7% had their BP monitors calibrated in the clinic. There was a trend towards Hispanic women being less likely to receive training compared to white women (p =0.07). There were no significant differences in training across categories of education and location of residence.
Conclusion
In this sample where nearly 40% of pregnant women used HBPM, we observed that only 1 in 3 received training for HBPM with little difference observed across demographic categories. Given the time constraints in clinic visits hindering appropriate training for HBPM, exploring alternative methods of HBPM training such as leveraging mobile health applications may be beneficial to ensure that pregnant women receive necessary training to effectively conduct HBPM.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Daily Diary Examination of the Associations of Adverse Childhood Experiences, Anticipated Discrimination, and Blood Pressure among Sexual and Gender Minority Adults
Pardee Lisa, Bochicchio Lauren, Caceres Billy
A First-In-Human Phase 1 Study of the Safety, Tolerability, and Pharmacodynamics of REGN7544, a Novel Natriuretic Peptide Receptor 1–Blocking Monoclonal AntibodyAhmed Mohsin, Morton Lori, Olenchock Benjamin, Herman Gary, Wynne Chris, Marin Ethan, Tuckwell Katie, Xu Meng, Cheng Xiping, Redington Emily, Koyani Bharatkumar, Mateo Katrina, Thakur Mazhar, Devalaraja-narashimha Kishor